Topic 1.1 Structure of Water and Hydrogen Bonding
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What is a polar covalent bond?
It’s the bond in H₂O where oxygen and hydrogen share electrons, making the molecule polar.
Where is the polar covalent bond in a water molecule?
In the two O–H bonds, where oxygen and hydrogen share electrons unequally.
Diagram a water molecule including the polar bond and partial charges labeled.
Oxygen (O): slightly negative (δ⁻)
Hydrogens (H): slightly positive (δ⁺)
Polar covalent bonds: the O–H bonds are polar because oxygen pulls electrons toward itself
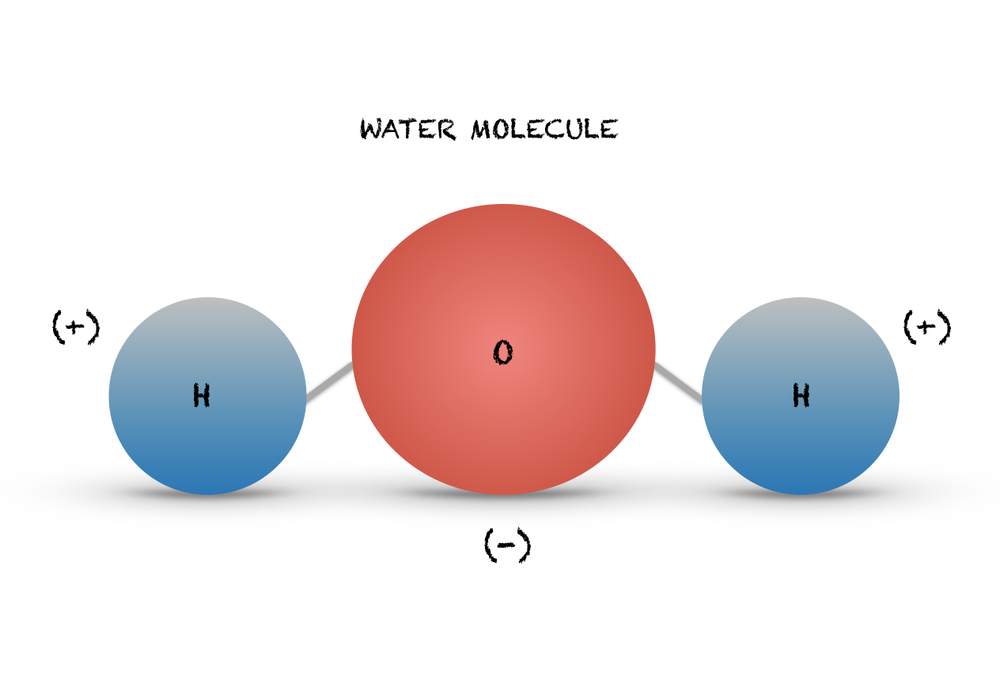
Describe why water is considered a polar molecule.
Because oxygen pulls electrons more strongly than hydrogen, the shared electrons spend more time near oxygen (δ–) than hydrogen (δ+). This unequal sharing creates partial charges, making H₂O polar.
What is a hydrogen bond?
A weak attraction between a slightly positive hydrogen atom (δ+) in one molecule and a slightly negative atom (like oxygen or nitrogen) in another molecule.
Where are hydrogen bonds found in water?
Between the hydrogen atom of one water molecule (δ+) and the oxygen atom of another water molecule (δ–).
Draw a diagram of TWO molecules including the hydrogen bond and the polar bonds labeled.
O–H bonds: polar covalent bonds (δ⁻ on O, δ⁺ on H)
Dashed line (—): hydrogen bond between molecules
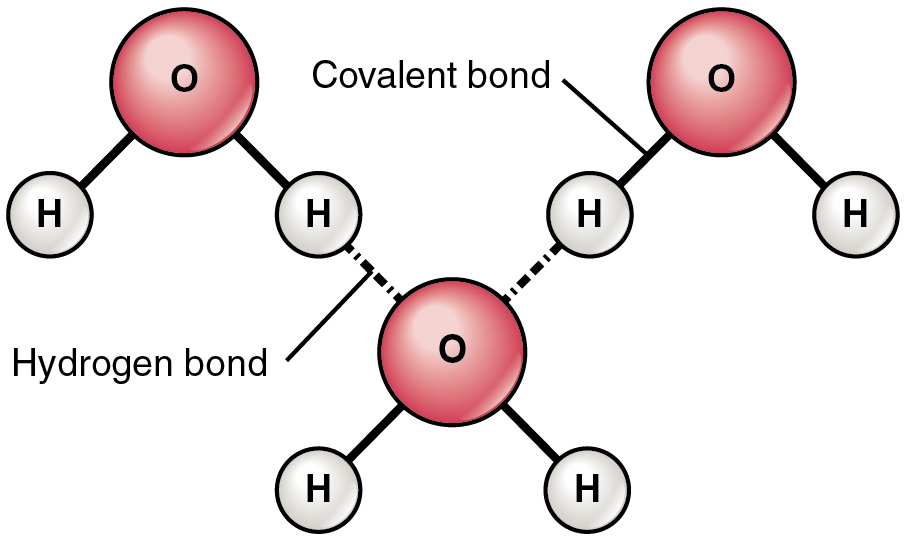
Identify three properties of water.
Cohesion – Water molecules stick to each other (helps with surface tension).
Adhesion – Water molecules stick to other surfaces (helps plants move water).
High specific heat – Water resists temperature changes (helps stabilize environments).
What is specific heat capacity?
The amount of heat energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1°C.
It explains why water heats up and cools down slowly compared to many other substances.
Describe how water has a high specific heat capacity.
Water can absorb or release a lot of heat energy without changing temperature much because its hydrogen bonds hold molecules together. This helps regulate Earth’s climate and maintain stable temperatures in organisms.
What is evaporate cooling?
Evaporative cooling happens when water evaporates and takes heat energy with it, cooling the surface it leaves.
Example: Sweating cools your skin because water absorbs heat to evaporate.
Describe how water is able to facilitate evaporative cooling.
Water’s high specific heat and strong hydrogen bonds allow it to absorb a lot of heat before evaporating. When water evaporates, it removes heat from the surface, cooling it down.
Example: Sweating cools the body because heat is taken away as water changes from liquid to gas.
Describe two ways that organisms maintain body temperatures.
Sweating – Water absorbs body heat as it evaporates, cooling the organism.
High specific heat of water in cells and blood – Water resists rapid temperature changes, keeping internal body temperature stable.
Describe a hydrogen bond.
A hydrogen bond is a weak attraction between a slightly positive hydrogen atom in one molecule and a slightly negative atom (like oxygen) in another molecule.
Example: Hydrogen bonds hold water molecules together, giving water its unique properties.
Identify THREE properties of water that are caused by hydrogen bonding.
Cohesion – Water molecules stick to each other (surface tension).
High specific heat – Water absorbs a lot of heat before changing temperature.
Evaporative cooling – Heat is used to break hydrogen bonds when water evaporates, cooling surfaces.
Compare and contrast cohesion and adhesion.
Cohesion: Water molecules stick to each other (e.g., surface tension).
Adhesion: Water molecules stick to other surfaces (e.g., water climbing up plant roots).
Similarity: Both involve hydrogen bonding and attraction between molecules.
Difference: Cohesion = water–water; Adhesion = water–other substances.
What is surface tension?
Surface tension is the “skin-like” layer on the surface of water caused by cohesion between water molecules.
Example: Water striders can walk on water because of surface tension.
Which of the properties of water cause surface tension?
Cohesion causes surface tension because water molecules stick tightly to each other through hydrogen bonds, creating a “skin” on the surface.
Using the properties of water, describe how water can move up a capillary tube to move from the roots to the leaves in a plant.
Water moves up a plant through capillary action, which involves:
Cohesion – Water molecules stick to each other, forming a continuous column.
Adhesion – Water molecules stick to the walls of the xylem (tube), helping it climb upward.
Transpiration – Evaporation of water from leaves pulls water upward through the xylem.
This process depends on hydrogen bonds holding water molecules together.
Using the properties of water, describe how a water strider can walk on water.
The water strider can walk on water because of surface tension, which is caused by cohesion between water molecules. The hydrogen bonds hold the surface tightly enough to support the insect’s weight.