broad spectrum antibiotics
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
agents for gram negatives
compared to gram positive, fewer antibiotics are available from gram negative infections
in addition to intrinsic resistance among gram negatives more and more infections now involve antibiotics resistant strains
urgent unmet need to develop further classes of agents with gram negative activity
UTI agents
nitrofurantoin
cephalexin
trimethoprim
Fosfomycin
colistin mode of action
Polymyxin group of antibiotics, polycationic peptide, binds to LPS outer membrane and phospholipids of cytoplasmic membrane causing destabilization, leakage and cell death. Has important anti-endotoxin activity
colistin activity
renewed interest dur to good gram negative activity
enterobacterales e.g. E. coli, K. pneumoniae
P. aeruginosa
some gram negs are intrinsically resistant e.g. Serratia
concentration dependent bactericidal activity
IV prodrug
colistin therapeutic use
combination therapy only
infections cause by some MDR gram negative bacilli
P. aeruginosa infection in CF (as it is often MDR in these patients)
broad spectrum agents
co-amoxiclav
cefalexin
cefuroxime
ceftriaxone
piperacillin-tazobactam
meropenem
ceftazidime
third generation cephalosporin, improved gram negative spectrum, especially P. aeruginosa
bind to penicillin binding proteins and interfere with cell wall enzymes. Unable to synthesize a cell wall, the bacteria dies
therapeutic uses: pseudomonas infections, e.g. in CF
ceftazidime activity
gram negative bacilli inducing P. aeruginosa
gram negatives that produce ESBLs are resistant
Poor gram pos activity
IV
aminoglycosides
gentamicin, tobramycin, amikacin
mode of action:
inhibits synthesis by binding to 30S ribosomal subunit
misreading of codons leading to non-functional proteins
aminoglycosides activity
aerobic gram negatives including pseudomonas
S. aureus
Mycobacterium
Bactericidal
IV
aminoglycosides therapeutic uses
often in combination with other antibiotics to provide gram negative cover
part of empirical combination treatment for serious infections e.g. endocarditis, pyelonephritis
significant adverse effects, nephrotoxicity, ototoxicity
therapeutic drug monitoring required for gentamicin
Gentamicin toxicity
renal toxicity
oto toxicity
toxicity usually from accumulation of the drug
therapeutic drug monitoring required for patient administered gentamicin
protein synthesis inhibitors mechanism
fully functional protein synthesis is essential to bacterial cell survival and growth
protein synthesis (translation) is mediated by the bacterial ribosome (2 subunits, 50S and 30S) which decode the info contained in mRNA to make proteins with the correct amino acid sequence
antibiotics that bind to ribosome at various location can disrupt this process
translation process may be prevented or may be compromised e.g. non-functional proteins produced
aminoglycosides provide good gram negative cover: gentamicin, tobramycin, amikacin
Tetrracyline
doxycycline, tetracycline, tigecycline
mode of action:
bind reversibly to 30S ribosomal subunit
prevents transfer RNA binding to attachment site and amino acids cannot be incorporated into proteins
tetracycline activity
bacteriostatic agents, tetracycline PO, tigecycline IV, doxycycline PO or IV
active against gram-pos (MSSA) and some gram neg, spirochetes e.g. treponema pallidum
tigecycline has improved gram neg spectrum, including enterobacterials
doxycycline - very good activity against atypical, Rickettsia, Chlamydia trachomatis, mycoplasma pneumoniae
tetracyclines therapeutic use
infections due to Rickettsia and other tick-borne disease, Chlamydia and mycoplasma pneumonia (doxycycline)
treatment of early gonorrhea or syphilis if patient is penicillin allergic
tigecycline SSTI, intra abdominal infection
tetracycline toxicity/adverse effects
photosensitivity, tooth discoloration especially tetracycline, not recommended for childeren
nucleic acid synthesis inhibitor ciprofloxacin mode of action
replication of DNA is essential for bacterial survival and growth
DNA gyrase/topoisomerase IV catalyzes the negative supercoiling of DNA for replication
quinolones inhibit DNA gyrase (a type II topoisomerase) and topoisomerase IV, preventing replication of DNA
selectivity - humans have an alternative topoisomerase II alpha for which quinolones have no affinity
ciprofloxacin activity
quinolones can enter easily via porins and therefore are often used to treat intracellular pathogens
bactericidal
IV or PO
most gram negs e.g. E. coli, L. pneumoniae, shigella
but also S. aureus and other staphylococci
ciprofloxacin therapeutic uses
pyelonephritis (where IV to oral switch is desirable)
gonorrhea (but resistance is a problem)
nor recommended for use in primary care unless UTI where there is proven resistance to other agents`
ciprofloxacin safety
FDA advise that a serious side effects of the antibiotic generally outweighs the benefit for patients which acute sinusitis, acute bronchitis or uncomplicated UTI where other options are available
systemic use may result in disabling or potentially permanent side effect involving tendons, muscles, joints, nerves, perhaps aorta and CNS
penicillins and cephalosporins mode of action
beta lactams binds directly to transpeptidase preventing cross linking
bactericidal
beta lactams
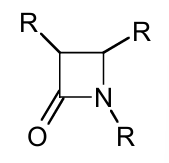
defined by the presence of a beta lactam ring
four main types: penicillins, cephalosporins, carbapenems e.g. meropenem, monobactams e.g. aztreonam
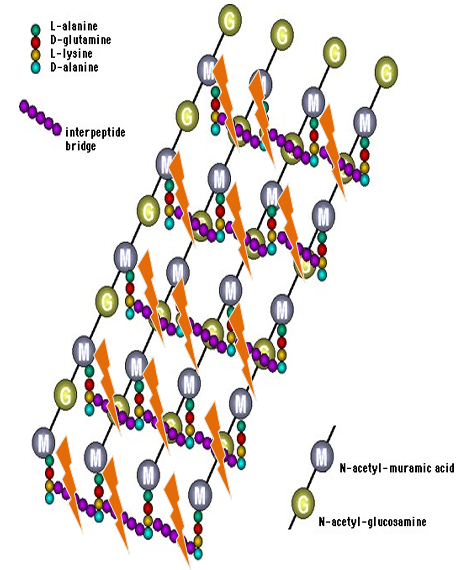
ESBL- producing Enterobacter ales produce extended spectrum beta lactamases to destroy beta lactam ring of penicillin. can be treated with carbapenems
cephalosporins (generally broad spec)
1st generation
good gram + activity
orally active e.g. cefaclor
used in treatment of respiratory and urinary infections
2nd generation
retain gram + activity but also exhibit gram - activity
oral and IV cefuroxime used for respiratory infections and surgical prophylaxis
3rd generation
good gram - activity, less staphylococcal activity, have some streptococcal activity
most IV
ceftriaxone
cefuroxime activity
broad spectrum
bactericidal;
S. aureus (not MRSA), penicillin susceptible S. pneumoniae, E. coli, Klebsiella spp.
available PO and IVce
cefuroxime therapeutic uses
prophylaxis for those undergoing orthopedic surgery, give gram+ cover also
given with metronidazole for intra abdominal infection or as prophylaxis before intra abdominal surgery
ceftriaxone activity
broad spectrum
bactericidal
S. aureus (not MRSA), penicillin susceptible S, pneumoniae, Aerobic gram- (e.g. E. coli, Klebsiella spp.), Neisseria spp.
lack of activity against P. aeruginosa, enterococci, listeria
available PO and IV
ceftriaxone therapeutic uses
prophylaxis for those undergoing orthopedic surgery, gram+ cover also
gram- cover for septic arthritis if suspicion of gonorrhea
given with metronidazole for intra abdominal infection or as prophylaxis before intra abdominal surgery
piperacillin tazobactam (tazocin) mode of action
combination of anti pseudomonal piperacillin and a beta lactamase inhibitor tazobactam
piperacillin - inhibits cell wall synthesis by inhibiting transpeptidase enzyme
tazobactam - protects piperacillin from degradation by beta lactamases
piperacillin tazobactam (tazocin) activity
MSSA, H. influenza, pseudomonas aeruginosa
IV
bactericidal
piperacillin tazobactam (tazocin) therapeutic uses
empiric therapy for healthcare associated infections e.g. pneumonia or abdominal infections
carbapenems
meropenem, ertapenem
mode of action:
same as cephalosporins/penicillins inhibit transpeptidase which is needed for crosslinking or peptidoglycan
carbapenems activity
broad spectrum against aerobes and anaerobic gram- bacilli that produce ESBLs
carbapenems therapeutic uses
intra abdominal infections where susceptibility confirmed
bloodstream infection where susceptibility confirmed
complicated UTI involving confirmed ESBL organism
ventilator associated pneumonia if ESBL confirmed
UTI agents hitrofuranation mode of actionn
unique and poorly understood mechanism. Binds to ribosomal proteins, blocking translation. Also directly damages DNA
UTI agent nitrofurantoin activity
some enterobacterales (e.g. urinary pathogens K. pneumoniae, E. coli including ESBL)
S. saphrophyticus
E. faecalis, E. faecium
bactericidal against urinary pathogens
PO (by mouth)
UTI agent nitrofurantoin therapeutic uses
acute uncomplicated urinary tract infections (acute cystitis) cause by susceptible strains of Escherichia coli or staphylococcus saprophyticus
UTI agents Fosfomycin mode of action
phosphonic acid derivative. inhibits bacterial wall synthesis (bactericidal) by inactivating the enzyme, pyruvyl transferase, which is required for synthesis of the cell wall
UTI agent Fosfomycin activity
S. aureus (including MRSA), P. mirabilis, E.coli (including ESBL), enterococci (including VRE)
bactericidal
PO but IV also available in some countries
UTI agent Fosfomycin therapeutic uses
urinary tract infection, including complicated UTI, pyelonephritis
UTI agent trimethoprim mode of action
folate synthesis inhibitor
bacteria have metabolic pathways to synthesize tetrahydrofolic acid
tetrahydrofolic acid is a cofactor needed for bacteria to make nucleotide bases (purines) for DNA synthesis
trimethoprim and sulphonamides block enzymes required for synthesis of tetrahydrofolate
no tetrahydrofolate = no purines = cell death
UTI agent trimethoprim activity
alone or inf combination with sulphmethoxazole (called co-trimoxazole)
also antifungal agent
E. coli, K. pneumoniae, S. aureus, S. epidermidis
PO, bacteriostatic
UTI agent trimethoprim therapeutic uses
susceptible uncomplicated urinary tract infections
reported increased resistance rates in Ireland
travelers diarrhea