PSY100 - Ch 14 The Troubled Mind: Psychological disorders
5.0(1)Studied by 10 people
Card Sorting
1/58
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:34 AM on 2/18/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
1
New cards
Psychological disorders
a syndrome characterized by clinically significant disturbance in an individual’s cognition, emotion regulation, or behaviour that reflects a dysfunction in the psychological, biological, or developmental processes underlying mental functioning
2
New cards
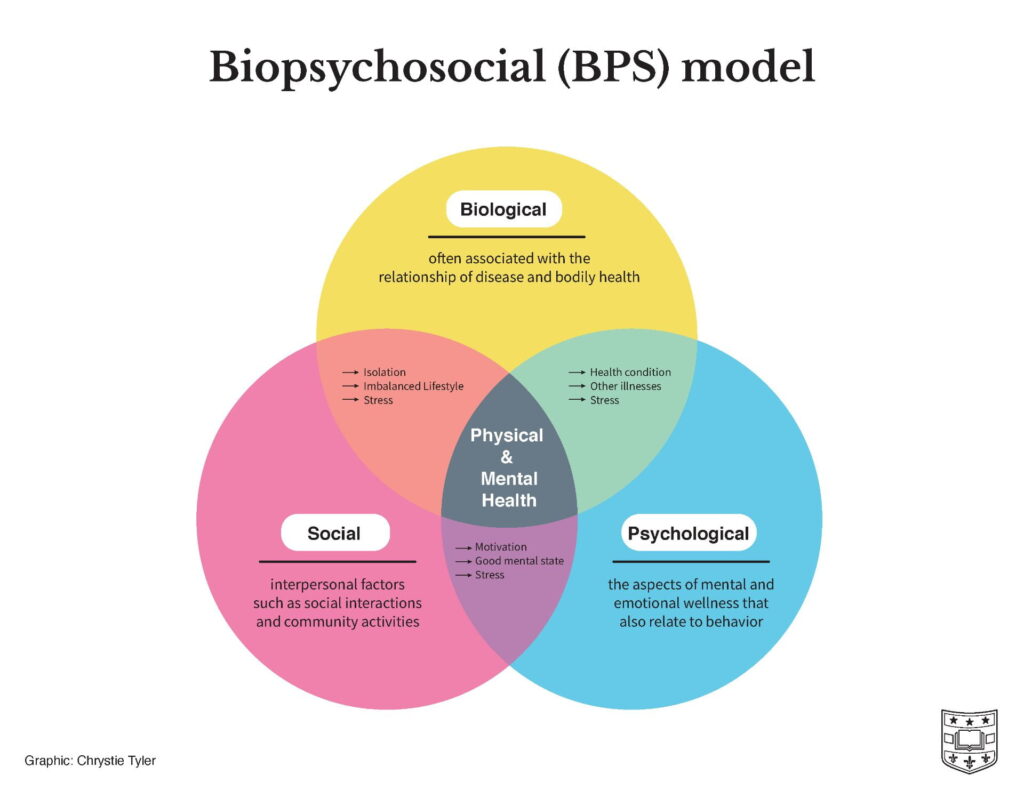
biopsychosocial model
emphasizes the interconnection between biological, psychological and socio-environmental factors.
3
New cards
evidence-based practice
combines the personal experience of the clinician, the best scientific evidence, and a consideration of patient values and expectations to tailor scientifically valid treatments to the individual
4
New cards
comorbidity
Two or more disorders in the same individual
5
New cards
abnormal behaviour
The study of psychological disorders
6
New cards
diathesis-stress model
A model that suggests that the experience of stress interacts with an individual’s pre-existing vulnerability to produce a psychological disorder
7
New cards
psychoanalytic/psychodynamic therapy
* Focus on bringing unconscious struggles into consciousness (free association, dream analysis)
* Insight: increase patient’s understanding of their own psychological processes
* Insight: increase patient’s understanding of their own psychological processes
8
New cards
Person/Client centered therapy
* Encouragement of personal growth through self-understanding → congruence
* Safe and comfortable setting, empathy, reflective listening
* unconditional positive regard
* Safe and comfortable setting, empathy, reflective listening
* unconditional positive regard
9
New cards
cognitive behavioural therapy
* Incorporates techniques from both cognitive therapy and behavioral therapy to correct faulty thinking and change maladaptive behaviors
* treats mood disorders like depression
* treats mood disorders like depression
10
New cards
Psychotropic medication/pharmacotherapy
therapy using psychotropic medication (drugs affecting mental processes)
11
New cards
anxiolytics
increases GABA activity for anxiety treatment (benzodiazepines)
12
New cards
antidepressants
increases serotonin levels (SSRIs)
13
New cards
Antipsychotics
blocks dopamine, reduces positive symptoms of schizophrenia (hallucinations, delusions, etc)
14
New cards
Neurodevelopmental disorders
* disorders typically diagnosed in childhood, yet often continue throughout one’s lifespan
* ADHD, Schizophrenia, autism, etc
* ADHD, Schizophrenia, autism, etc
15
New cards
autism spectrum disorder (ASD)
characterized by deficits in social relatedness and communication skills that are often accompanied by repetitive, ritualistic behaviour
16
New cards
ASD symptoms
* Little to no eye contact
* Failure to develop a normal theory of mind
* No language abilities or delayed acquisition of language to normal skills
* Difficulty maintaining conversations with others because of their social skills deficits
* High levels of repetitive, routine behaviour
* Extremely limited and focused preoccupations
* Unusually increased or decreased sensitivity to stimuli
* Failure to develop a normal theory of mind
* No language abilities or delayed acquisition of language to normal skills
* Difficulty maintaining conversations with others because of their social skills deficits
* High levels of repetitive, routine behaviour
* Extremely limited and focused preoccupations
* Unusually increased or decreased sensitivity to stimuli
17
New cards
ASD causes
* Strong evidence for genetic connection
* Environmental factors interacting with genetic factors associated with ASD during sensitive periods of brain development
* Parental age
* Environmental factors interacting with genetic factors associated with ASD during sensitive periods of brain development
* Parental age
18
New cards
attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
characterized by either unusual inattentiveness, hyperactivity with impulsivity, or both
19
New cards
ADHD symptoms
* The inability to maintain sustained attention or on-task behaviour for an age-appropriate length of time (problems completing and organizing work, following instructions)
* Engaging in structural activities is challenging (waiting in line), behaviour is noisy, active, and appear to take action without thinking
* Engaging in structural activities is challenging (waiting in line), behaviour is noisy, active, and appear to take action without thinking
20
New cards
ADHD is 2 times more common in … than …
men, women
21
New cards
ADHD causes
* Genetics play a significant role in the development of ADHD
* Environmental factors: lead contamination, low birth weight, and prenatal exposure to tobacco, alcohol, and other drugs
* Underactive frontal lobes or smaller amygdala, basal ganglia, and hippocampus
* Environmental factors: lead contamination, low birth weight, and prenatal exposure to tobacco, alcohol, and other drugs
* Underactive frontal lobes or smaller amygdala, basal ganglia, and hippocampus
22
New cards
Schizophrenia spectrum
A disorder characterized by hallucinations, delusions, disorganized thought and speech, disorders of movement, restricted affect, and avolition or asociality
23
New cards
Schizophrenia: Positive symptoms
excess in behaviour
* Delusions: false personal beliefs based on incorrect inferences about reality
* Hallucinations: false sensory experiences
* Disorganized Speech: loosening of associations; speech pattern in which thoughts are disorganized or meaningless
* Disorganized Behaviour: disorganized or abnormal motor behaviour, e.g., catatonia
* Delusions: false personal beliefs based on incorrect inferences about reality
* Hallucinations: false sensory experiences
* Disorganized Speech: loosening of associations; speech pattern in which thoughts are disorganized or meaningless
* Disorganized Behaviour: disorganized or abnormal motor behaviour, e.g., catatonia
24
New cards
Schizophrenia: Negative symptoms
deficits in functioning, harder to treat
* Isolation, withdrawal
* Apathy
* Blunted emotion
* Slowed, monotonous speech
* Isolation, withdrawal
* Apathy
* Blunted emotion
* Slowed, monotonous speech
25
New cards
Schizophrenia: Treatment
* Pharmacological: antipsychotics are very effective
* Side effects: tardive dyskinesia (results in uncontrollable sudden erratic motor behaviors
* Second-gen meds: clozapine (lower risk of tardive dyskinesia)
* No effect on negative symptoms
* Side effects: tardive dyskinesia (results in uncontrollable sudden erratic motor behaviors
* Second-gen meds: clozapine (lower risk of tardive dyskinesia)
* No effect on negative symptoms
26
New cards
mood disorders
your general emotional state or mood is distorted or inconsistent with your circumstances and interferes with your ability to function.
27
New cards
common mood disorders
major depression, dysthymia (dysthymic disorder), bipolar disorder, mood disorder due to a general medical condition, and substance-induced mood disorder.
28
New cards
depressive attributional style
attributes failures to internal, global, stable causes
29
New cards
Beck’s Cognitive Triad
negative views about oneself → negative views about the world → negative views about the future → repeat
30
New cards
bipolar disorder
a mental illness that causes unusual shifts in a person's mood, energy, activity levels, concentration, and ability to carry out day-to-day tasks
31
New cards
manic episodes
elevated mood, increased activity, diminished need for sleep, grandiose ideas, racing thoughts, and extreme distractibility
32
New cards
BPD: Type 1
* extreme highs (manic episodes, irritable to invincible, more frequent with lack of treatment) and low
33
New cards
BPD: Type 2
* not as extreme
34
New cards
BPD: treatment
* lithium, used for treatment
* Patients tend to refuse treatment as it will dampen their ability to emote
* Patients tend to refuse treatment as it will dampen their ability to emote
35
New cards
major depressive disorder
* characterized by lengthy periods of depressed mood, loss of pleasure in normal activities, disturbances in sleep and appetite, difficulty concentrating, feelings of hopelessness, and possible thoughts of suicide
* presence of depressive mood and anhedonia
* presence of depressive mood and anhedonia
36
New cards
anhedonia
loss of the ability to feel pleasure
37
New cards
electroconvulsive therapy
treats depression
procedure, done under general anesthesia, in which small electric currents are passed through the brain, intentionally triggering a brief seizure
procedure, done under general anesthesia, in which small electric currents are passed through the brain, intentionally triggering a brief seizure
38
New cards
deep brain stimulation
involves implanting electrodes within certain areas of the brain to regulate abnormal impulses
39
New cards
anxiety disorders
* characterized by excessive anxiety in the absence of true danger
40
New cards
generalized anxiety disorder
characterized by excessive anxiety and worry that is not correlated with particular objects or situations
41
New cards
GAD: symptoms
Hypervigilance → fatigue, irritability, headaches, etc.
42
New cards
specific phobias
fears of specific objects
43
New cards
social anxiety disorder
* characterized by an unrealistic fear of being scrutinized and criticized by others
44
New cards
agoraphobia
* unrealistic fear of open spaces, being outside the home alone, or being in a crowd
* often claustrophobic
* often claustrophobic
45
New cards
Panic Disorders
* characterized by repeated panic attacks and fear of future attacks
46
New cards
Panic Attack
* the experience of intense fear and autonomic arousal in the absence of real threat
47
New cards
anxiety disorders: symptoms
* Autonomic system arousal
* Worry/anxiety/tenseness
* Restlessness
* Excessive startle response
* Worry/anxiety/tenseness
* Restlessness
* Excessive startle response
48
New cards
anxiety disorders: causes
* Cognitive Factors
* attention to and perception of threat
* Ambiguous stimuli
* interpretation of bodily sensations (panic disorder)
* attention to and perception of threat
* Ambiguous stimuli
* interpretation of bodily sensations (panic disorder)
49
New cards
anxiety disorders: biological factors
* Genetics; inhibited temperamental style
* Fear circuitry dysfunction (amygdala, prefrontal cortex)
* Problems with the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis → the system responsible for the release of cortisol into the bloodstream during periods of stress
* Fear circuitry dysfunction (amygdala, prefrontal cortex)
* Problems with the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis → the system responsible for the release of cortisol into the bloodstream during periods of stress
50
New cards
anxiety disorders: treatment
* Anxiolytics: xanax → increase GABA
* Cognitive-Behavioural Therapy
* Exposure Therapy (phobias)
* Cognitive-Behavioural Therapy
* Exposure Therapy (phobias)
51
New cards
obsessive compulsive disorders
* associated with intrusive obsessions and compulsions; anticipates catastrophe and loss of control
52
New cards
obsession
* recurrent, intrusive, and unwanted thoughts or ideas or mental images; often include fear of contamination, of accidents, or of one’s own aggression
53
New cards
compulsions
* repetitive, ritualistic behaviour associated with high anxiety, particular acts that one feels driven to perform over and over again
54
New cards
OCD: causes
* Strong genetic vulnerability, childhood trauma
* Classical (anxiety paired to some event, originally linked to one thing grows to many other things) and operant conditioning (behaviours linked with relief)
* Classical (anxiety paired to some event, originally linked to one thing grows to many other things) and operant conditioning (behaviours linked with relief)
55
New cards
learned helplessness
A state in which experiencing random or uncontrolled consequences leads to feelings of helplessness and possibly depression
56
New cards
narcissistic personality disorder (NPD)
A disorder characterized by grandiosity, need for admiration, and low empathy
57
New cards
post-traumatic-stress-disorder (PTSD)
A disorder caused by the experience of trauma, which leads to flashbacks, dreams, hypervigilance, and avoidance of stimuli associated with the traumatic event
* recently added DSM-5 (Trauma and stressor-related disorders
* recently added DSM-5 (Trauma and stressor-related disorders
58
New cards
dissociative disorder (ex: DID)
A disorder characterized by disruptions in a person’s identity, memory, or consciousness
59
New cards
schizophrenia: biological + environmental causes
* Genetic component
* Structural and functional differences in the brain → frontal lobe dysfunction, enlarged ventricles
* Environmental stress → socioeconomic status, prenatal environment
* Drug use (THC)
* Structural and functional differences in the brain → frontal lobe dysfunction, enlarged ventricles
* Environmental stress → socioeconomic status, prenatal environment
* Drug use (THC)