Biochemistry lecture 7
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Michaelis - Menten equation
Used to describe
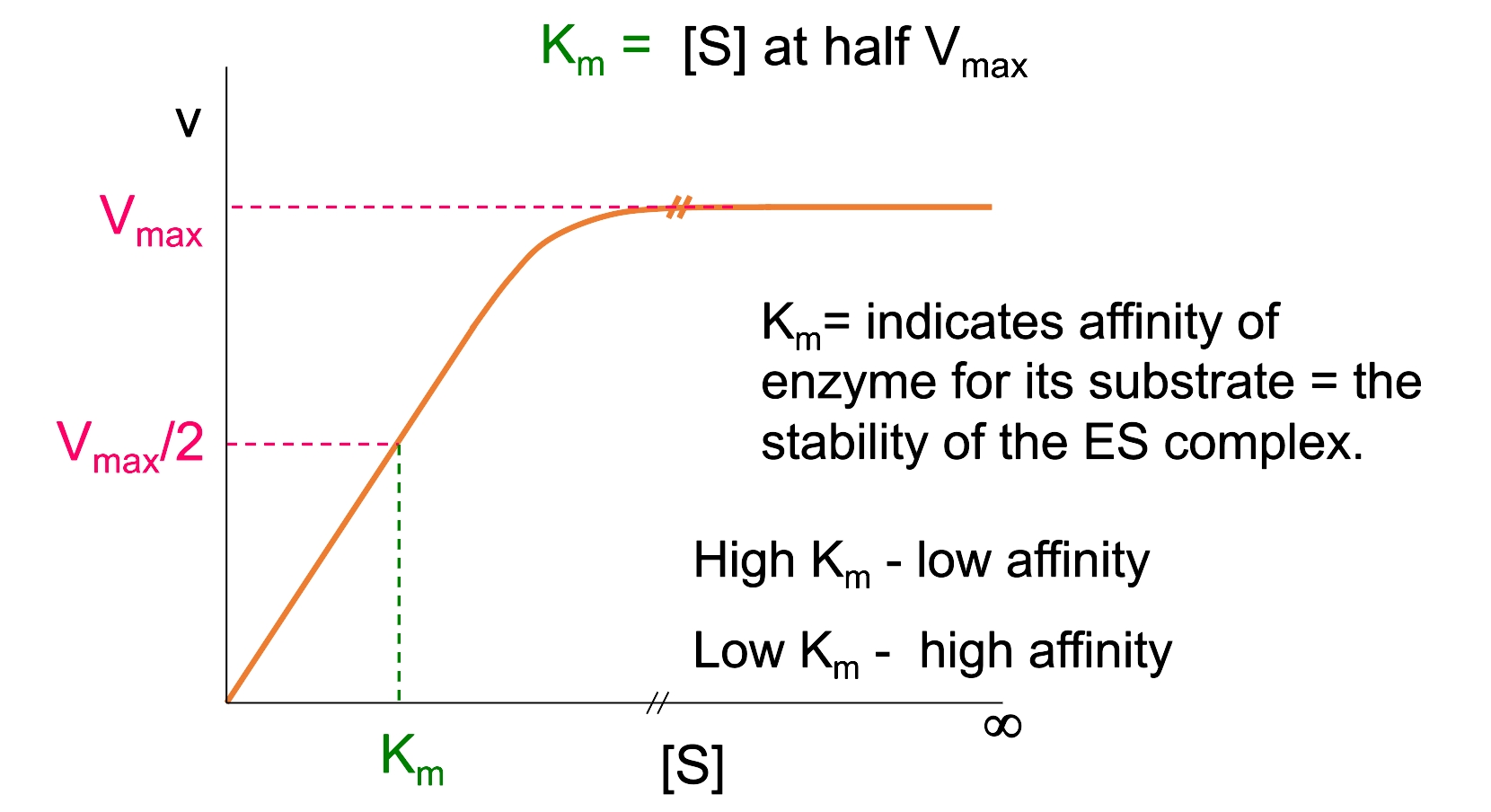
𝑣 is rate of velocity at a specified [S]
Vmax is maximum value of v attainable by the enzyme under the given conditions (impossible to reach in practise but can be estimated)
[S] substrate concentration
Km = Michaelis constant (see previous lecture)
![<p class="Paragraph WhiteSpaceCollapse SCXP87361487 BCX8" style="text-align: left;">Used to describe</p><ul><li><p class="Paragraph WhiteSpaceCollapse SCXP87361487 BCX8" style="text-align: left;">𝑣 is rate of velocity at a specified [S]<span style="line-height: 0px;"></span></p></li></ul><ul><li><p class="Paragraph WhiteSpaceCollapse SCXP87361487 BCX8" style="text-align: left;">V<span style="background-color: inherit;">max</span> is maximum value of v attainable by the enzyme under the given conditions (impossible to reach in practise but can be estimated)<span style="line-height: 0px;"></span></p></li><li><p class="Paragraph WhiteSpaceCollapse SCXP87361487 BCX8" style="text-align: left;">[S] substrate concentration<span style="line-height: 0px;"></span></p></li><li><p class="Paragraph WhiteSpaceCollapse SCXP87361487 BCX8" style="text-align: left;">K<span style="background-color: inherit;">m</span> = Michaelis constant (see previous lecture)<span style="line-height: 0px;"></span></p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/86759b99-d344-4371-a9d5-7745e49b60b4.jpg)
Michaelis kinetics
Curve indicates saturation of enzymes with substrates
Kcat
way of comparing enzymes
the turnover number, is a useful measure of enzyme efficiency
Maximum number of molecules of substrate converted per active site per time (usually s), how many they can turnover in certain amount of time
Kcat = Vmax/[Et]
E.g. chymotrypsin = 100 s-1
What type of constant is Kcat?
is the specificity constant, useful if you wish to compare the activity of an enzyme against different substrates. Units of s-1 M-1
Higher is better!
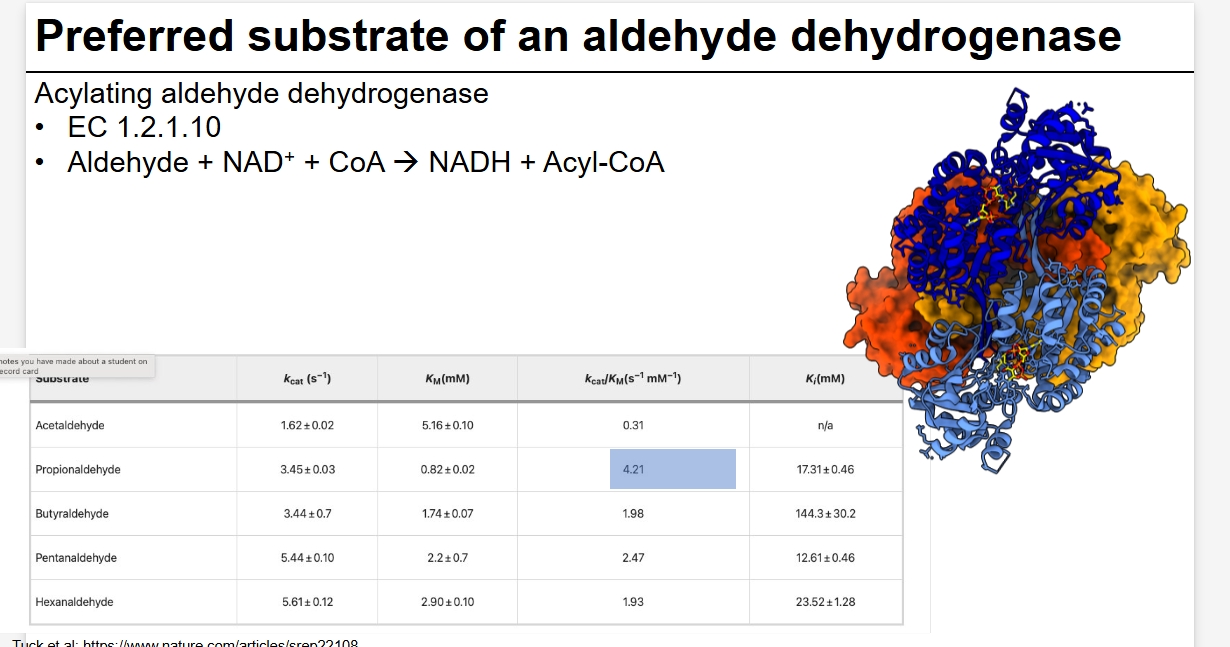
Preferred substrate of aldehyde dehydrogenase
BP1 - its classification
BP2 - reactions
Calc Kcat/Km can measure enzyme with highest enzyme activity - useful to compare enzyme with varying substrates or if activity changes in various conditions
How is enzyme activity controlled?
Enzyme inhibitors - Reduce the rate of enzyme catalysed reactions
Classified based on how they act:
Irreversible - usually bind to AS uncontrollably via C bond
Reversible:
Competitive
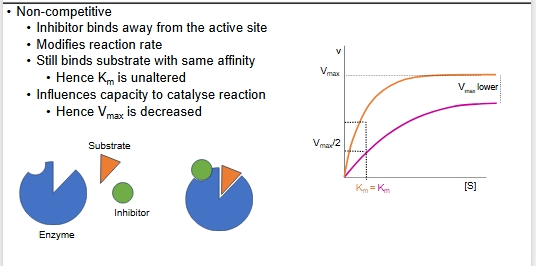
Non-competitive - binds to allosteric site
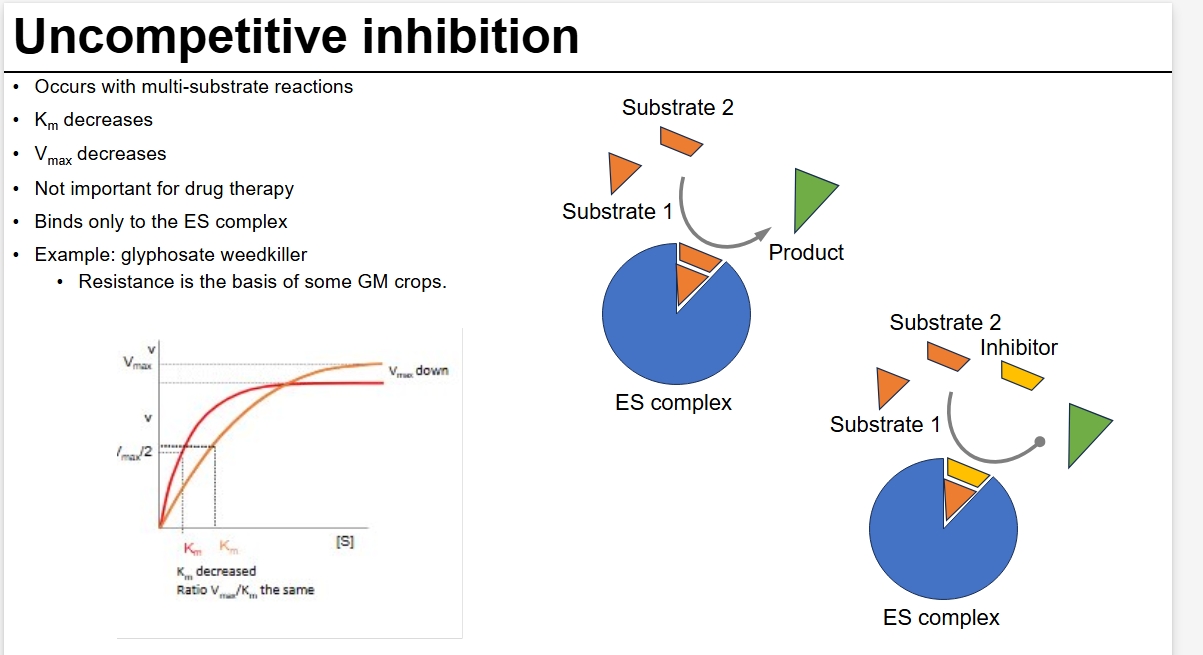
uncompetitive - bind after S binds to lock it in
Irreversible inhibitors
Bind irreversibly to enzyme
Usually bind via a covalent bond
Bind to an amino acid side chain at or near the active site
Commonly bind to either Ser (-CH2-OH) or Cys (-CH2-SH) side chains
Binding permanently inactivates the enzyme
Usually prevents substrate binding
Sarin (example)
Di-isopropylfluorophosphate:
Sarin nerve gas
Covalently binds to a serine residue in acetylcholine esterase
Prevents breakdown of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine
Leads to continual activation of nerves in muscles
Aspirin
Salicylic acid a component of willow bark
Acetylated form produced in late 19th Century by Bayer
Key medicine with uses as an anti-inflammatory drug
Binds to Prostaglandin H2 synthase at S530 and transfers acetyl group
Penicillin (I inhibitor)
Binds to Serine in PBPs
Irreversibly blocks active site
More examples
Aspirin, which inhibits cyclooxygenase 1 and 2 enzymes.
Penicillin, which inhibits DD-transpeptidase from building bacterial cell walls.
Sulbactam, which prohibits penicillin-resistant strains of bacteria from metabolizing penicillin.
Allopurinol, which inhibits uric acid production by xanthine oxidase in the treatment of gout.
AZT (zidovudine) and other chain-terminating nucleoside analogues used to inhibit HIV-1 reverse transcriptase in the treatment of HIV/AIDS.
Eflornithine, one of the drugs used to treat sleeping sickness, is a suicide inhibitor of ornithine decarboxylase.
Sarin is a suicide inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase.
5-fluorouracil acts as a suicide inhibitor of thymidylate synthase during the synthesis of thymine from uridine. This reaction is crucial for the proliferation of cells, particularly those that are rapidly proliferating (such as fast-growing cancer tumours). By inhibiting this step, cells die from a thymine less death because they have no thymine to create more DNA. This is often used in combination with Methotrexate, a potent inhibitor of dihydrofolate reductase enzyme.
Exemestane, a drug used in the treatment of breast cancer, is an inhibitor of the aromatase enzyme.
Tumeric
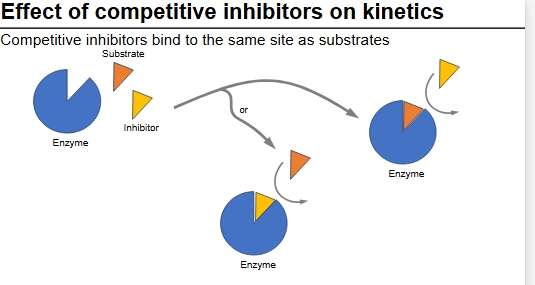
Competitive inhibitors
Compete with substrate for access to active site
Often have similar structure to substrate
When bound to enzyme prevents binding of substrate
Can be overcome by increasing [S] until it out-competes inhibitor
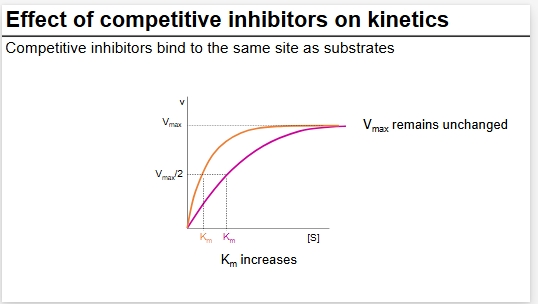
Diagram of CI
MM plot of CI on kinetics
Total final Vmax remains unchanged but higher S required for Vmax to be reached
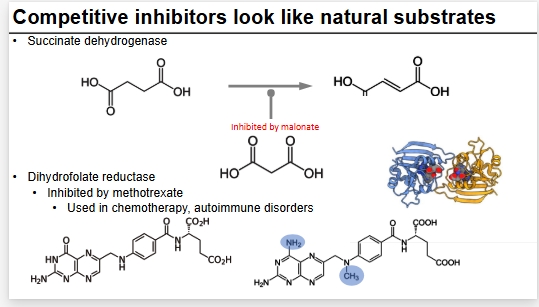
Examples of CI
Other types of CI
Most useful therapeutic agents
Most drugs mimic transition states:
Bind enzymes 10 to the 3 – 10 to the 6 times tighter than natural substrates
e.g. Tamiflu, Acarbose – Type II diabetes:
Non-hydrolysable mimic of carbohydrates
Binds alpha-glucosidases – e.g. alpha-amylase
Prevents digestion of natural carbohydrates
Cheap, but not very effective on its own
Statins – target hepatocytes and inhibit HMG-CoA reductase:
enzyme converts HMG-CoA into mevalonic acid, a cholesterol precursor.
Statins bind 1000 x tighter than HMG-CoA
NC inhibition
UC inhibition
Note
Learn the diagrams/graphs of three types of inhibition!
Learn Km and Vmax changes
What reaction conditions influence enzyme activity?
Enzymes are sensitive to changes in their physical and chemical environments
Temperature
pH
Salts
Other chemicals
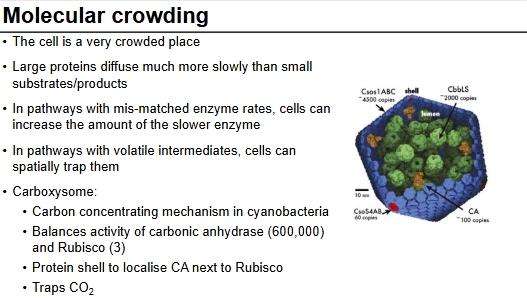
Molecular crowding
pH on enzyme activity
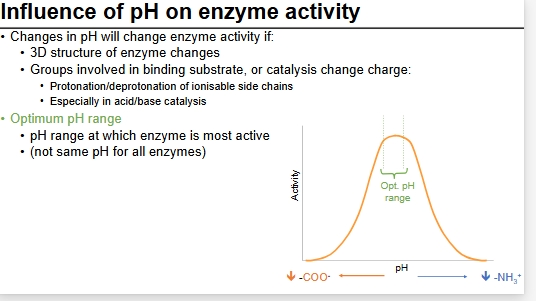
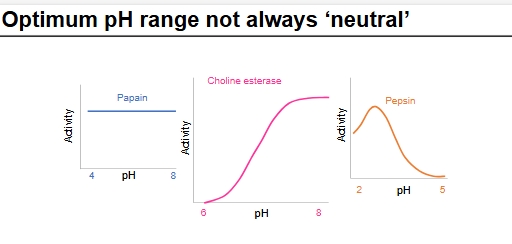
Is optimum pH always neutral?
NO
Papain - enzyme activity flat between 4 + 8, denatures elsewhere
Choline esterase and pepsin - in diff acidic/basic environments so adapted to be at optimum in their environment
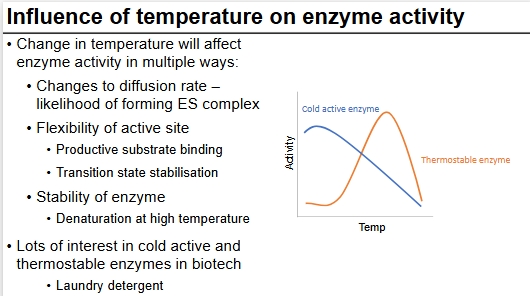
Temps effect on enzyme activity
Can also have optimums at different temperatures
Molecular crowding
Due to cell being crowded, enzymes and substrates may not be able to meet and have reactions, so this can be altered to increase activity