Interspecific Competition and Resource Partitioning
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
What is coexistence in ecological terms?
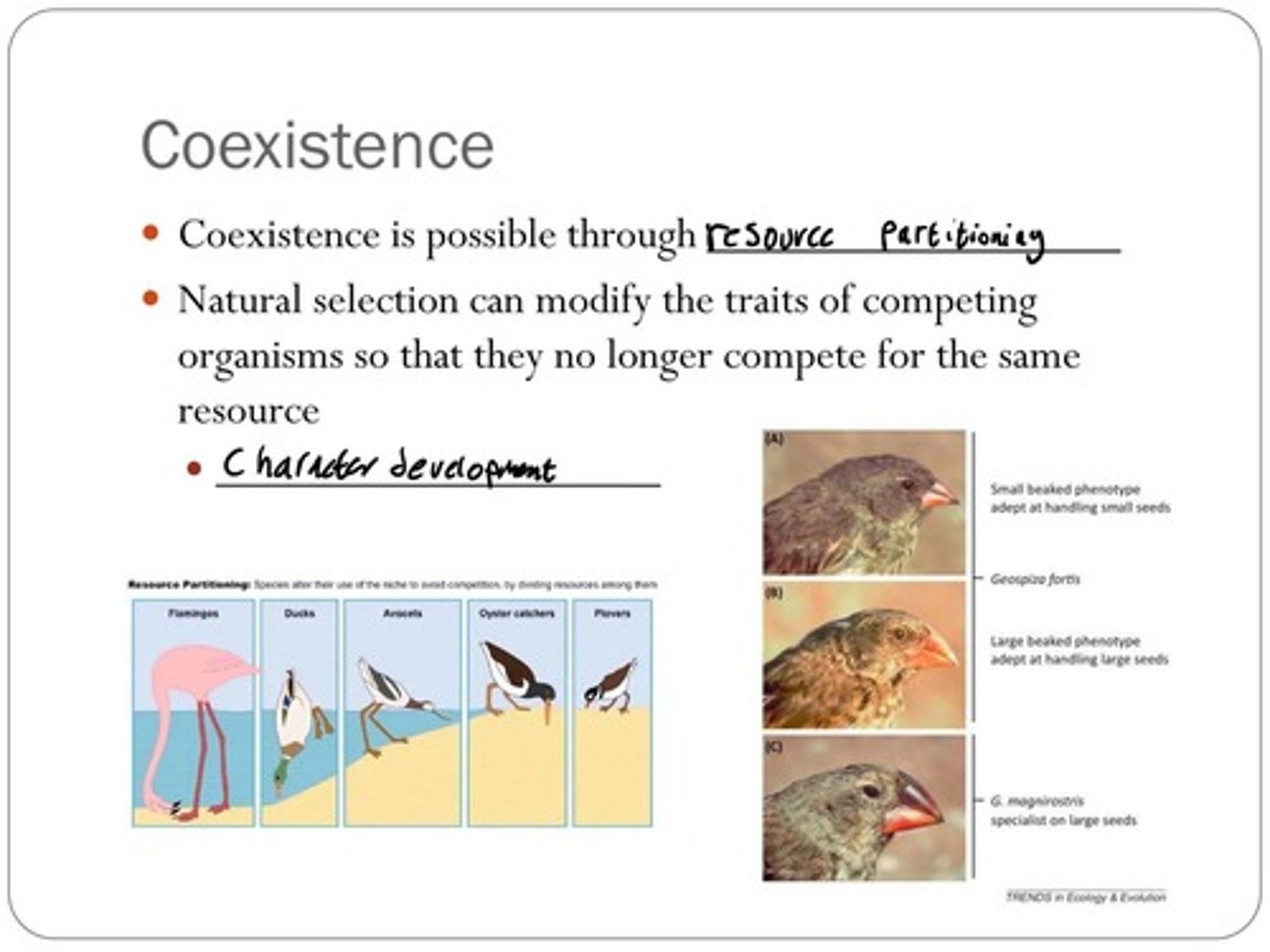
Coexistence is possible through resource partitioning, allowing species to share resources without direct competition.
How can natural selection affect competing organisms?
Natural selection can modify the traits of competing organisms so that they no longer compete for the same resource.
What is resource partitioning?
Resource partitioning occurs when species alter their use of the niche to avoid competition by dividing resources among them.
Name some species that exhibit resource partitioning.
Oyster catchers, flamingos, ducks, avocets, and plovers.
What are the two phenotypes of Geospiza finches mentioned?
Small beaked phenotype adept at handling small seeds (Geospiza fortis) and large beaked phenotype adept at handling large seeds (G. magnirostris), which is a specialist on large seeds.
What role does competition play in niche development?
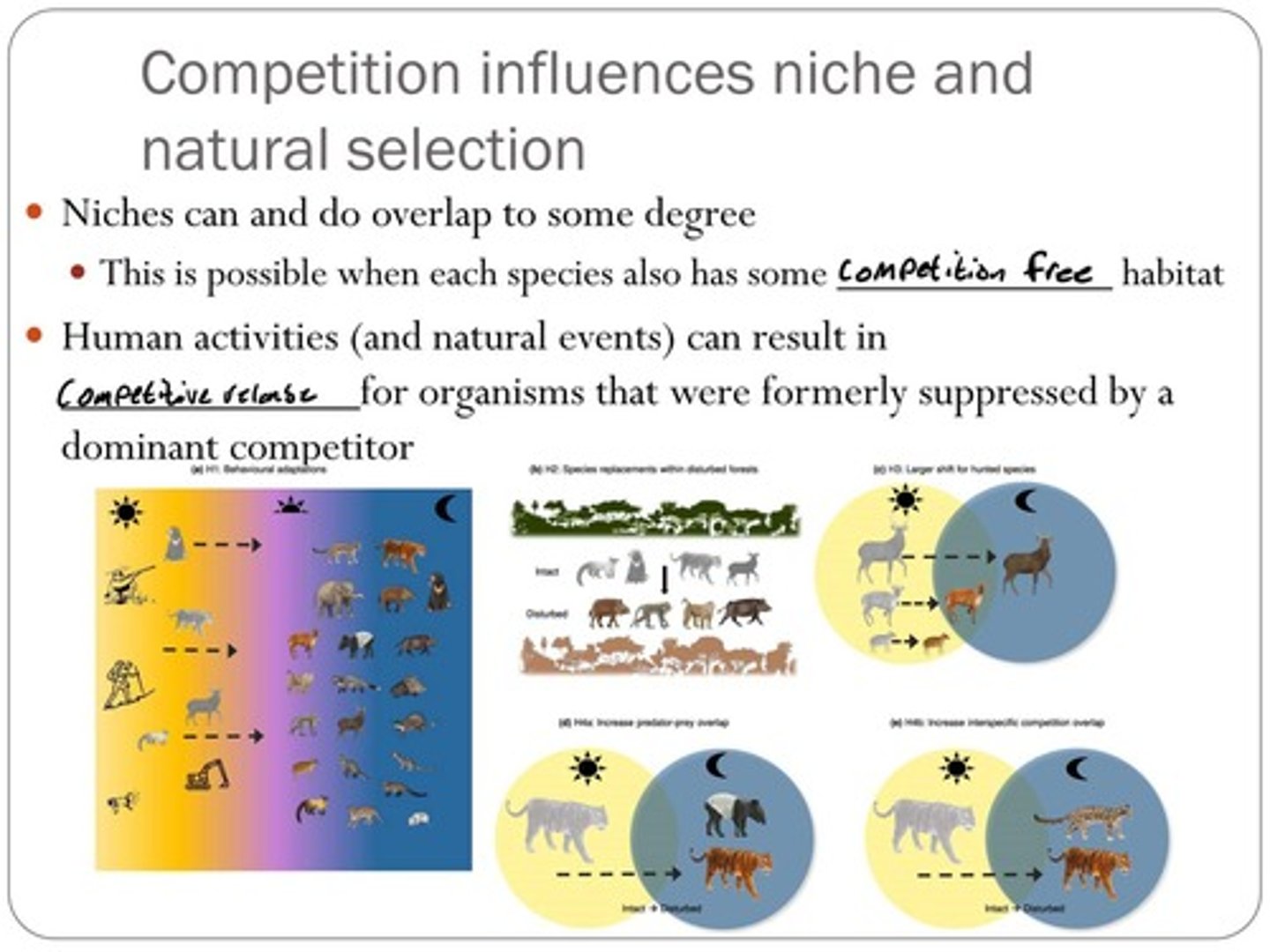
Competition influences niche and natural selection, allowing niches to overlap to some degree.
What is competitive release?
Competitive release occurs when human activities or natural events result in organisms that were formerly suppressed by a dominant competitor to thrive.
What are some hypotheses related to competitive release?
H1: Behavioral adaptations, H2: Species replacements within disturbed forests, H3: Larger shift for hunted species, H4a: Increase predator-prey overlap, H4b: Increase interspecific competition overlap.
What is the Lokta-Volterra Model?
The Lokta-Volterra Model describes the dynamics of biological systems in which two species interact, typically as predator and prey or as competitors.
What factors can affect competition besides resources?
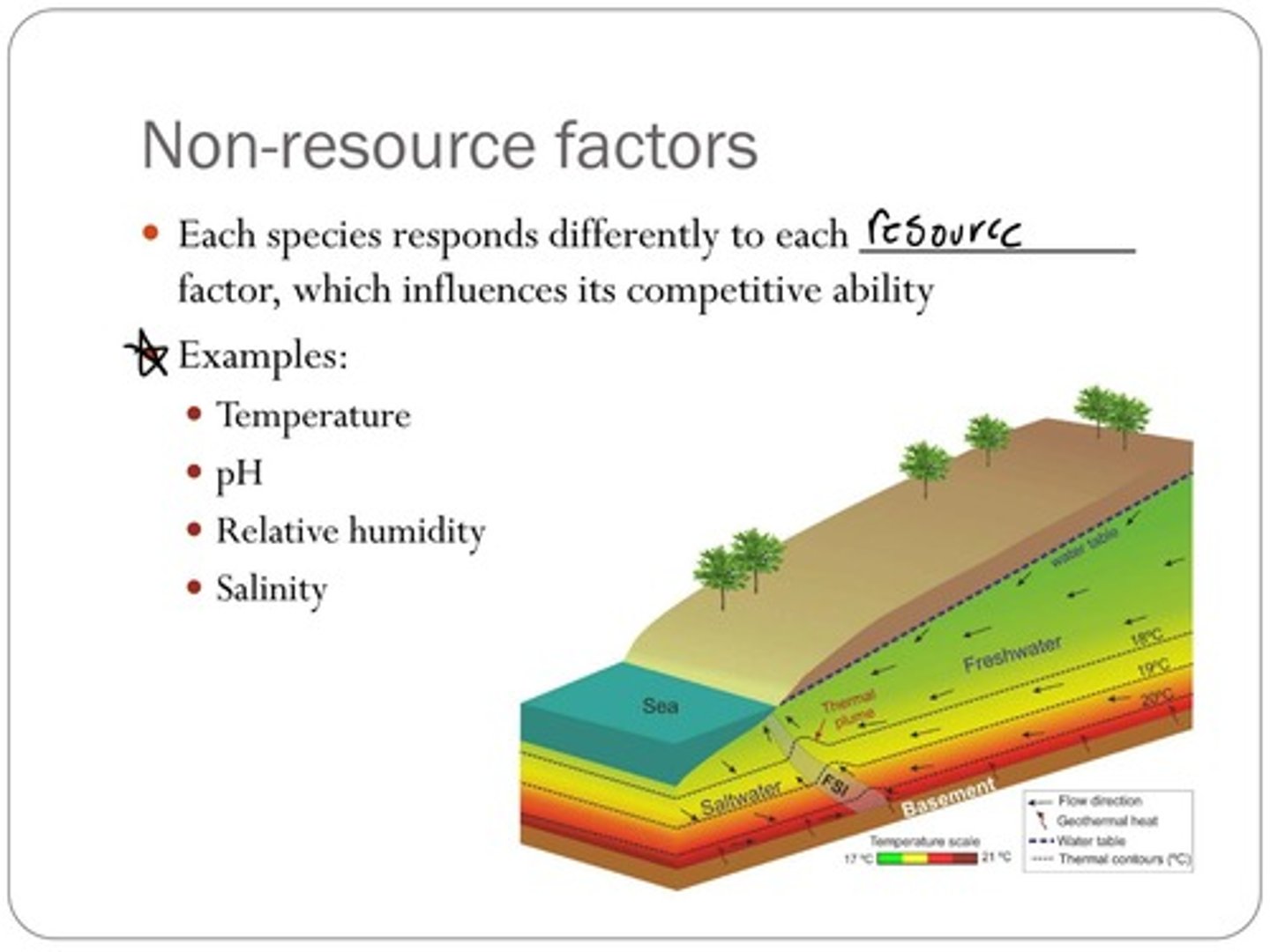
Non-resource factors can also affect competition.
How does competitiveness vary along environmental gradients?
Competitiveness varies along environmental gradients, such as moisture availability varying with elevation.

What happens to tree species along an environmental gradient?
Multiple tree species could occur anywhere along the gradient, but their relative competitiveness is not equal.
What resources do trees compete for?
Trees compete for light, nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), water, and micronutrients.
How can winning the battle for one resource affect competition for others?
Winning the battle for one resource can lead to increased acquisition of other resources.
What is asymmetric competition?
Asymmetric competition occurs when one species has a greater advantage over another in acquiring resources.
What is the significance of tree composition in competition?
The composition of larger competitors, such as different proportions of spruce, fir, and beech, can influence competition outcomes.
What does the term 'interspecific competition' refer to?
Interspecific competition refers to competition between different species for the same resources.
What is the impact of faster-growing trees on slower-growing trees?
Faster-growing trees can limit the growth of slower-growing trees, potentially leading to their death.
What is the relationship between competition and resource availability?
Species with similar niche requirements will often compete for multiple resources, affecting their survival and growth.
What is the role of environmental gradients in tree species distribution?
Environmental gradients affect where different tree species can thrive based on their competitive abilities.
What is the overall learning objective regarding interspecific competition?
The objective is to understand the dynamics of interspecific competition and how it shapes ecological interactions.
What is the Lokta-Volterra Model used to describe?
It is used to describe interspecific competition between species.
What does the Competitive Exclusion Principle state?
Two species that compete directly for the same resource cannot coexist; one will exclude the other.
What are non-resource factors that can affect competition?
Factors such as temperature, pH, relative humidity, and salinity.
How can annual variations in rainfall influence competition in grasslands?
They can influence the identity of the dominant competitor.
What is meant by competition for multiple resources?
It refers to the competition between species for different types of resources, which can vary in their availability.
What is the significance of relative competitiveness of species along environmental gradients?
It indicates that species may perform differently depending on the environmental conditions they encounter.
What is resource partitioning?
It is a strategy that allows two species to coexist by utilizing different resources or the same resource in different ways.
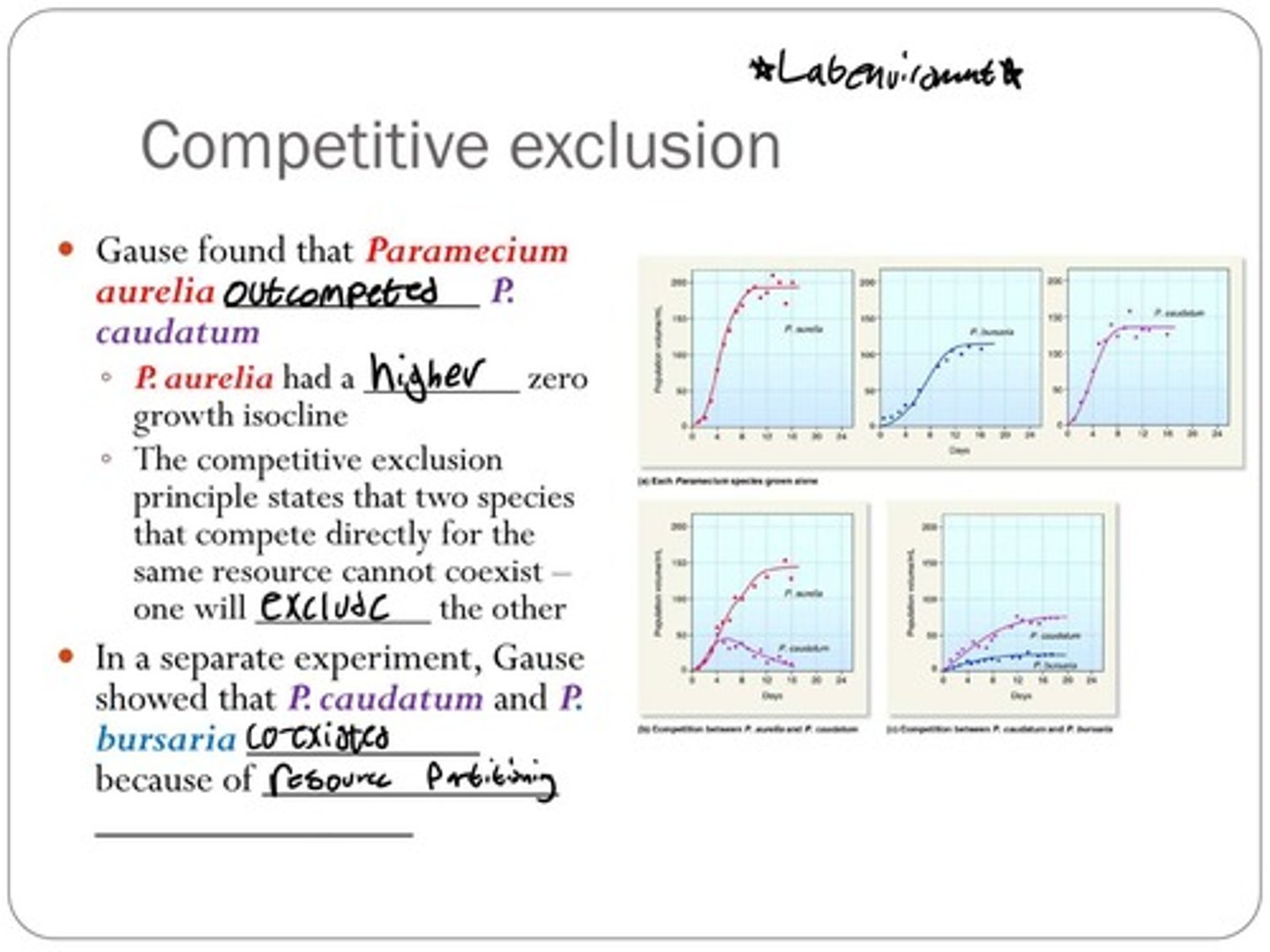
How did Gause demonstrate competitive exclusion with Paramecium species?
He showed that P. aurelia outcompeted P. caudatum due to a higher growth isocline.
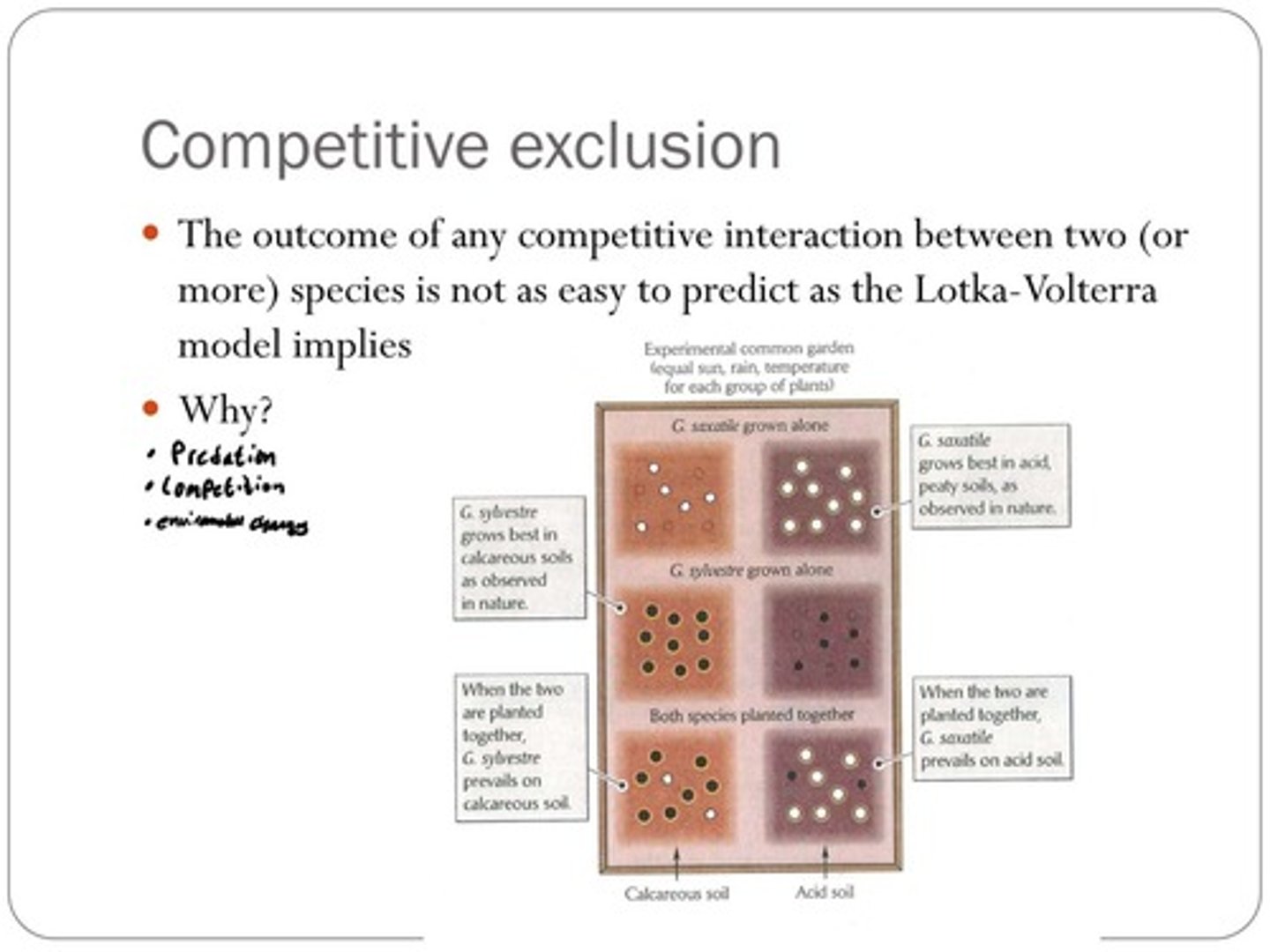
What was the outcome when G. sylvestre and G. saxatile were planted together in calcareous and acid soils?
G. sylvestre prevailed in calcareous soil, while G. saxatile thrived in acid soil.
What role do temporal changes in the environment play in competition?
They can influence the competitive dynamics between species over time.
What is the impact of climatic extremes on vegetation distribution?
Climatic extremes can significantly alter the distribution and dominance of vegetation types.
What is meant by density-independent controls on population size?
These are factors that affect population size regardless of the population density, such as climate variations.
What are some examples of non-resource factors that influence competitive ability?
Temperature, pH, relative humidity, and salinity.
What does normalized ecological performance indicate?
It shows how well a species performs relative to others under specific environmental conditions.
How can competition be influenced by climatic characteristics?
Climatic characteristics can determine the availability of resources and the suitability of habitats for different species.
What is the significance of decision trees in ecological studies?
They help in predicting outcomes based on various environmental factors and species interactions.
How does competition for multiple resources affect species interactions?
It complicates predictions about which species will dominate, as they may compete for different resources.
What was the result of Gause's experiment with P. caudatum and P. bursaria?
They coexisted due to resource partitioning despite competing for the same resources.
What does the term 'temporal variation' refer to in ecology?
It refers to changes in environmental conditions over time that can affect species competition.
How do climatic averages influence vegetation distribution predictions?
They provide baseline data for understanding how vegetation might respond to future climatic changes.
What is the relationship between competitive exclusion and environmental changes?
Environmental changes can alter the competitive dynamics, making it difficult to predict outcomes based solely on the Lokta-Volterra model.
What is interspecific competition?
Competition between two or more species for a limiting resource.
What does the Lotka-Volterra model describe?
The possible outcomes of competition between species.
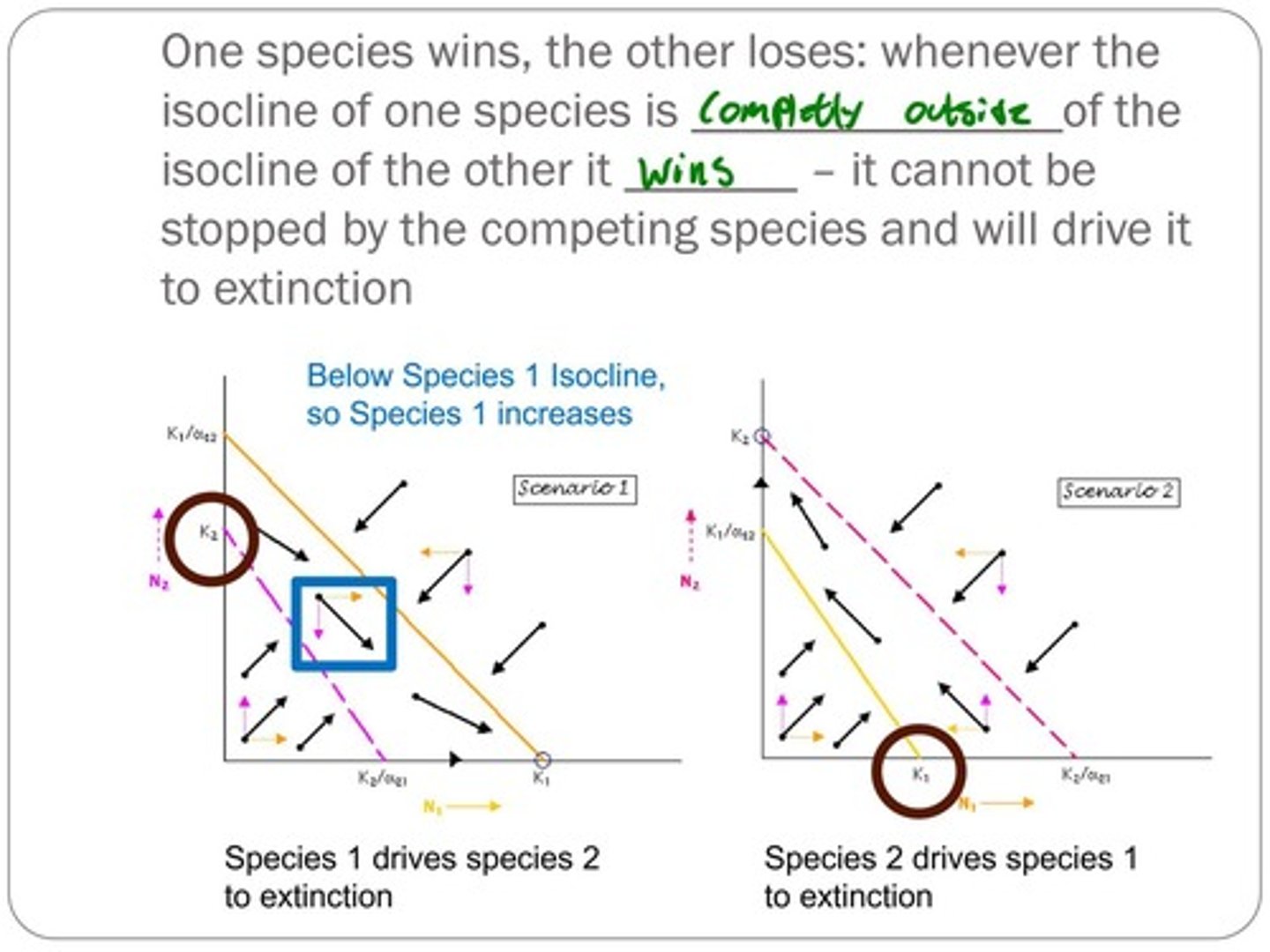
What are the potential outcomes of competition according to the Lotka-Volterra model?
1. Species 1 wins (species 2 goes extinct). 2. Species 2 wins (species 1 goes extinct). 3. Either species can win. 4. They can coexist.
What is the significance of zero growth isoclines in the context of competition?
They represent combinations of two species' populations at which the population growth rate is zero.
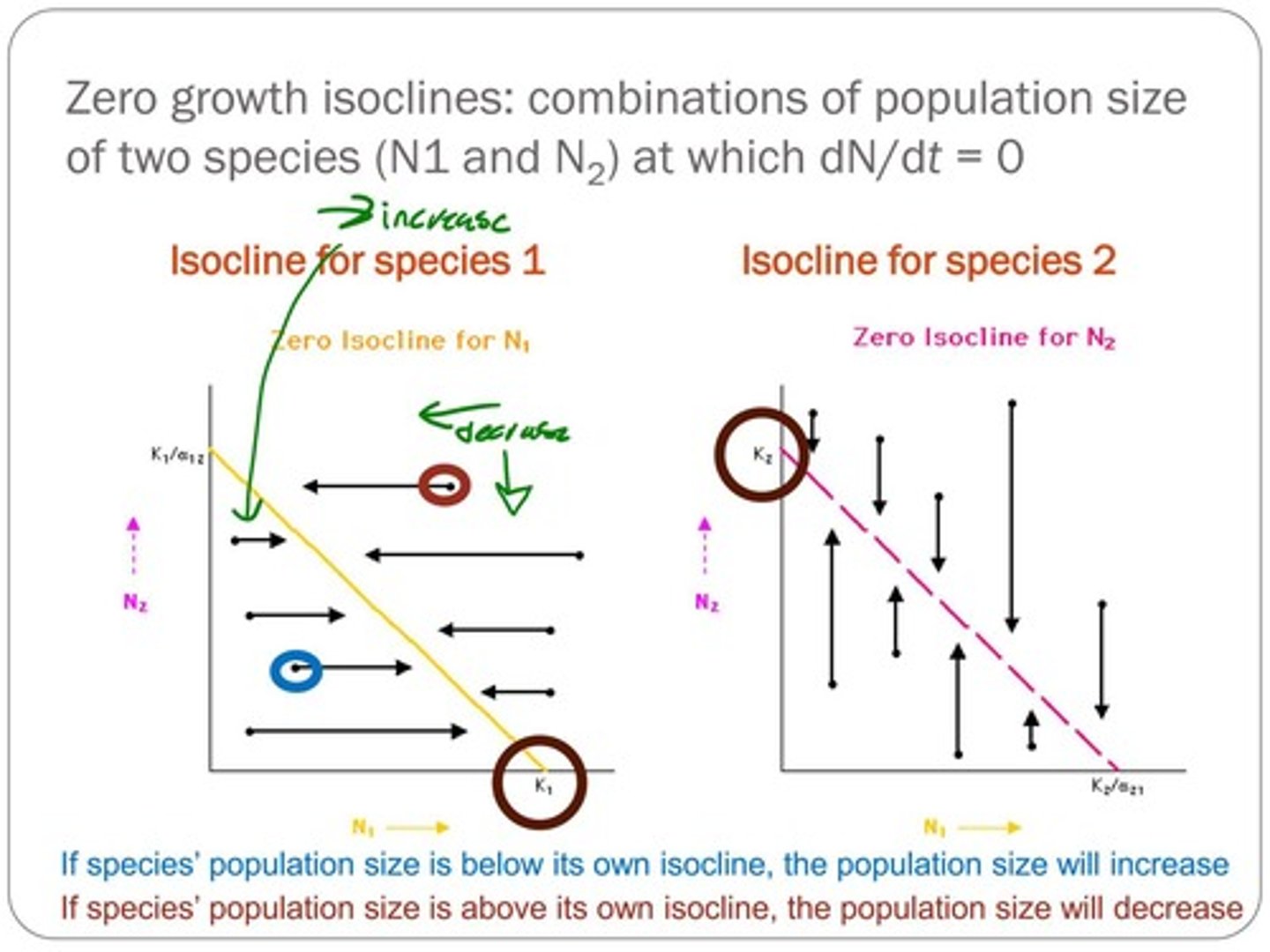
What happens to a species' population if it is below its own isocline?
The population size will increase.
What happens to a species' population if it is above its own isocline?
The population size will decrease.
What are the competitive exclusion principles?
One species wins and drives the other to extinction when its isocline is completely outside that of the other species.
What are the logistic equations for species growth in the Lotka-Volterra model?
1. ▲N₁/▲t = r₁N₁ (K₁ - N₁ - αN₂/K₁) 2. ▲N₂/▲t = r₂N₂ (K₂ - N₂ - βN₁/K₂) where α and β are competition coefficients.
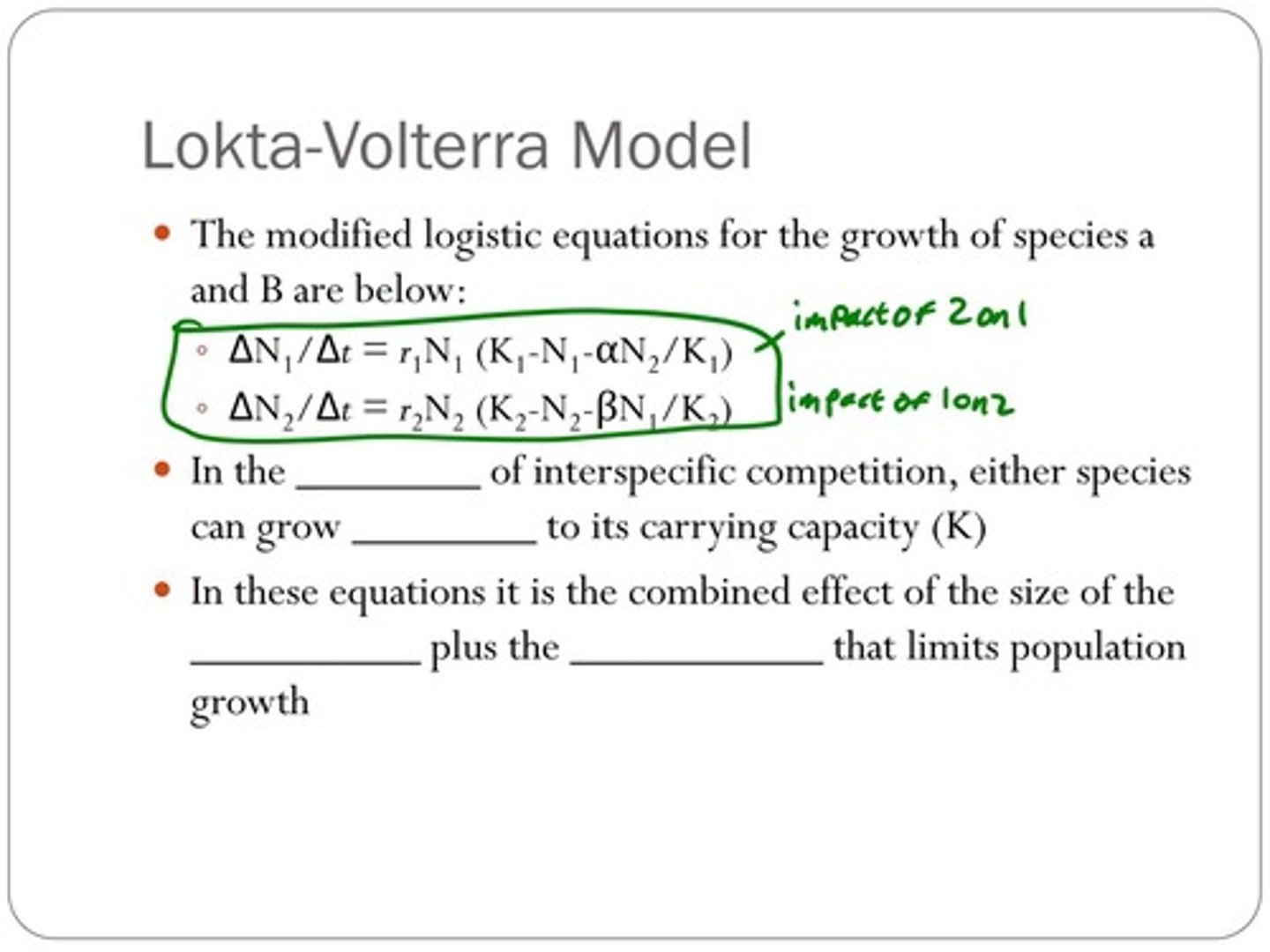
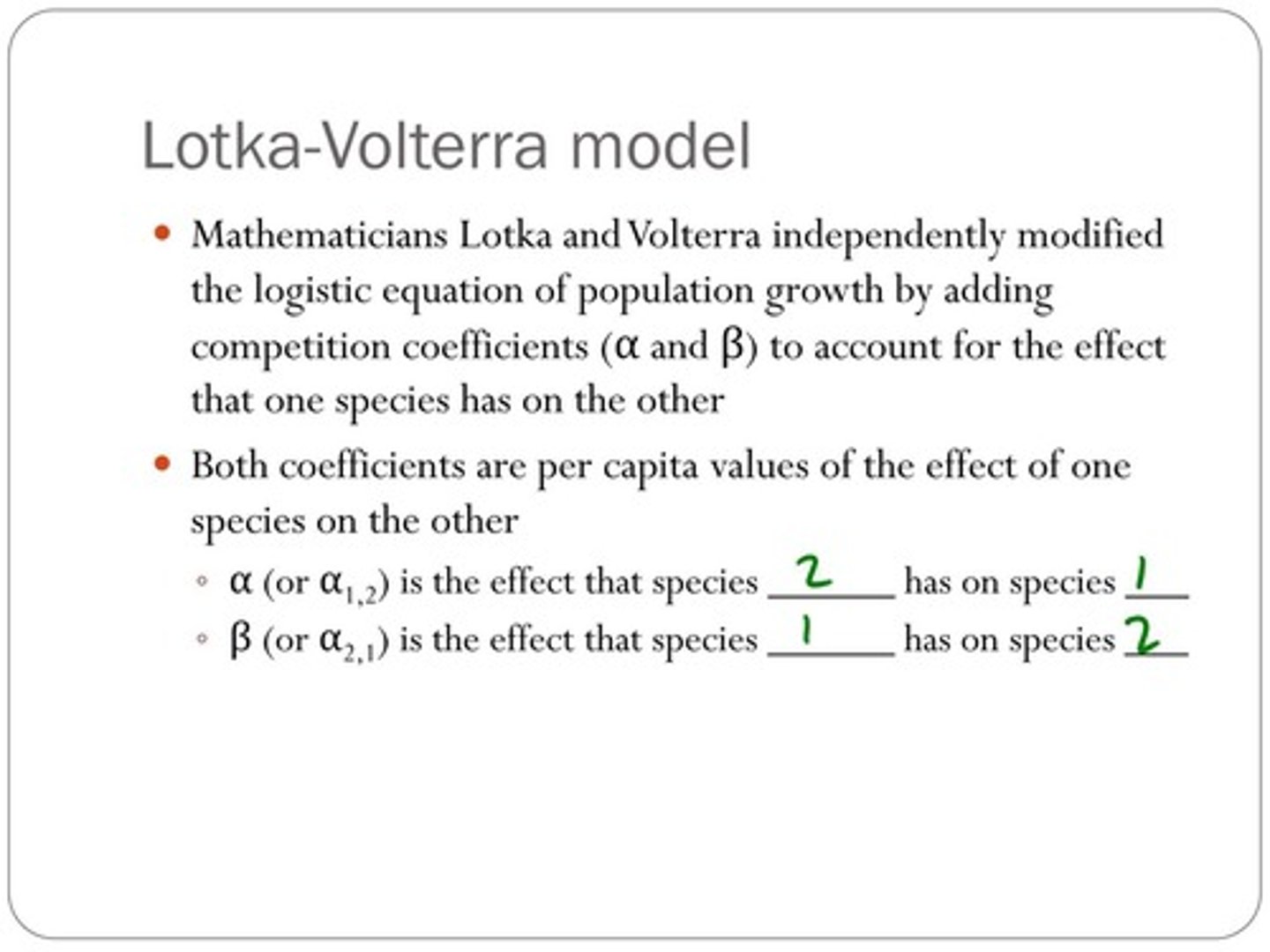
What do the competition coefficients (α and β) represent in the Lotka-Volterra model?
They are per capita values of the effect that one species has on another.
What is a resource in the context of interspecific competition?
A consumable item that, when consumed, reduces the amount available for others.
What are examples of resources that species compete for?
Space, water, and food.

What is exploitation competition?
Using a resource before others can access it.
What is interference competition?
Active defense of a resource against others.

What is the outcome of interspecific competition?
Both species are adversely affected, leading to a (-,-) outcome.
What factors can affect competition besides resource availability?
Non-resource factors such as space and environmental conditions.
What is the role of carrying capacity (K) in population growth?
It limits population growth as the population approaches it.
What does the term 'competitive exclusion' imply?
One species will outcompete another for resources, leading to the latter's extinction.
What does the term 'coexistence' mean in the context of species competition?
Both species can exist in the same environment without one driving the other to extinction.
How does the starting population size affect competition outcomes?
The outcome depends on the initial numbers of each species and how they change over time.
What is the relationship between population growth rate and carrying capacity?
The population growth rate declines as the population size approaches carrying capacity.
What is the significance of the isocline for species 1 and species 2?
They indicate the population sizes at which each species' growth rate is zero.
What is the impact of resource consumption on population growth?
When resource availability decreases, population growth also decreases.
What are the learning objectives related to interspecific competition?
Overview of interspecific competition, Lotka-Volterra model, competitive exclusion, non-resource factors, competition for multiple resources, and adaptation to competition.