pulse & blood pressure
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
What is blood pressure?
The force of the blood against the walls of all vessels carrying blood to and from the heart.
What term describes high blood pressure?
Hypertension
What term describes low blood pressure?
Hypotension
What can hypertension lead to?
Heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, vision impairment, dementia
What are the avoidable risk factors for high blood pressure?
Smoking & exposure to secondhand smoke
Diabetes
Being obese or overweight
High cholesterol
Unhealthy diet
Physical inactivity
What are the unavoidable risk factors for high blood pressure?
Family history of high blood pressure
Race/ethnicity
Increasing age
Gender (males)
Chronic kidney disease
What are signs and symptoms of hypotension?
Dizziness/lightheadedness, fainting, blurred vision, nausea, fatigue, lack of concentration.
Hypotension is a blood pressure less than ______.
90/60
What is orthostatic hypotension?
AKA Postural hypotension, is low BP that happens when standing after sitting or lying down
What can orthostatic hypotension be utilized to assess?
Can help assess low fluid volume
What is systolic pressure?
Systolic pressure indicates how much pressure your blood is exerting against your artery walls when the heart beats.
Which number in 120/80 is the systolic pressure?
120 is the systolic pressure.
What is diastolic pressure?
Diastolic pressure indicates how much pressure your blood is exerting against your artery walls while the heart is resting between beats.
Which number in 120/80 is the diastolic pressure?
80 is the diastolic pressure.
What is pulse? What is pulse expressed in- can you put the abbreviation?
A wave of blood created by alternate expansion and recoil of elastic arteries after each contraction of the left ventricle of the heart. Pulse is expressed in beats per minute, BPM.
Describe the following pulse site: Temporal
Above and lateral to the eye where the temporal artery passes over the temporal bone of the head
Describe the following pulse site: Carotid
At the side of the neck where the carotid artery runs between the trachea and the sternocleidomastoid muscle
Describe the following pulse site: Apical
At the apex of the heart
Describe the following pulse site: Brachial
At the inner aspect of the biceps muscle of the arm or medially in the antecubital space
Describe the following pulse site: Femoral
Where the femoral artery passes alongside the inguinal ligament
Describe the following pulse site: Popliteal
Where the popliteal artery passes behind the knee
Describe the following pulse site: Posterior Tibial
On the medial surface of the ankle where the posterior tibial artery passes behind the medial malleolus
Describe the following pulse site: Dorsalis Pedis
Where the dorsalis pedis artery passes over the bones of the foot, on an imaginary line drawn from the middle of the ankle to the space between the big and second toes
Which pulse site is used for blood pressure?
Brachial artery
What is a common pulse site utilized in adults?
Radial pulse
What instrument can be used to assess a weak pulse?
Doppler machine
What can increase a pulse?
Exercise, stimulants, excitement, fever, shock
What can decrease a pulse?
Sleep, depressants, heart disease, coma
What is the term for a fast heart rate greater than 100 bpm?
Tachycardia
What is the term for a slow heart rate less than 60 bpm?
Bradycardia
The average adult heart beats 72 bpm, what is the normal range for an adult?
60-100
Which age group will have higher resting rates?
Children and newborns
What factors affect pulse rate?
Age, sex, exercise, fever, medications, dehydration, stress, position, heart diseases
Define the term palpation
examination by applying slight pressure to a pulse point with fingertips
Define the term auscultation
examination by listening, usually with a stethoscope
What is an example of a pulse that is palpated?
Radial Pulse
What is an example of a pulse that is auscultated?
Apical Pulse
When do you assess apical pulse?
Patients with heart disease, irregular heart rates, patients that are prescribed medications that affect the heart rate, preferred method of measuring heart rate in children
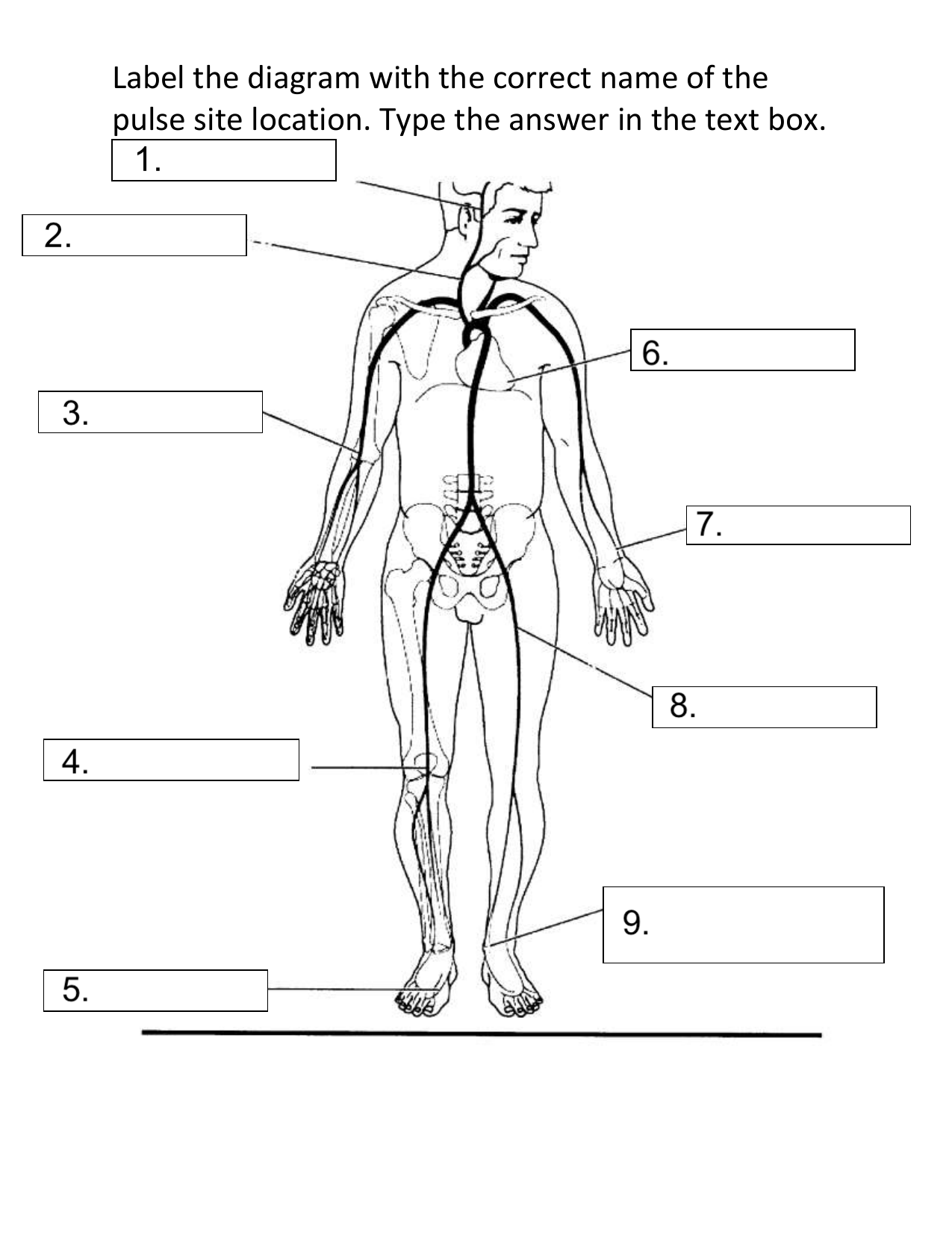
What pulse site is #1 on the diagram?
Temporal
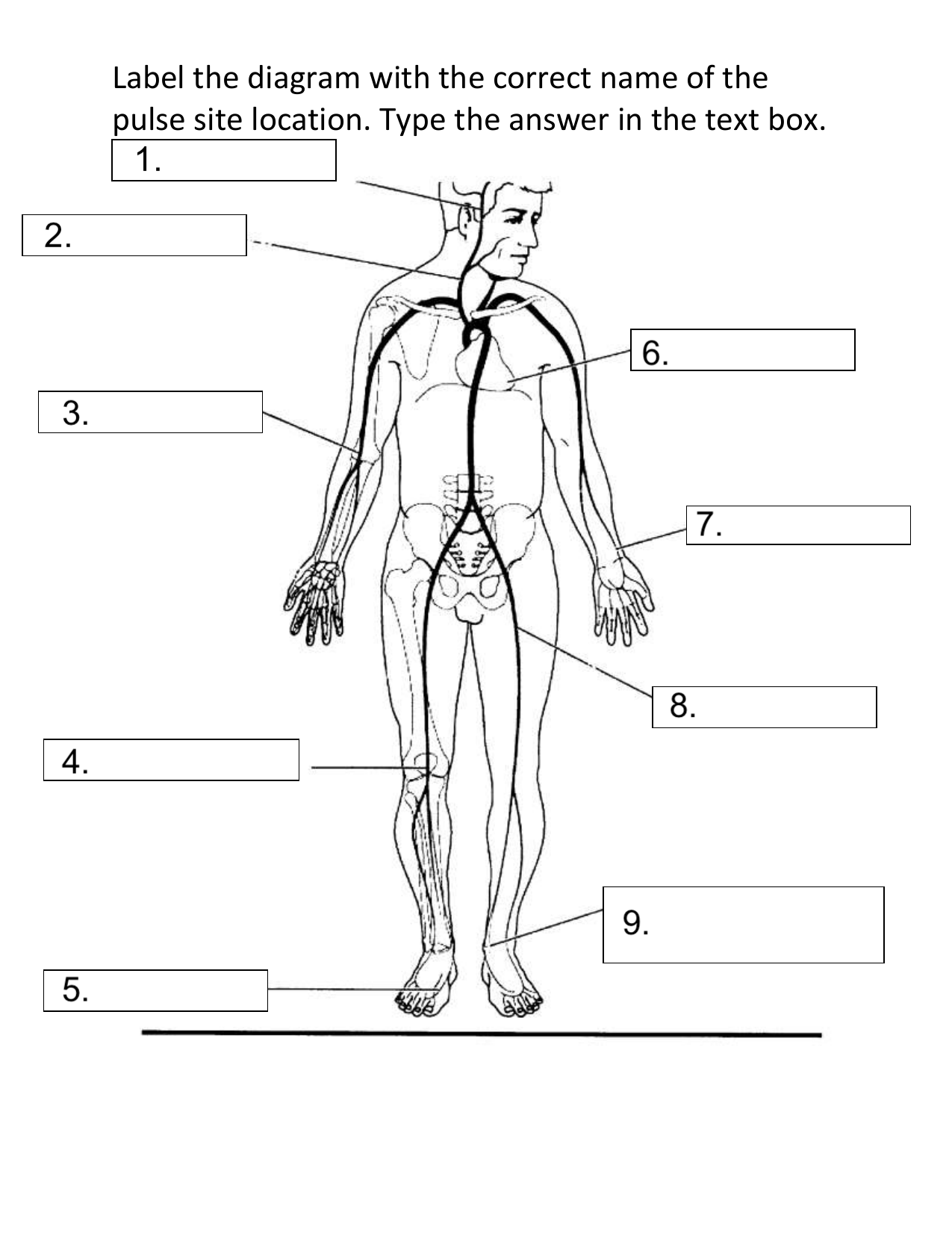
What pulse site is #2 on the diagram?
Carotid
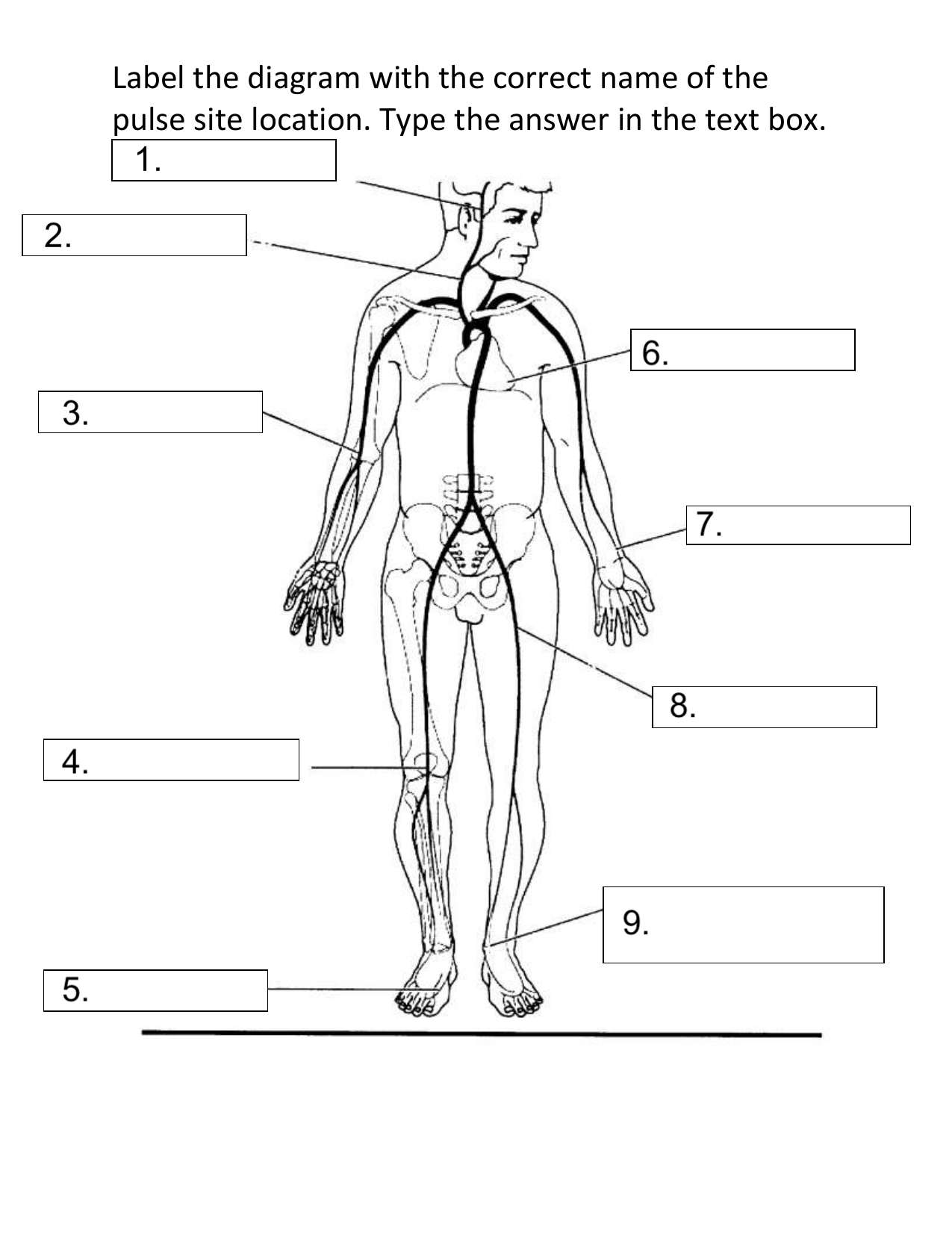
What pulse site is #3 on the diagram?
Brachial
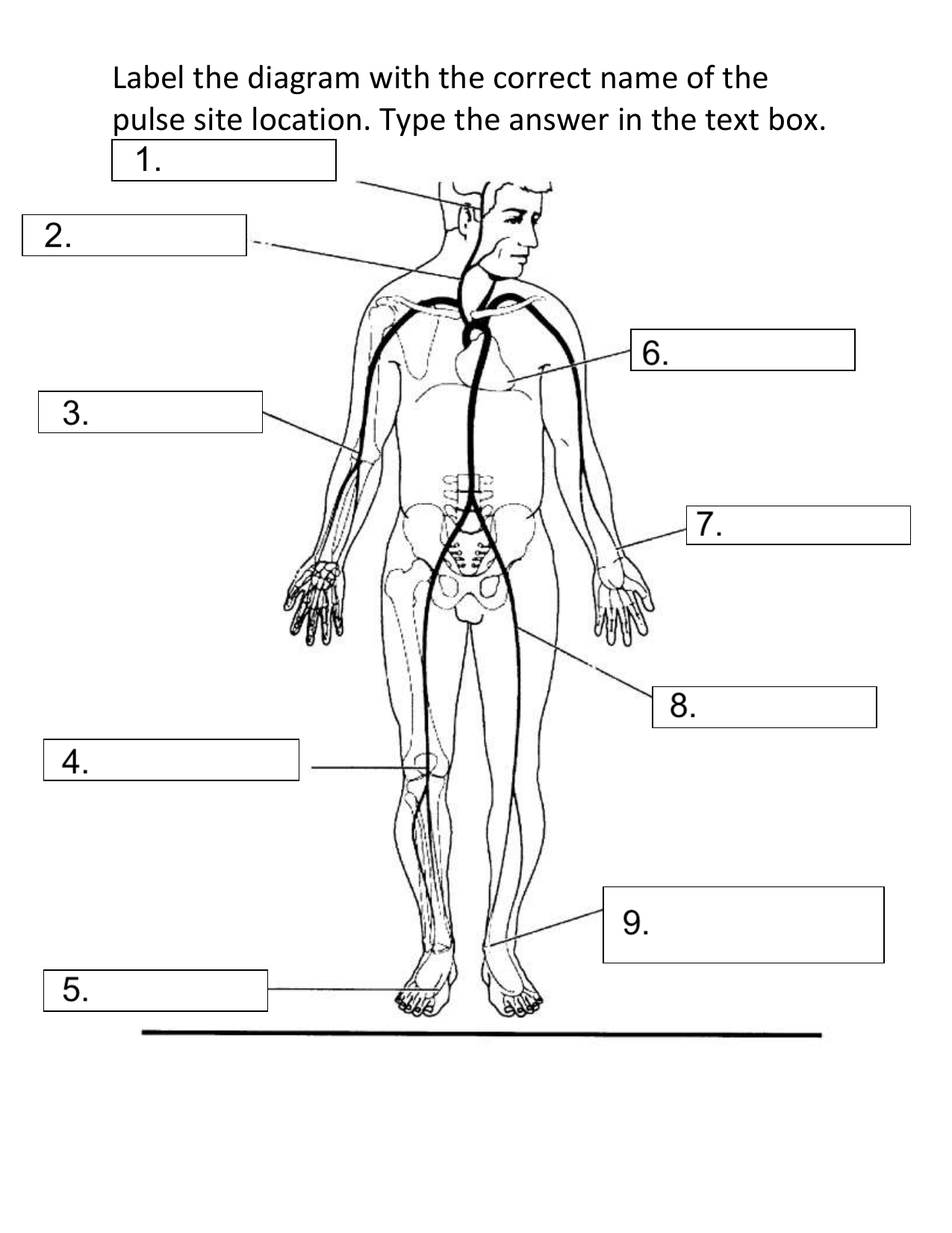
What pulse site is #4 on the diagram?
Popliteal
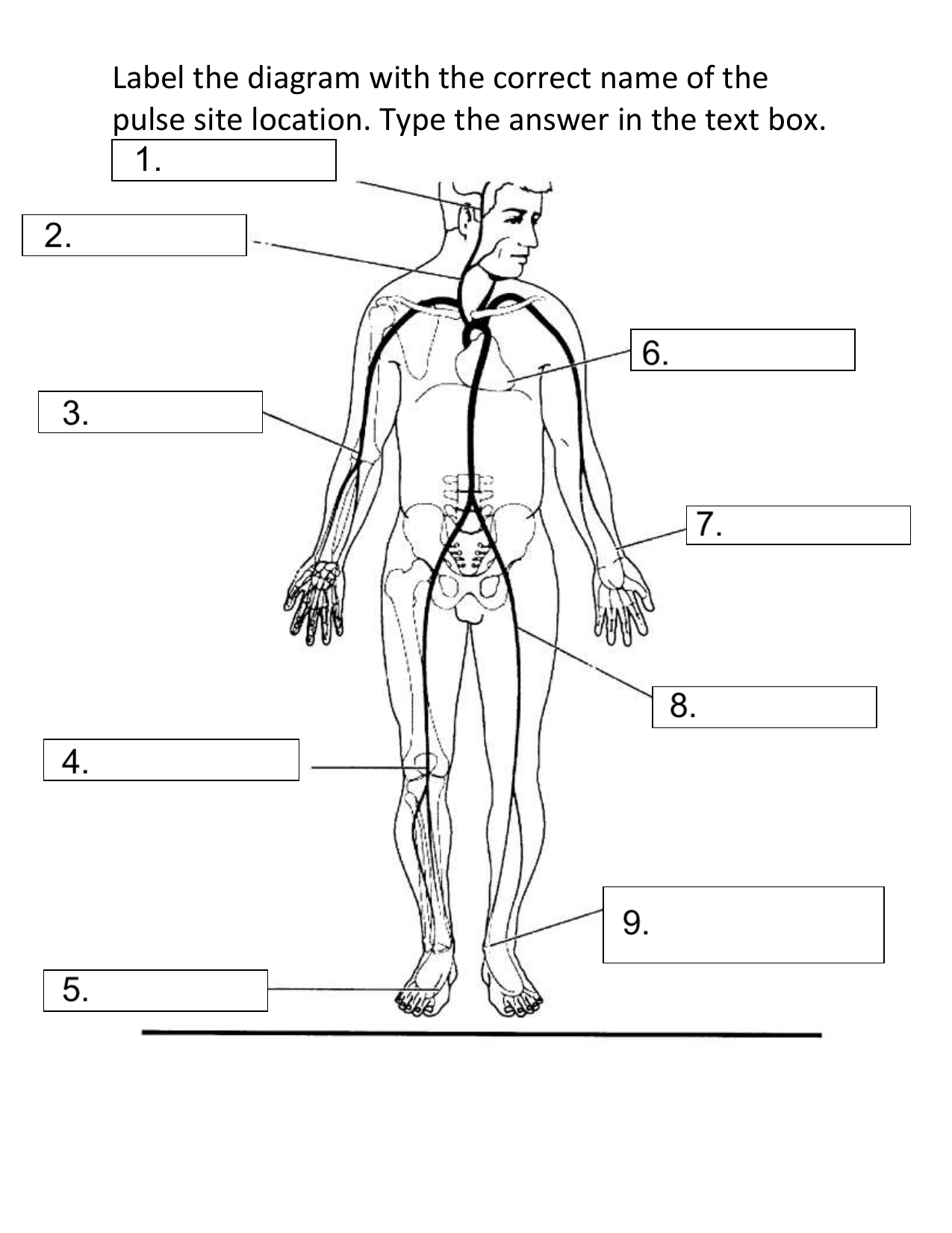
What pulse site is #5 on the diagram?
Dorsalis Pedis
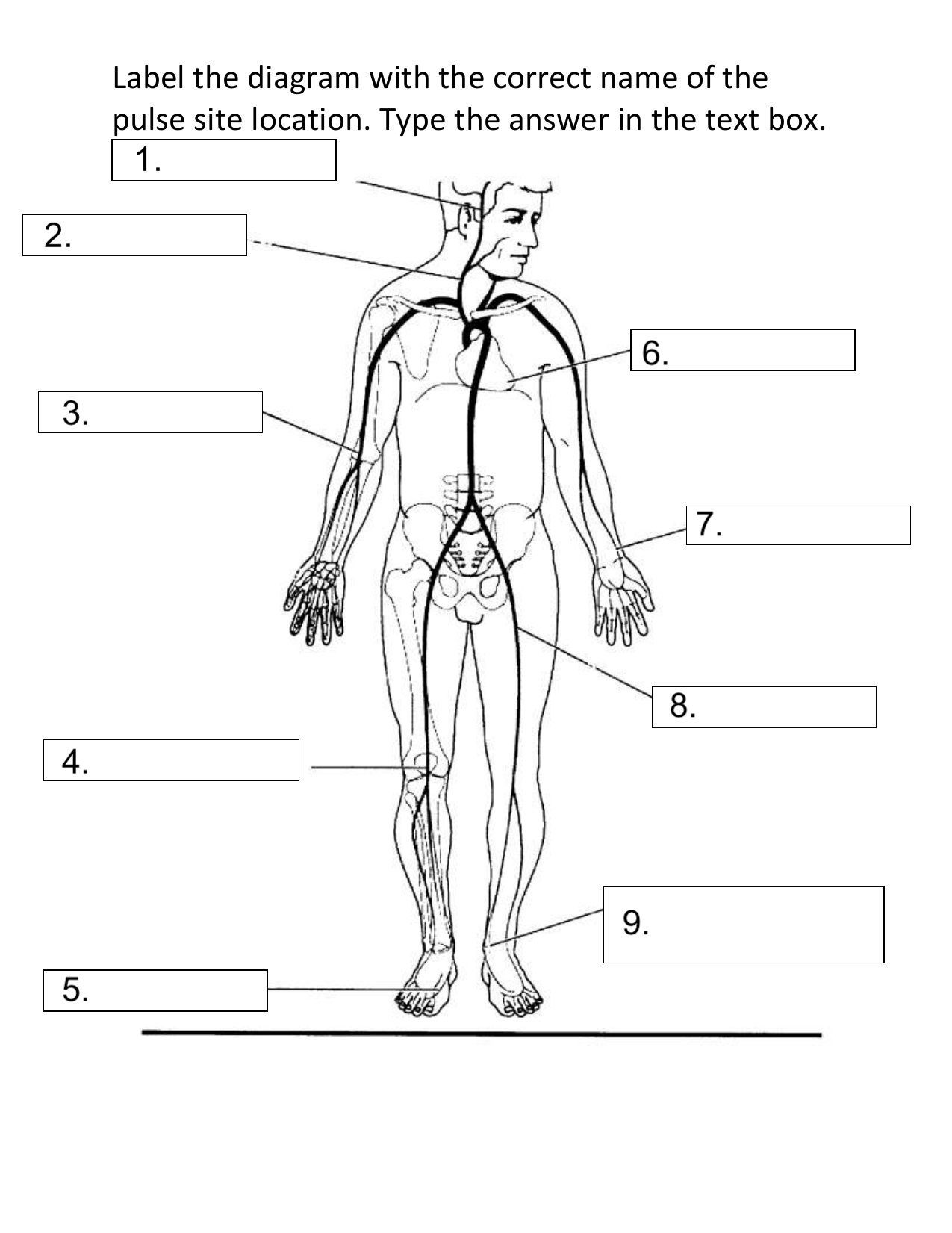
What pulse site is #6 on the diagram?
Apical
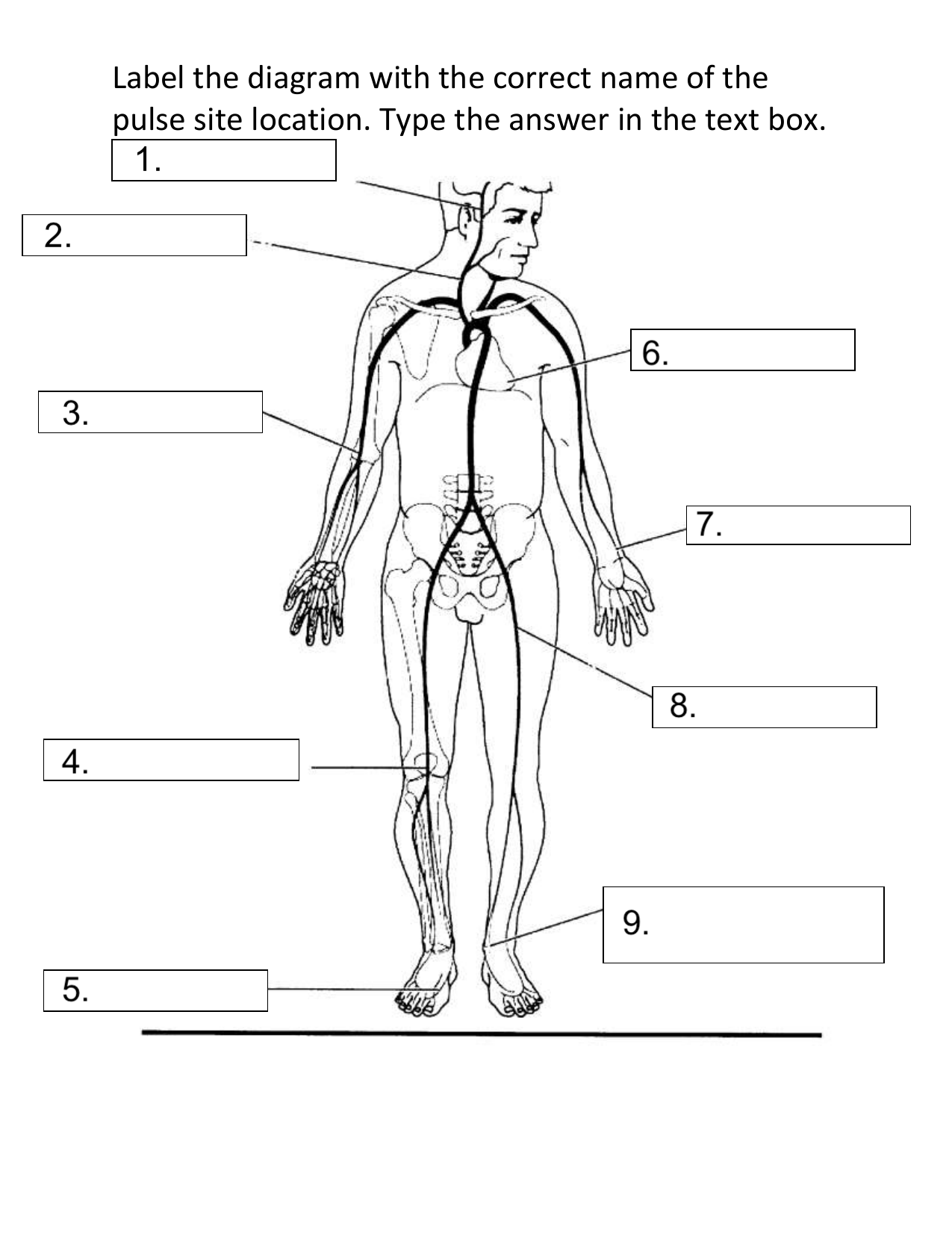
What pulse site is #7 on the diagram?
Radial

What pulse site is #8 on the diagram?
Femoral
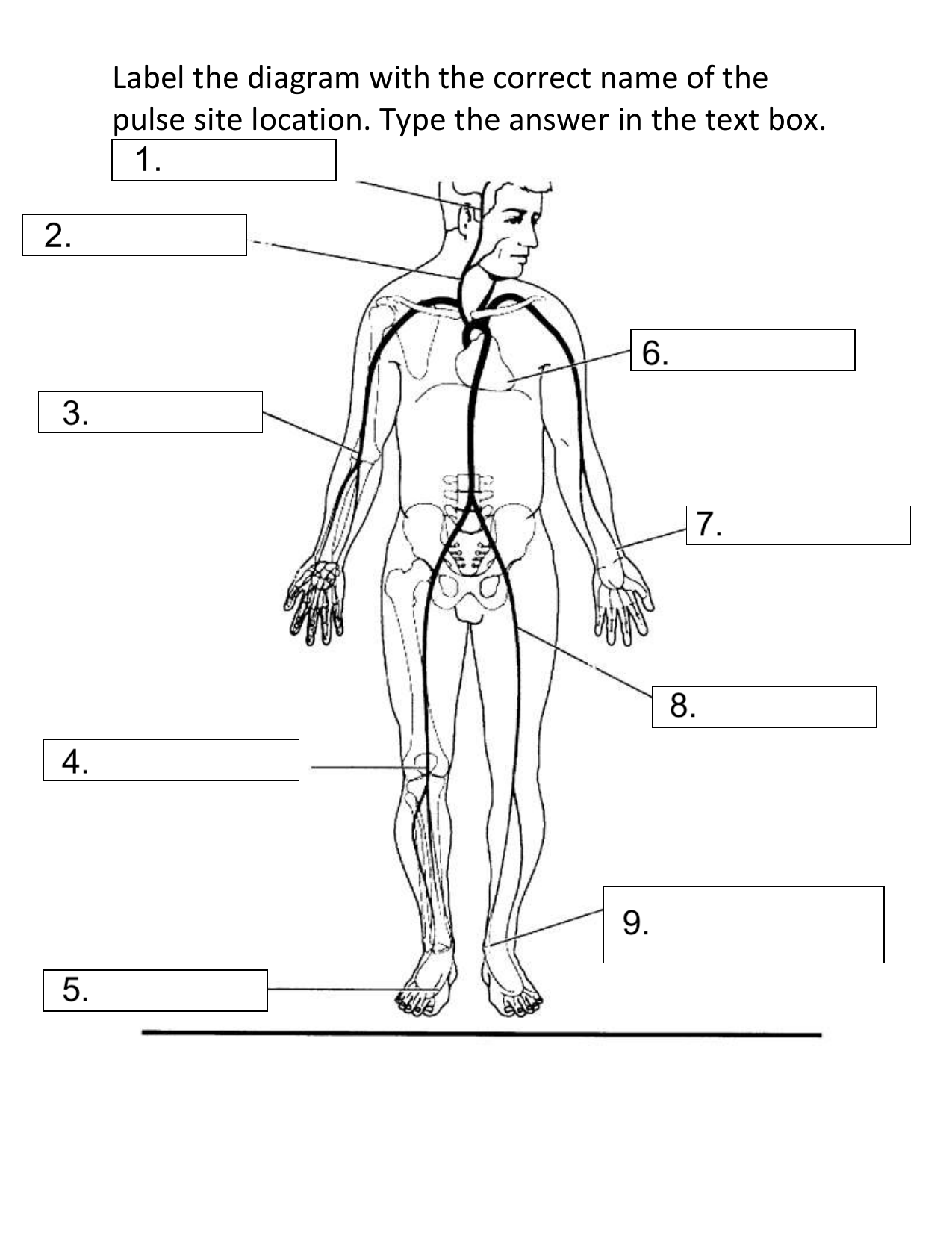
What pulse site is #9 on the diagram?
Posterior Tibial