Late Tooth Development- Biomedicine in Relation to Dentistry II
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
What will amelobasts secrete?
Inner molar of crown of tooth
What will odontoblasts secrete?
Dentin of the crown
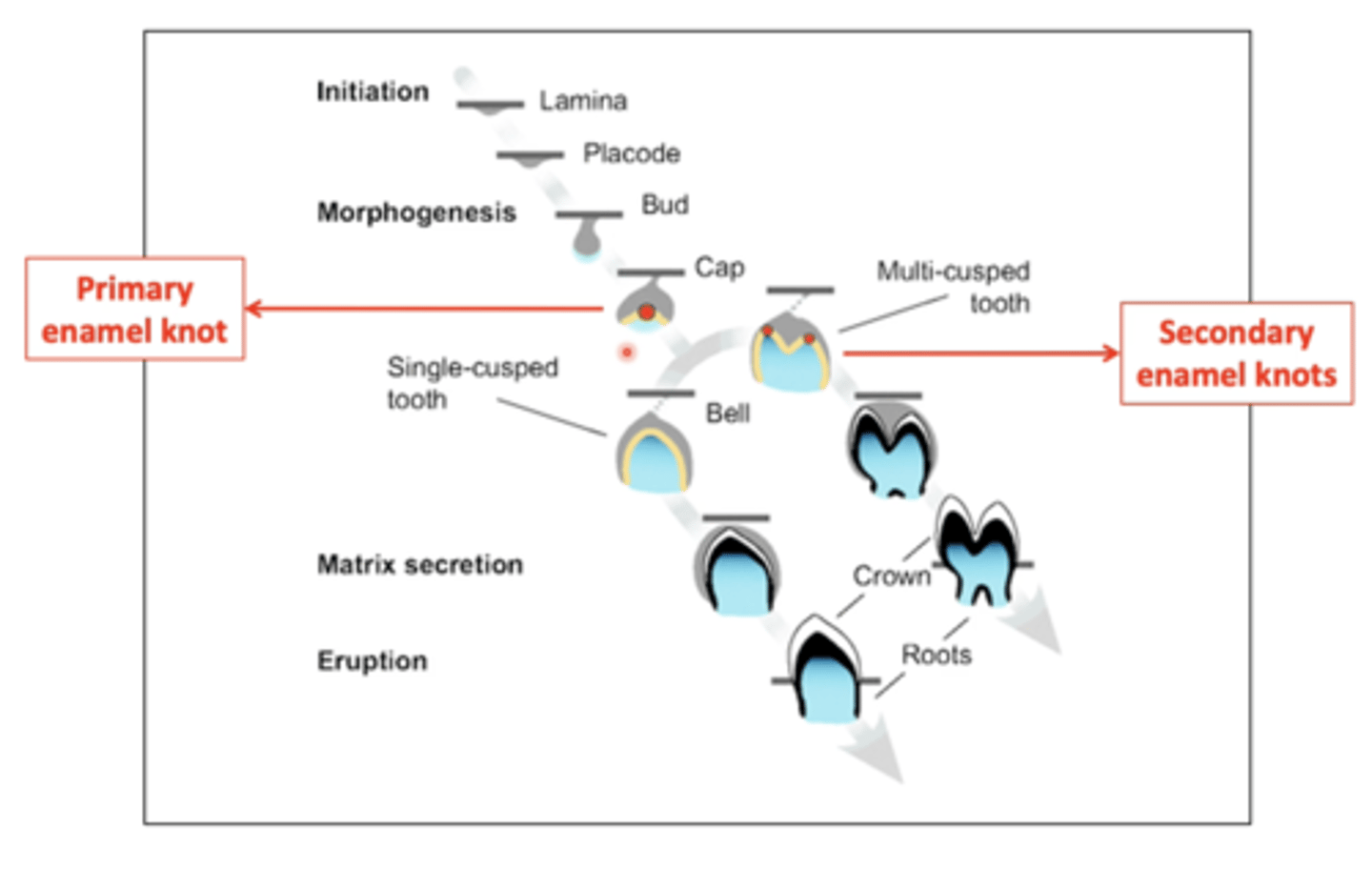
Where does the primary enamel knot (PEK) sit?
On top of a ball of condensed mesenchyme called the dental papilla, which will give rise to the dental pulp and odontoblasts
Do cells in the PEK divide?
No
What do cells in the PEK do?
They secrete signalling molecules which include BMPs, FGFs, Wnts, and Shh
What is the role of the PEK?
1. The juxtaposition of the non-proliferative cells of the PEK & the proliferative cells of the rest of the epithelial cap is believed to drive the bending of the inner enamel epithelium into a cap shape
2. PEK secretes signalling molecules that influence the proliferation & differentiation of cells of developing tooth germ
When is the PEK present?
At cap stage of tooth development; it's later eliminated by programmed cell death (apoptosis)
Do multicusped teeth have more than 1 single PEK at the cap stage?
No, both monocusped & multicusped teeth have only 1 single PEK at the cap stage
What is the significance of the PEK in molars?
It marks the position of the first buccal cusp in a molar
When is the early and late bell stage?
Early bell stage: 14th week
Late bell stage: 20th week
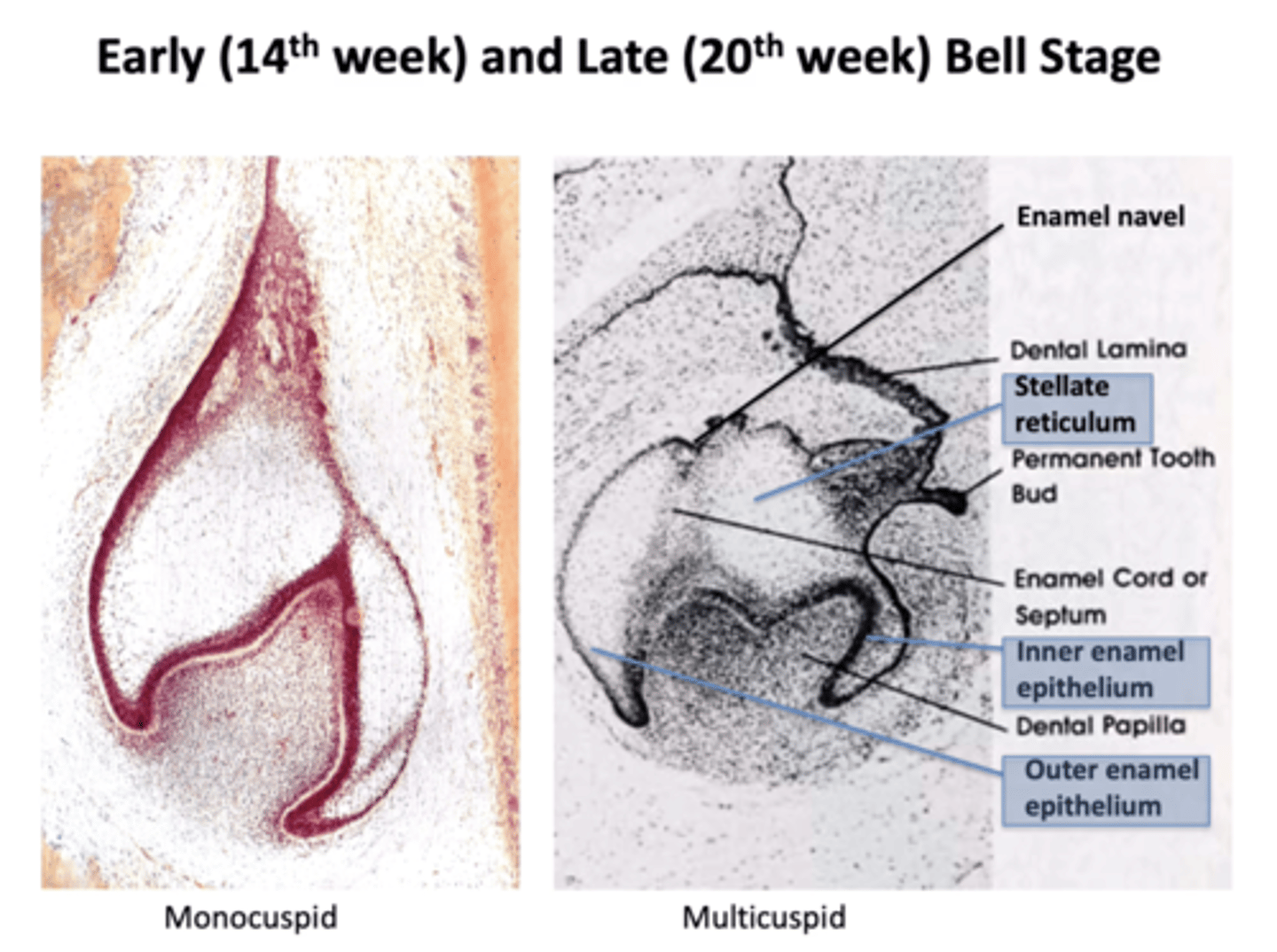
What is the predominant cell type of the enamel organ at the bell stage?
Stellate reticulum at the centre of the bell
What is the enamel cord/septum?
Localisation of cells on an enamel organ that appear from either the incisal edge (on a monocusped tooth) or from the tip of the first cusp (to develop in a multicusped tooth) to an enamel knot
What is the cervical loop?
Point where OEE meets IEE
Deepest part of the enamel organ
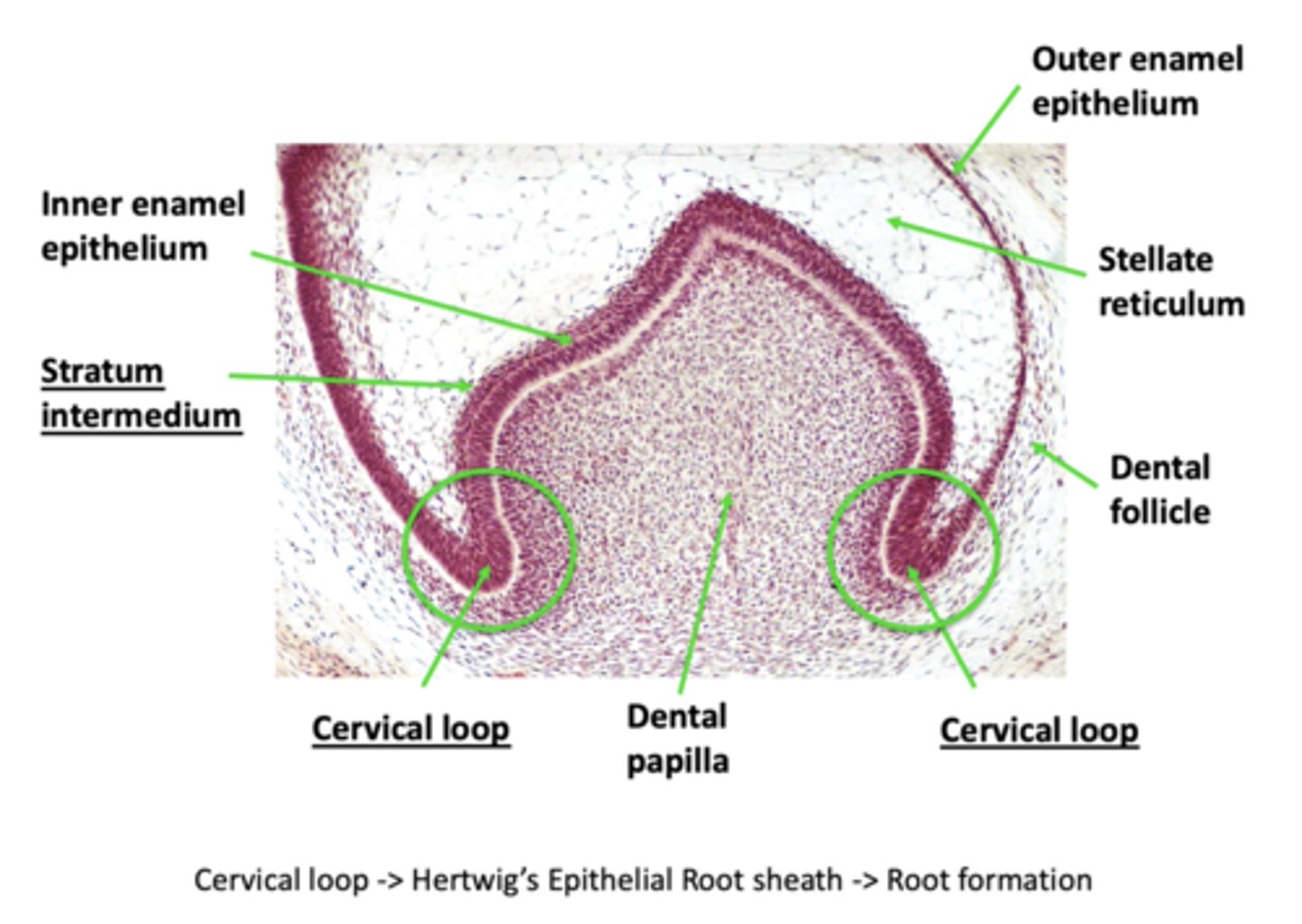
What is Hertwig's epithelial root sheath?
HERS - shape the root(s) by inducing dentin formation in the root area so that it is continuous with coronal dentin
HERS will determine if the root will be curved or straight, short or long, as well as single or multiple
What are the 3 layers of the dental follicle at the late bell stage?
Inner layer (formed of condensed mesenchymal cells)
Loose connective tissue (in between outer & inner layer)
Outer layer (lining the bony crypt)
What is different about the loose connective tissue compared to the outer and inner layers?
Loose connective tissue appears avascular whereas inner & outer layers exhibit high concentrations of blood vessels
What is established during the bell stage?
Tooth crown shape
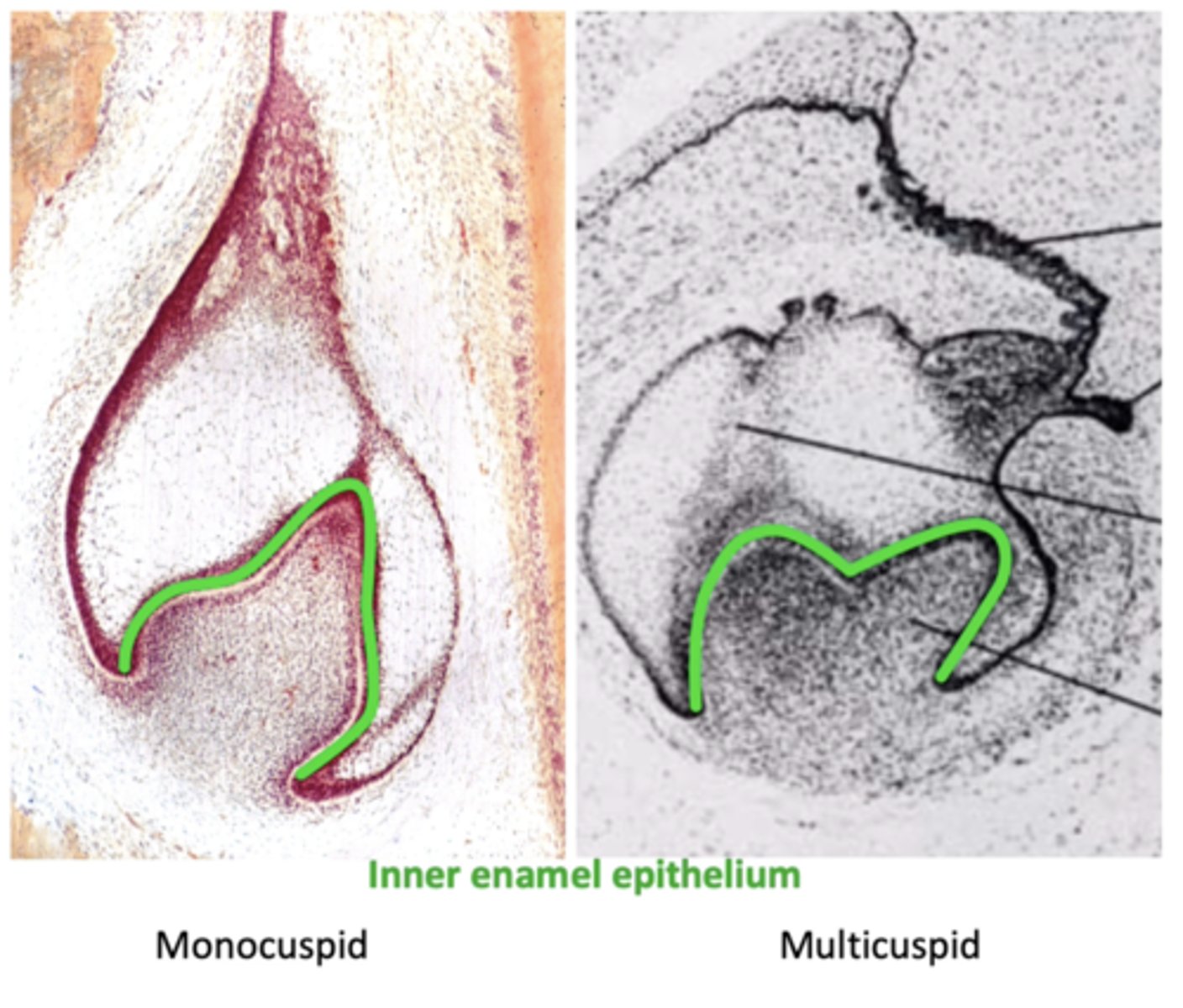
Where do secondary enamel knots (SEK) form?
In multicusped teeth only
What does the number of SEK determine?
No. of cusps
Diagrammatically show the stages of tooth development.
What is believed about the different rates of division within the IEE?
It leads to folding of the IEE
What do the non-proliferative areas do in the bell stage of multicusped teeth?
They buckle and form a cuspal outline
What begins to form at the late bell stage?
Tooth buds for permanent teeth
Where do tooth buds for permanent teeth develop?
At the deepest extremity of the dental lamina, on the lingual side
What is the new lamina that arises on the lingual side known as?
Successional lamina
Does the tooth bud for the permanent teeth always develop in the same way?
No, the successional lamina only forms in that way for permanent teeth that have had a deciduous precursor
How does the tooth bud develop for permanent teeth that don't have deciduous precursors?
Dental lamina extends posteriorly beneath the oral epithelium in the ectomesenchyme and the backward extension of the dental lamina will lead to the tooth germs for the permanent molars developing
What is the difference between an accessional tooth and successional tooth?
Accessional tooth: permanent tooth with no predecessor
Successional tooth: permanent tooth with a tooth predecessor
What breaks down at the late bell stage and what is the effect of this?
Dental lamina, and so the developing tooth is then completely disconnected from the epithelium of the oral cavity
What does the dental lamina break down into?
Clusters of epithelial cells and if they persist, they're known as Epithelial Pearls of Serres
What can Epithelial Pearls of Serres cause?
Cysts
Odontomas
Supernumerary teeth
How can continuous tooth generation be induced in mice?
By activating Wnt/beta-catenin signalling
What does an overexpression in the Wnt pathway lead to?
Increase in tooth number
What is histogenesis in tooth development?
Terminal differentation of specialised cells that give rise to fully formed dental tissues
When does hard tissue formation start?
Late bell stage
Which specialised cells produce which mineralised tooth tissues?
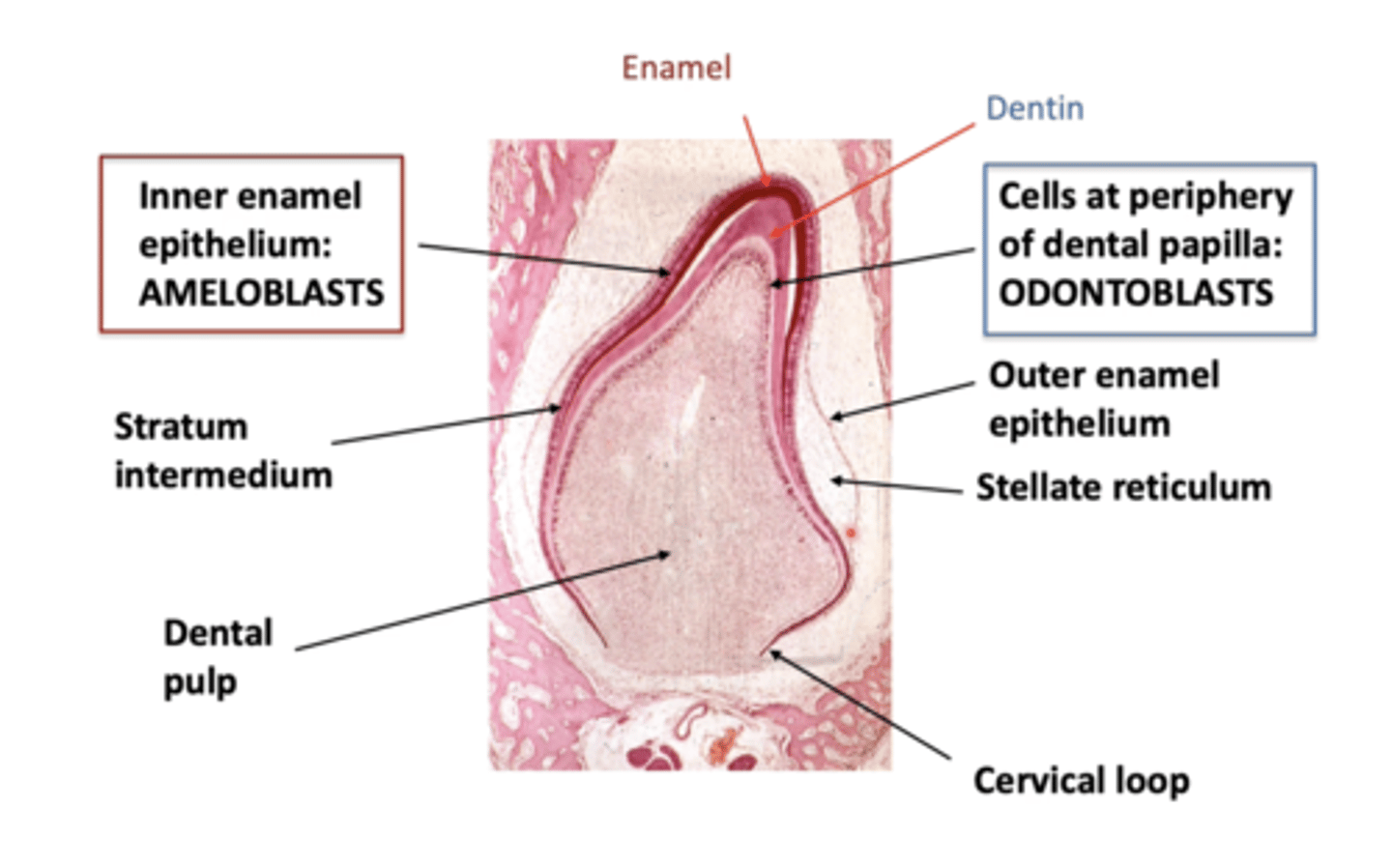
Where does the enamel and dentin start forming?
At the apex of the crown and in multicusped teeth, they start forming simultaneously at the tip of each one of the cusps of the tooth crown
How do the odontoblasts and ameloblasts differentiate?
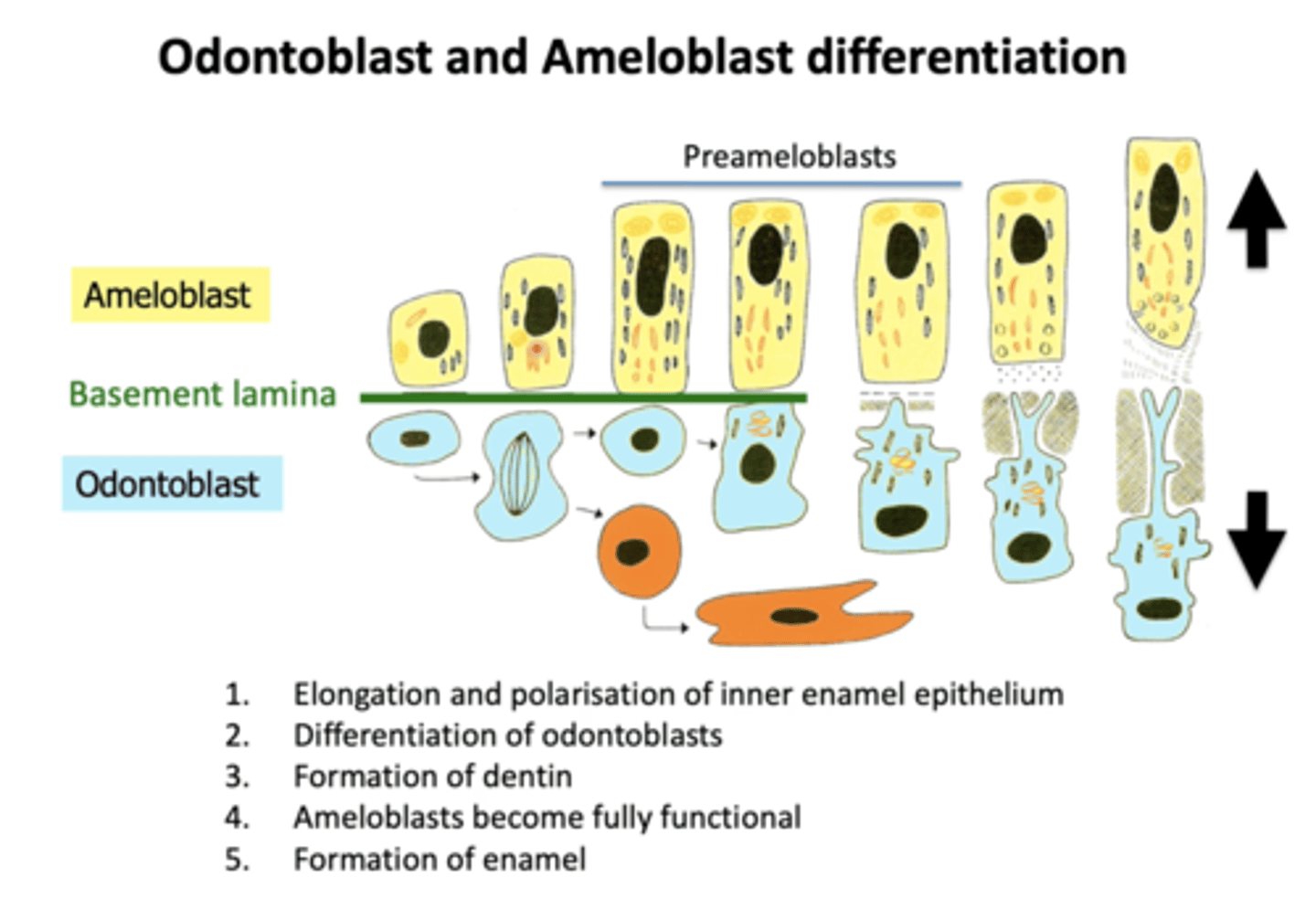
What crucial thing happens before enamel formation?
The stellate reticulum collapses at the tip of the cusp