GABA receptors
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
true or false: GABA receptors are the most abundant neurotransmitter receptors in the brain
false - second most abundant (glutamate receptors are the most abundant)
what are the 2 main classes of GABA receptors
ionotropic (ligand-gated ion channels that cause opening for ion to pass through)
metabotropic (GPCR that work more slowly and trigger intracellular cascades)
how do ionotropic GABA receptors work
binding of GABA causes opening of channel pore to allow influx of Cl- and effluc of HCO3-
what types of GABA receptors are present within ionotropic GABA receptors
GABAA receptors
GABAC receptors
what do GABAA receptors do
control most of synaptic transmission at GABAergic synapses in brain
what do GABAC receptors do
expressed mainly in the retina so is ivolbed with retinal signalling process
what effect do GABAₐ receptor agonists and allosteric modulators have in epilepsy models
suppress epileptic seizures
what effect do GABAₐ receptor antagonists have in
they can induce epileptic seizures
what does this suggest about the role of GABAₐ receptors in the brain
Enhancing GABAₐ activity reduces neuronal overexcitation, while blocking it increases seizure risk
what does the binding of GABA to metabotropic GABA receptors do
binding of GABA activates heterotrimeric G proteeins and intracellular signalling pathways which regulate activity of various voltage-gated ion channels
what are GABAB receptors
metabotropic GABA receptors
true or false: most GABA receptors are expressed presynaptically
false - expressed mainly postsynaptically
where are GABAₐ receptors found
expressed in all neurons in brain
main role of GABAₐ receptors
normal brain function
anxiety
epilepsy
panic disorders
insomnia
which drugs target GABAₐ receptors
benzodiazepines
barbiturates
anaesthetics
alcohol
what other substances modulate GABAₐ receptors
stress hormones
neurosteroids
what type of structure do GABAₐ receptors and GABAc receptors
pentamers (made of 5 subunits)
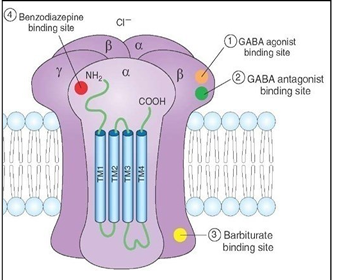
how many genes encode GABAₐ receptors and what are their groups
16 genes grouped into α, β, γ, δ, ε, θ, π subunits
how are GABAₐ receptors assembled
in the endoplasmic reticulum, typically from 2 α subunits, two β subunits, and one γ, δ, ε, π or θ subunit
what are GABAc receptors composed of
formed from ρ (rho) 1–3 subunits
what determines functional properties of GABAₐ receptors
GABA affinity
channel properties
drug selectivity
expression patterns
subcellular localisation
what type of inhibition do do GABAʙ receptors mediate
slow inhibitory response via G-protein coupled mechanisms
how do GABAʙ receptors work
activate Gi/o proteins → inhibits adenylyl cyclase → reduces cAMP and PKA → opens K+ channels (hyperpolarisation) → closes Ca2+ channels (reduces neurotransmitter release)
what is a specific agonist of GABAʙ receptors
baclofen
what is the structure of GABAʙ receptors
dimers of GABAʙ1 and GABAʙ2 subunits
GABA binds to GABAʙ1 (on extracellular domain)
G-proteins bind to GABAʙ2 (on intracellular domain)
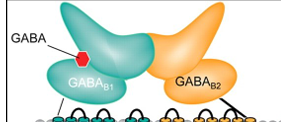
where are GABAʙ receptors located
postsynaptic membrane - produce slow IPSPs
presynaptic GABA terminals - act as autoreceptors (inhibit GABA release)
presynaptic glutamate terminals - act as heteroreceptors (inhibit glutamate release)
what is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter in the spinal cord and brainstem
glycine
what are glycine receptors
ligand-gated chloride channels that are hetero-pentamers of α and β subunits
how many isoforms exist for glycine receptors
4 α isoforms and 1 β isoform
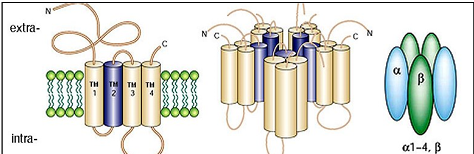
what happens when glycine receptors are activated in mature neurones
Cl- ions enter cell causing hyperpolarisation in postsynaptic neurone and reduced neuronal firing
what blocks glycine receptors and what are the effects
strychnine - competitive antagonist
causes over-excitation, pain, muscle cramps and exaggerated startle responses
apart from the spinal cord and brainstem, where else does glycine act as an inhibitory neurotransmitter
in the retina via glycinergic amacrine cells