Data and Knowledge Management (all 3 slideshows)
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Data degradation
the gradual deterioration of data quality over time
What is a Database Management System (DBMS)?
A set of programs that provides users with tools to create and manage databases
What is a Relational Database?
A database that organizes data into tables, using primary and foreign keys to represent relationships between entities.
What is an Entity-Relationship Diagram (ERD)?
A conceptual diagram that visually represents the structure of a database, showing how entities (tables) relate to each other.
What is the Minimal Data Rule in database design?
"All that is needed is there, and all that is there is needed."
Ensures only necessary data is included.
What is an Entity in an ERD? and what does it look like?
A thing, event, or person in an organization's environment about which data is collected

What is an Attribute in an ERD? and what does it look like?
A characteristic or property of an entity (e.g., Student ID, Name, GPA).
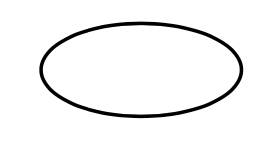
What is a Relationship in an ERD? and what does it look like?
An association between entities (e.g., A Student enrolls in a Course).
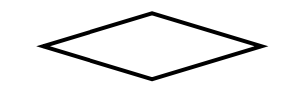
What is a Composite Entity (Associative Entity)? and what does it look like?
An entity that represents both an entity and a relationship, with its own properties (e.g., OrderLine connecting Orders and Products).
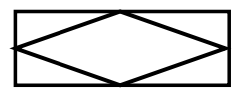
what are keys?
(identifiers)
columns that can be used to identify a row
What is a Primary Key?
A unique identifier for each record in a table (e.g., Student ID in a Student table).
Represented by underlined attributes in an ERD.
What is a Foreign Key?
A non-key attribute in one table that appears as a Primary Key in another table (e.g., Department ID in Employee table).
aka cross reference key
What is a Composite Key (Concatenated Key)?
A key made up of two or more attributes to identify a record (e.g., Student ID + Course ID to identify a Grade record).
key characteristics
can be simple (a single field) or composite
will not change in value
not be null
What are Special Types of Attributes in an ERD?
Multivalued Attributes → Can hold multiple values for a single entity occurrence
Derived Attributes → Not stored in the database but computed from existing attributes (e.g., Age derived from Birth Date).
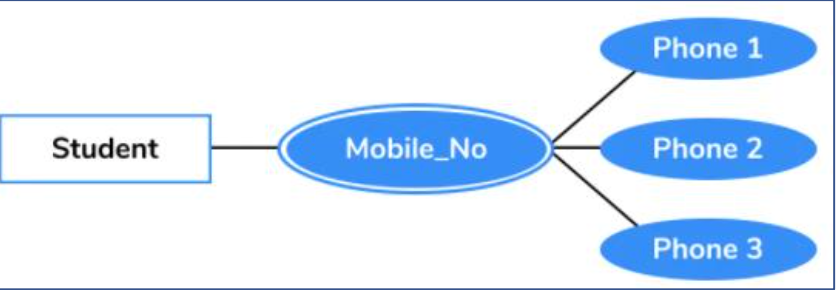
is this a multivalued or derived attribute
multivalued
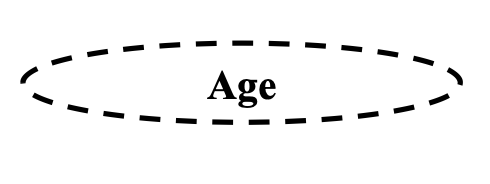
is this a multivalued or derived attribute
derived
How is an entity represented in a database table?
Each entity in an ERD is converted into a table in the database.
What is the difference between "relation" and "relationship" in databases?
Relation refers to a table in a relational database.
Relationship is the relationship between entities in an
ERD (cardinality relationships)
How are attributes represented in a relational database?
Each attribute in the ERD is converted into a column in the corresponding database table.
Why is a primary key important?
Ensures uniqueness of records.
establishes relationships between tables.
Helps in indexing and fast data retrieval.
what is a one-to-one (1:1) cardinality relationship?
Each entity in the relationship will have exactly one related entity
what is a one-to-many (1:M) cardinality relationship?
An entity on one side of the relationship can have many related entities, but an entity on the other side will have a maximum of one related entity
what is a many-to-many (1:M) cardinality relationship?
Entities on both sides of the relationship can have many related entities on the other side
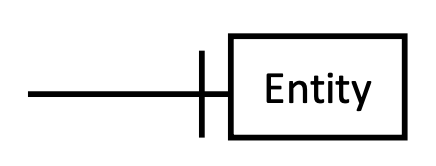
What does a single vertical line represent in an ERD? (also draw it)
represents one in a relationship.
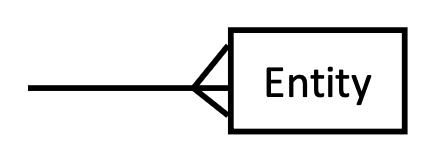
What does a crow’s foot represent in an ERD? (draw it too)
represents many in a relationship
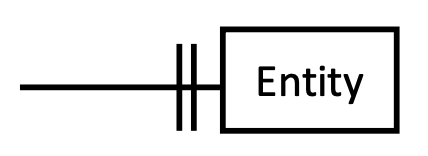
How are mandatory relationships represented in an ERD? (draw it too)
shown using another vertical line (||).
How are optional relationships represented in an ERD? (draw it)
using a circle (O)
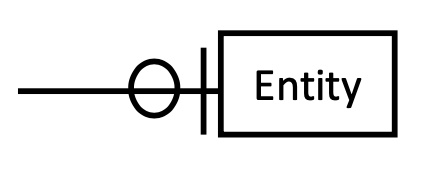
what does a mandatory single look like?

what does an optional single look like?
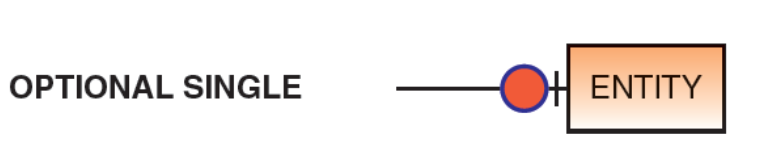
what does a mandatory many look like?
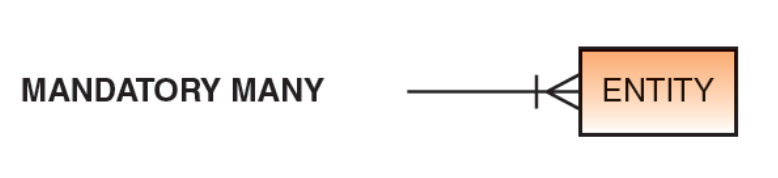
what does an optional many look like?
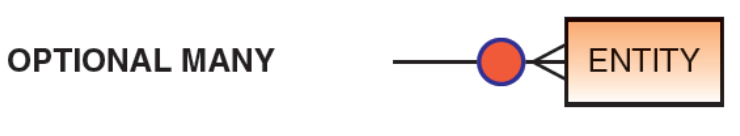
What is an associative entity?
A special type of entity used to break many-to-many (M:M) relationships into two one-to-many (1:M) relationships.
What is a key rule for relationships connected to an associative entity?
All relationships going into an associative entity should be many (M).
What primary keys does an associative entity include?
the primary keys of the tables it breaks.
Can an associative entity have other attributes besides primary keys?
Yes!
What is an anomaly in database normalization?
anything that deviates from the standard and can cause issues
What are the three types of anomalies in databases?
Insertion Anomaly
Deletion Anomaly
Modification Anomaly
What is an insertion anomaly?
occurs when we cannot add a new attribute to a table unless another attribute is also added.
What is a deletion anomaly?
occurs when deleting one row also removes other necessary data.
Why do anomalies exist in database tables?
Because two different themes are stored in the same relation, leading to redundancy and unnecessary dependencies.
What is normalization in databases?
A process of organizing a relational database to eliminate anomalies, etc.
What is the First Normal Form (1NF)?
A table is in 1NF if:
It contains only atomic values (no multivalued attributes).
There are no repeating groups in the table.
What is an atomic value in 1NF?
a value that cannot be further divided or contain different values
all relations are in 1st NF, T/F
True
What is Second Normal Form (2NF)?
A table is in 2NF if:
It is already in First Normal Form (1NF).
Every non-key attribute is fully functionally dependent on the entire primary key (i.e., no partial dependencies).
What is a partial dependency?
occurs when a non-key attribute depends only on part of a composite primary key, rather than the whole key.
What is Third Normal Form (3NF)?
A table is in 3NF if:
It is already in Second Normal Form (2NF).
It has no transitive dependencies
What is a transitive dependency?
occurs when a non-key attribute depends on another non-key attribute instead of directly depending on the primary key.