PSYC110-Module 1
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
What is the scientific method?
A systematic study (fixed organised)
Via observation and experimentations (empirical, can be used as evidence)
Is psychology a science?
Yes, it is a science because it follows the scientific method
We do these things to human behaviour and process
Describe
Explain
Predict
What are 5 key principles of psychological science?
1. Empiricism
2. Scepticism
3. Tentativeness
4. Openness
5. Anti-authoritarianism
What is empiricism
What is scepticism?
Evidence needs to be checked and questioned
What is tentativeness?
Evidence can change
What is openess?
Scientific research is available to the community
What is anti-authoritarianism?
Theory not accepted on faith alone
Make sure theory is based on scientific evidence
What is the cycle of science?
Theory or observation
Prediction/hypothesis
Research design
Data description and analysis
Lead to report writing
What is theory and observation?
A step in the cycle of science
We have a theory or observe something that we want to explore further and understand further
Eg. music will benefit development
What is prediction/hypothesis?
A step in the cycle of science
Make a predication about the relationship between variables in theory/observation
E.g.. The more hours listen to music will increase IQ as shown on higher scores on IQ test
What is falsifiability?
The idea that a theory or hypothesis should have the potential to be proven wrong
Evidence can prove a hypothesis wrong
What is research design?
A step in the cycle of science
Deciding how and when we will manipulate the variables
We use different research designs
Descriptive
Quantitative
Survey
What is data- description and analysis
A step in the scientific cycle
Collect data, organise and describe it
Two types of stats
Descriptive
Organise
Summaries
Inferential
Make inferential statistics
What is report writing?
A step in the scientific cycle
Sharing findings with the rest of the world
What are the types of research design?
There are three
Quantitative research
Qualitative research
Mixed methods research
What is quantitative research?
Numbers are assigned to variables
Findings, observations and what is found are numerical
Deductive
What is qualitative research?
Data are words
Evidence, results that are collected are descriptive, characteristics
Uses inductive reasoning (specific to general)
Provides deeper understanding, and very descriptive
Advantage
Provide in depth description and understanding
Disadvantaged
Time- takes a lot of time
Subjectivity
Hard to generalise to greater population
Reflexivity- monitoring personal bias
What are the 6 characteristics of qualitative research?
There are multiple sources (different places- schools, uni, library)
Mainly uses inductive but can also use deductive
Natural setting
Emergent design- design can change once data collection begins
Participants meaning
Research is a key instrument
What is the epistemological background of qualitative research?
Epistemology refers to the theory of knowledge, how we know things
In qualitative research there are two types
Phenomenology: knowledge based on person’s perceptions and experiences
Social constructionism: knowledge that reality is based on social factors
What is mixed methods research?
Combines quantitative and qualitative methods in the same study
What are the different types of quantitative research?
Descriptive
Correlational research
Experimental research
What is descriptive research?
A type of quantitative research
Describe something that is happening
What is correlational research?
Looking at the variables as they occur naturally
Not actively manipulating variables
There are different types of relationships variables can have
Positive: changes in the IV are met with the same directional change in the DV (bottom left to top right)
Negative: Changes in the IV are met with the opposite direction change in the DV (top left, bottom right)
No relationship: No directional change
Correlation studies show the relatedness and relationship between variables
What are the four alternative relationships between variables in correlation research?
A causes B
B causes A
There could be a third variable (C) that causes the relationship between A-B, makes it look like A B are related, which they are, but they are RELATED BECAUSE OF THE THIRD variable- known as the third variable problem
Relationship is known by chance
To know which out of the four relationships the variables have, you need experimental research
What is experimental research?
Establishes cause and effect relationship- causality
There needs to be selection or manipulation of variables
There also needs to be control of other variables
Advantages
Establishes a cause and effect relationship
A lot of internal validity
Disadvantages
Not the best external validity
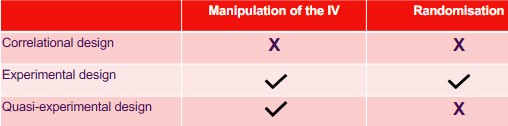
Not always possible to manipulate variables - hard to control or manipulate the amount people smoke - in that case we use quasi-experimental research
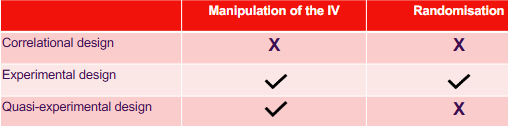
How do we control variables?
Keep constant
Make sure characteristics are the same
However very time consuming
Randomise
Ensures extraneous variables that may have an impact have an equal chance of being in both group (group exposed to IV and group not)
What are extraneous variables
Variables that have the POTENTIAL to impact what is being measured
Hard to distinguish if the IV or extraneous variable causes the changes in the DV
What is the process of quantitative research?
1. Define the question
2. Design a method
What is variable?
Characteristics or condition that changes or has different values
It varies
There are relationships between variables
What are the types of variables?
Independent variable
Dependent variable
What is the independent variable?
Have the potential cause in the relationship
Independent on other variables
Can be selected or manipulated
What changes or is the focus
What is the dependent variable
What is being measured
What changes potentially due to the independent variable
What are the different types of experimental designs?
Repeated measure (within subject)
Independent groups (between)
Match subject designs
What is repeated measure design?
A type of experimental research design
The SAME group of PARTICIPANTS is administered different “levels“ or conditions of IV at different types
Same participants in experimental group and control group
Advantage
Eliminates or minimises participant differences between the two groups
Disadvantage
Order effects - overcome through counterbalance (person 1 experience A then B, person 2 experience B and then A )
What are independent group design?
A type of experimental research design
Different groups of participants are administered differ levels or conditions of the IV
Different participants in the experimental and control groups
Advantage
No order effect
Disadvantage
More resources needed - more participants
More random variability between the two groups
What are matched research design?
A type of experimental research design
Participants are matched on important variables or characteristics
Participants in both control and experimental groups have similar characteristics and chosen based on those shared characteristics
Advantage
No order effect
Reduced differences between participants
Disadvantage
Needs a lot of resources