Lecture 17 - Energy of Food Pt 1
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Why does the body break down Glucose into ATP?
Glucose contains too much concentrated energy to use safely. ATP are smaller, safer, energetic molecules
What does ATP stand for?
Adenosine triphosphate
Which part of the ATP molecule carries the usable energy?
The third phosphate
Anaerobic
A process that does not require oxygen
Aerobic
A process that requires oxygen
What is the Matrix of the mitochondria?
The fluid inside the mitochondria
What are the Cristae of the mitochondria?
The folds within the mitochondria
What unique genetic structure do mitochondria possess?
Their own DNA (mtDNA), which is acquired only from your mom
Glycolysis
Glyco = sugar; lysis = split
Where does Glycolysis occur in the cell?
In the cytosol
Is glycolysis aerobic, anaerobic, or both?
It is the first step for BOTH anaerobic and aerobic processes
What is the starting molecule for Glycolysis?
Glucose (a monosaccharide)
Pyruvate
The product of splitting glucose
What is the net ATP yield from Glycolysis?
2 ATP (4 are made, but 2 ATP are added initially)
Besides ATP and Pyruvate, what other high-energy product is formed during Glycolysis?
NADH (an electron carrier)
When does the body perform anaerobic respiration/fermentation?
When there is no oxygen
What is the primary purpose of fermentation?
To take electrons from NADH so that NAD can be regenerated to break down more glucose
What are the two different types of fermentation?
Alcohol fermentation and Lactic acid fermentation
What are the products of Lactic Acid Fermentation?
Lactic acid/lactate (formed when NADH adds electrons directly to pyruvate)
What is the purpose of producing a small quantity of ATP via anaerobic respiration?
It is better than dying; it allows ATP production in low oxygen environments
What is the first step of aerobic cellular respiration within the mitochondria?
The Kreb Cycle (also known as the Citric Acid Cycle)
What happens to Pyruvate before it enters the Kreb Cycle?
It is turned into Acetyl CoA, producing CO2 and NADH
What are the goals of the Kreb Cycle?
Make a small bit of ATP and generate high energy electrons in carriers (FADH2 and NADH)
What is the simple meaning of "Oxidative Phosphorylation"?
Use oxygen to make ATP!
What are the two stages of Oxidative Phosphorylation?
Electron transport chain and ATP Synthase
In the electron transport chain (ETC), what brings the high energy electrons?
Electron carriers (NADH and FADH2)
What is the essential action of the ETC?
The movement of electrons down the chain is used to pump H+ outside the mitochondria
What picks up the electrons at the end of the ETC, and what does it become?
Oxygen picks up the electrons and turns into water
How does ATP Synthase make a BUNCH of ATP?
It uses the flow of H+ (moving back into the mitochondria due to high concentration outside).
Which step yields more ATP: the Krebs cycle or oxidative phosphorylation?
Oxidative phosphorylation
what do you get when you ignite methane/cellulose
fire
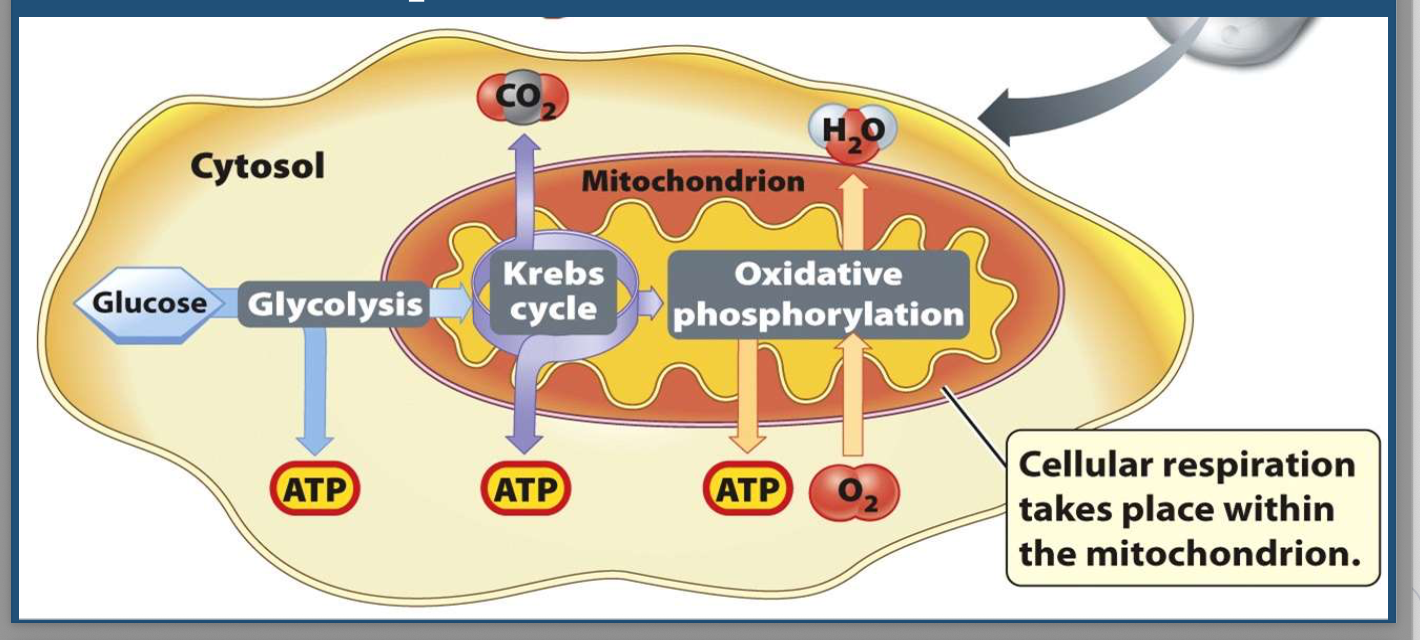
draw cellular respiration
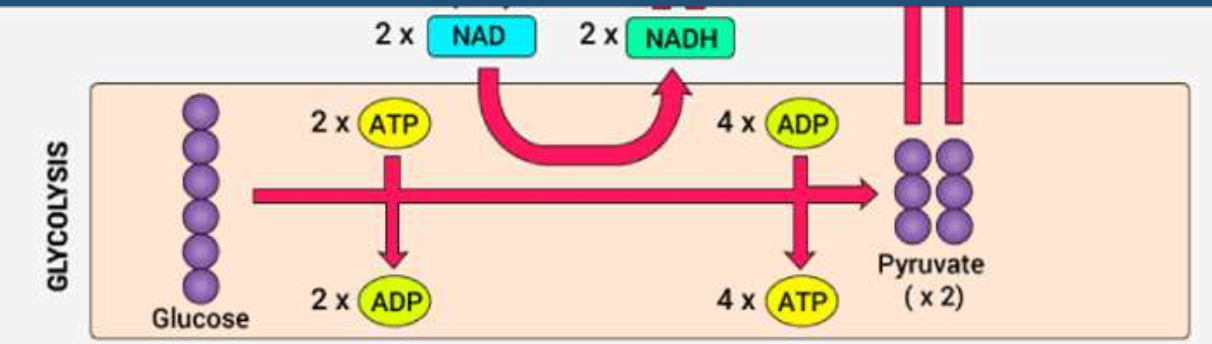
draw glycolysis
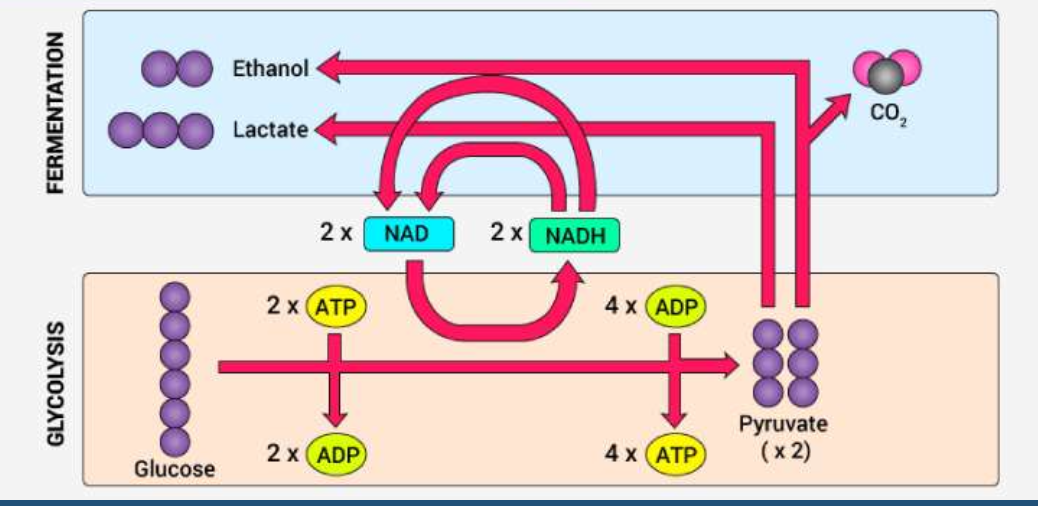
What process is this
anaerobic respiration
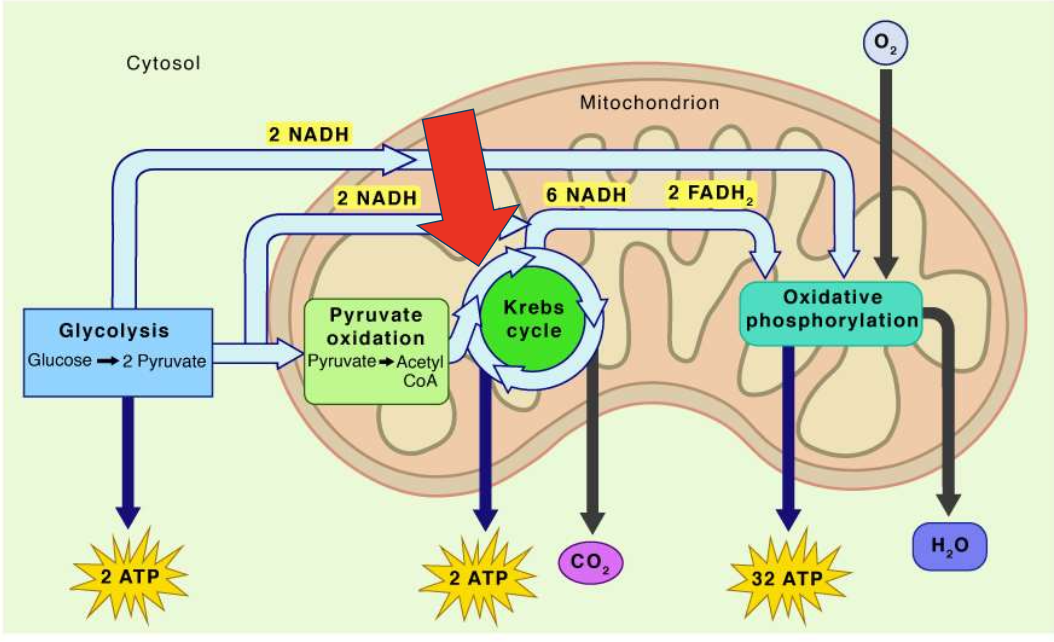
what process is this
aerobic respiration
draw aerobic respiration
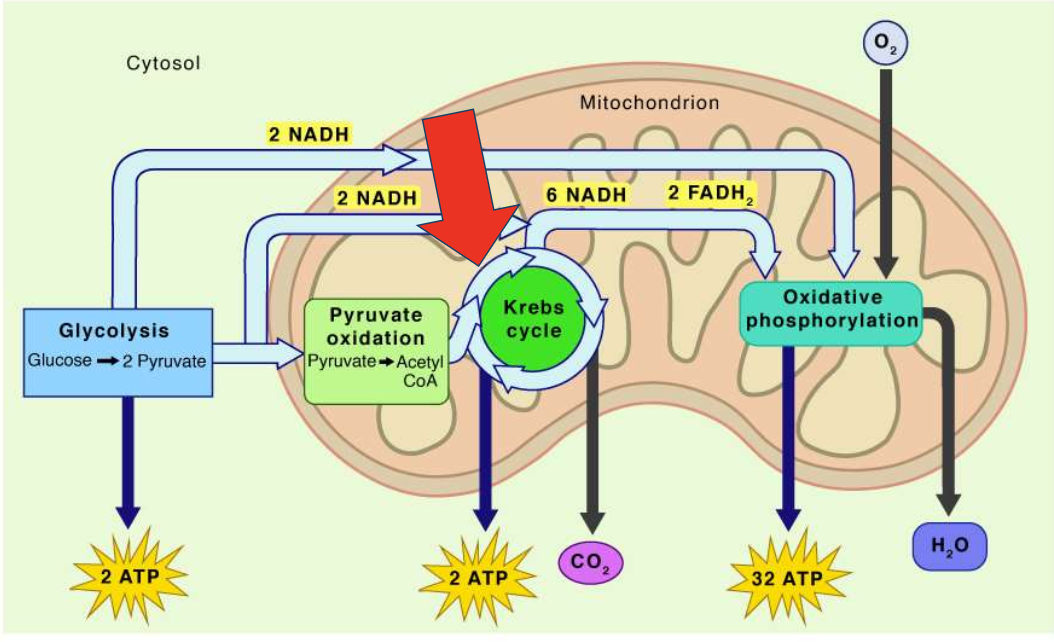
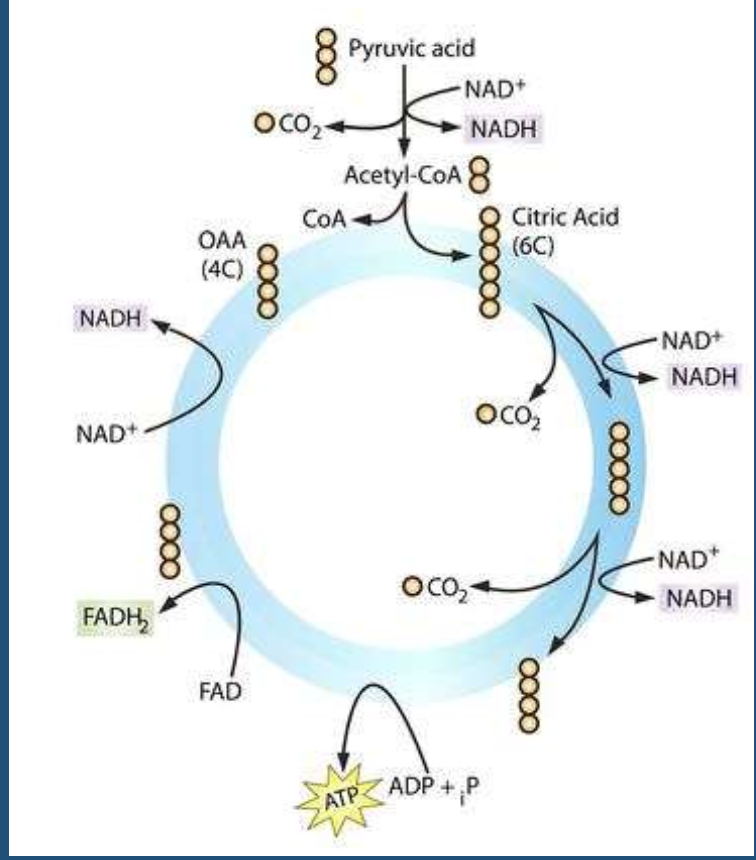
what process does this show
krebs cycle (citric acid cycle)
Does glycolysis take place inside or outside the mitochondria?
outside the mitochondria
Which gives more ATP, the Krebs cycle (1) or oxidative phosphorylation (2)?
Oxidative phosphorylation gives more ATP