QC Lab - Experiment 2: Preparation and Standardization of 1N Sodium Hydroxide Solution
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
standardization
Process of determining the exact concentration of a solution
Titration is one type of analytical procedure often used in this
titrant
solution with known volume and concentration
titrand/analyte
solution with known volume but unknown concentration
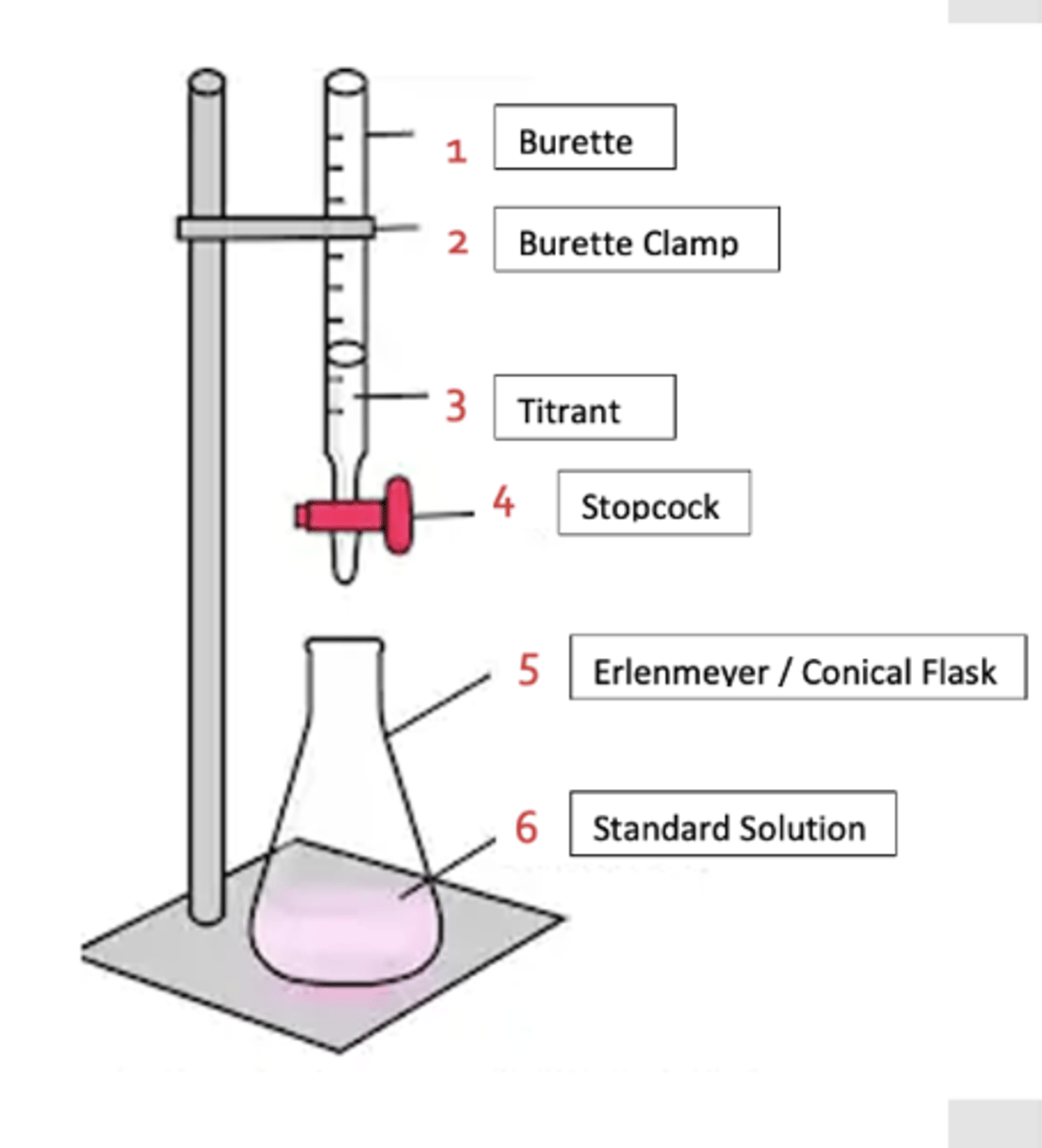
burette
-iron stand with burette clamp firmly attached (to stand)
- titrant placed inside
erlenmeyer/conical flask
- beneath burette
- standard solution: inside with primary/secondary standard + indicator
standard solution
primary/secondary standard + indicator
primary standard
A standard that is sufficiently accurate that it cannot be calibrated or subordinate to other standards.
Used to standardize secondary standards
Used in titration to determine an unknown concentration and in other analytical chemistry techniques
- sodium carbonate, sodium tetraborate, potassium hydrogen phthalate/potassium diphthalate
6 properties of primary standard
1. high purity
2. stable
3. low hygroscopisity
4. high equivalent weight
5. non toxic
6. relatively cheap
low hygroscopisity
primary standard low tendency to absorb moisture from the air
secondary standard
Chemical that has been standardized against a primary standard
sodium hydroxide
- lye (oldest name), caustic soda, soda lye
- crystalline odorless solid
- solid form = white
- liquid form = colorless
- deliquescent: absorbs moisture from air and dissolves into it
+ water = exothermic
- corrosive: solid/50% solution
When dissolved in water or neutralized with acid, it liberates substantial heat which may be sufficient to ignite combustible materials.
It is used in the manufacture of soaps, rayon, paper, explosives, dye stuff and petroleum products, etc.
lye, caustic soda, soda lye
sodium hydroxide other names
white
color of sodium hydroxide in solid form
colorless
color of sodium hydroxide in liquid form
deliquescence
absorbs moisture from air and dissolves into it (difference from hygroscopic)
corrosive
cause damage to living tissue = solid/50% solution
hard soap
sodium hydroxide soap
soft soap
potassium hydroxide soap
permanent
no longer colorless even with continuous swirling
pink coloration
faint pink (dark - too much = overtitrated pink)
titer
used to compute normality
total volume of liquid added from burette
normality
weight (PS)/molar mass (PS)/n (PS) x 1000/titer (mL)
IBR - FBR
acid
n = # of hydrogen ions
base
n = # of hydroxyl (OH) ions
salt
n = # of ionic charge