W10 Prismatic Effects
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
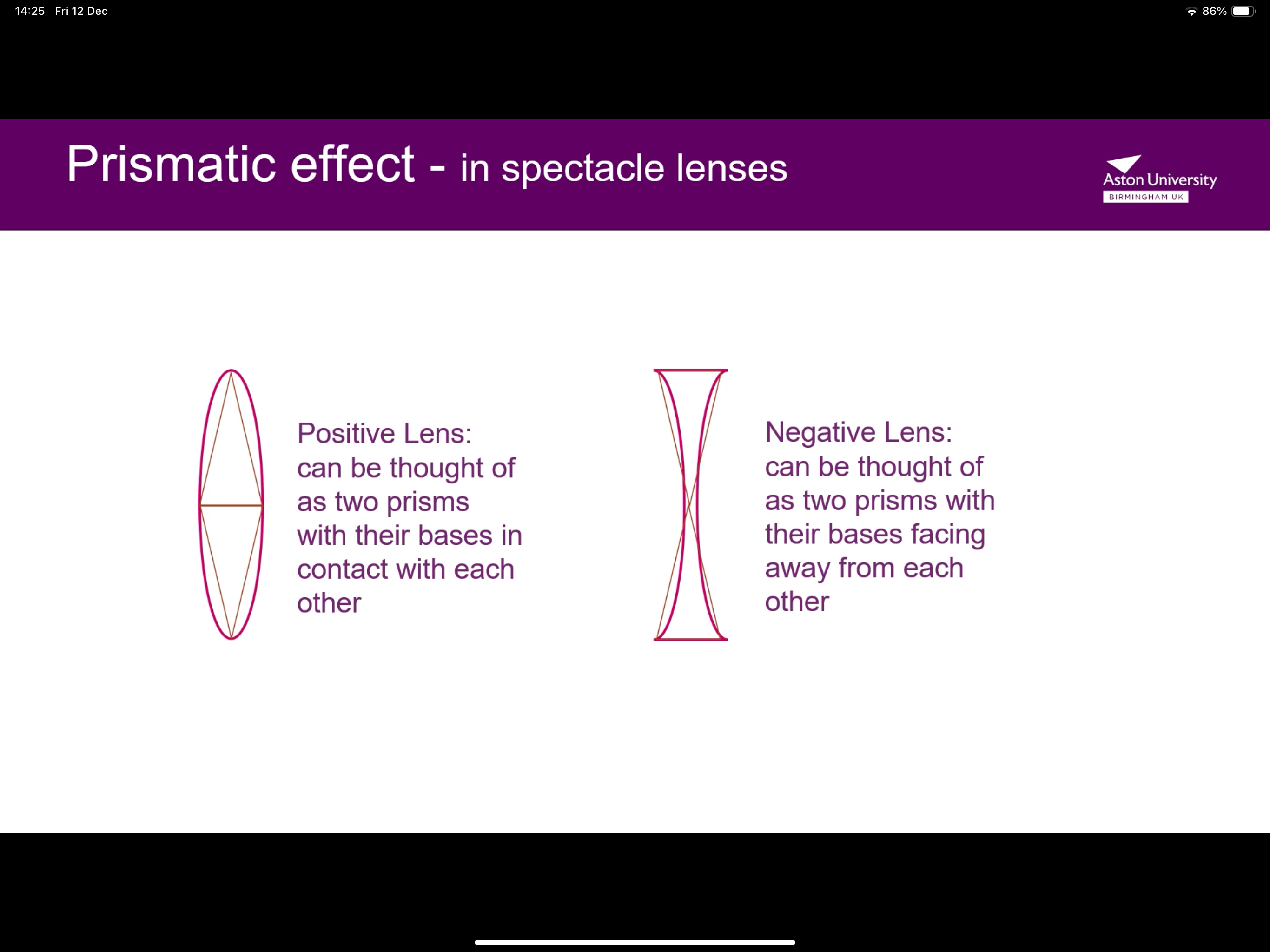
What is the difference between a positive lens and a negative lens diagram?
+ve has the bases of the 2 prisms touching, -ve has the bases of the 2 prisms on opposite ends
What would happen if a light ray passed through the optical centre of a lens?
It would pass through where the “bases” touch and it would pass through undeviated
What would happen if a light ray passed through any other point of a lens?
Deviation will occur as though the light is passing through a prism- the further away from the base, the more of an effect it will have
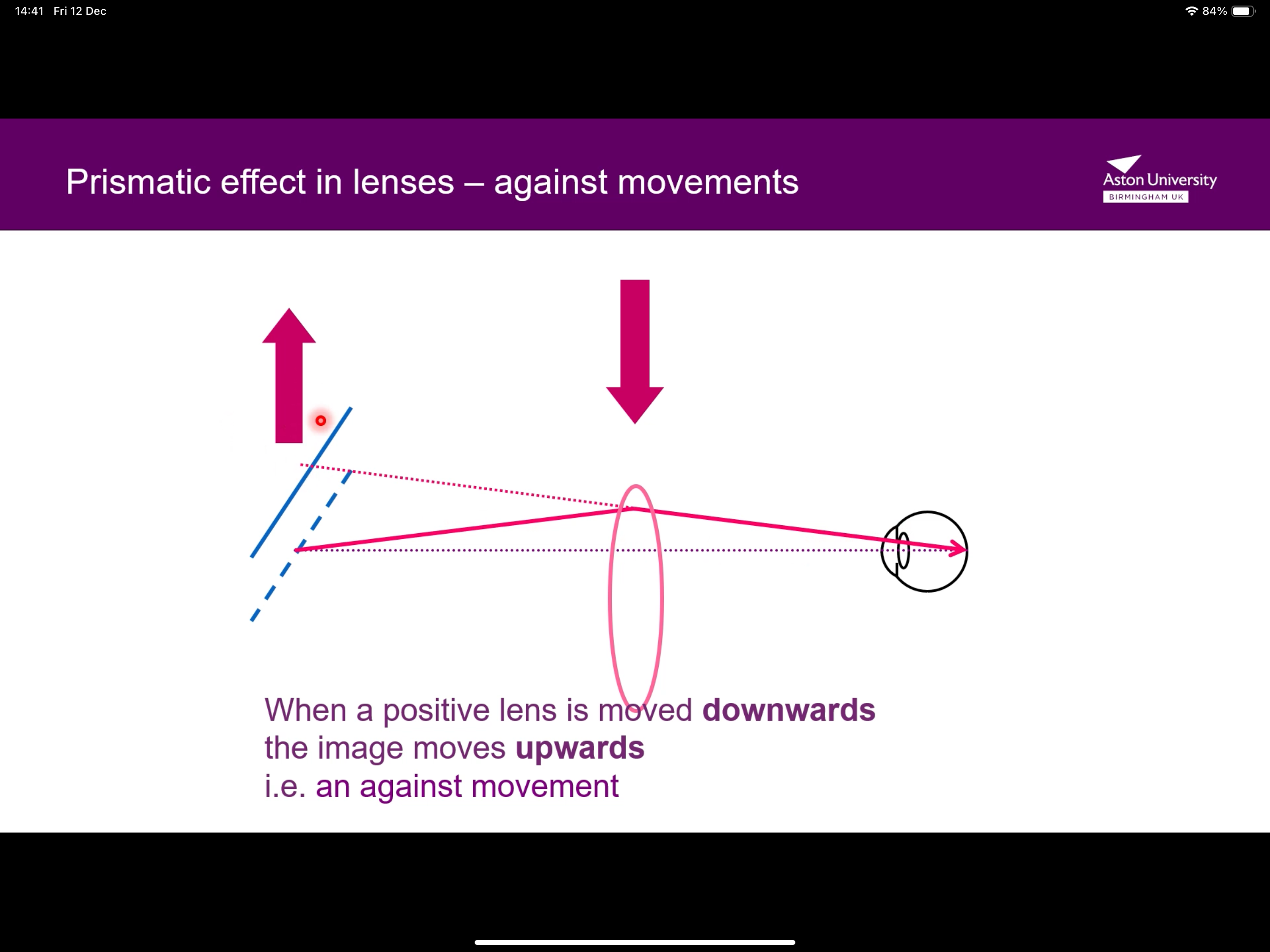
What happens when a positive lens moves downwards?
As the lens moves downwards, the light passes through the top part of the lens, so the light is deviated towards the base, but LOOKS to the eye as though it’s gone upwards, making the image go up, causing an against movement
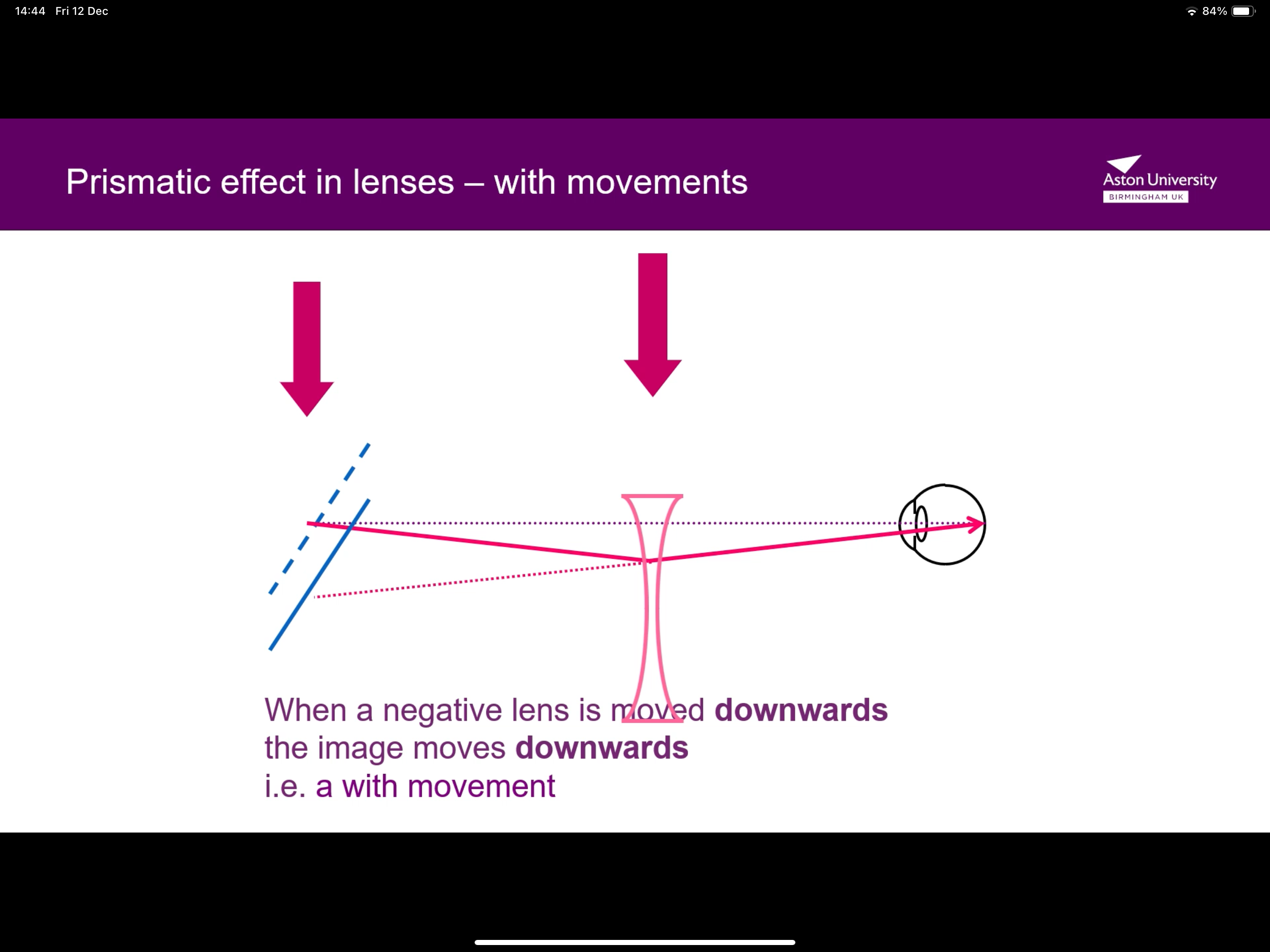
What happens when a negative lens moves downwards?
As you move the lens downwards, direction of light appears to look downwards, making the image go down, causing a with movement
How do you know if a lens has a with or an against movement?
Positive lens has an against movement, negative lens has a with movement
What is the optical centre of the lens?
The only point on the lens where there is no prismatic effect- does NOT have to coincide with the geometrical centre of the uncut lens. Ideally where the Px looks through in their spectacles and aligns with pupil
What does Prentice’s rule show?
The further away we are from the optical centre, we will have more prism as C is bigger
The bigger the magnitude (plus or minus), the bigger the prismatic effect
What is decentration?
The movement of a lens
What is the sign convention for decentration?
If something moves downwards and outwards (away from nose) it is positive and if something moves upwards and inwards (towards nose) it is negative
How tot counteract anisometropia (difference in power between 2 eyes?)
A counteracting prism is used to reduce the differential prism so the patient can maintain single vision
What happens with anisometropia?
When the difference in power exceeds 1 the ocular muscles cannot cope with the difference, causing the patient to experience double vision