ECON UNIT 1 VOCAB
0.0(0)Studied by 1 person
Card Sorting
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:10 PM on 9/15/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
1
New cards
scarcity
we have unlimited wants but limited resources
2
New cards
choices
economics is the study of choices
3
New cards
economics
study of how individuals and societies deal with scarcity
4
New cards
trade-offs
alternatives that we give up whenever we choose one course of action over others
5
New cards
opportunity cost
the most desirable alternative given up as a result of a decision
6
New cards
microeconomics
study of small economic units such as individuals, firms, and industries
7
New cards
macroeconomics
study of the large economy as a whole or economic aggregates
8
New cards
theoretical economics
the use of the scientific method to make generalizations and abstractions to develop theories
9
New cards
policy economics
theories that are applied to fix problems or meet economic goals
10
New cards
positive statements
based on facts. Avoids value judgements (what is)
11
New cards
normative statements
includes value judgements (what ought to be)
12
New cards
utility
satisfaction
13
New cards
marginal
additional
14
New cards
allocate
distribute
15
New cards
shortages
occur when producers will not or cannot offer goods or services at current prices. Shortages are temporary
16
New cards
price
amount buyer (or consumer pays)
17
New cards
cost
amount seller pays to produce a good
18
New cards
investment
the money spent by BUSINESSES to improve their production
19
New cards
goods
physical objects that satisfy needs and wants
20
New cards
consumer goods
created for direct consumption (ex: pizza)
21
New cards
capital goods
created for indirect consumption (ex: over, blenders, knives) - Goods used to make consumer goods
22
New cards
services
actions or activities that one person performs for another (teaching, cleaning, cooking)
23
New cards
accountants
look at only explicit costs
24
New cards
economists
look at explicit and implicit costs
25
New cards
explicit costs
the traditional "out-of pocket costs" of decision making
26
New cards
implicit costs
the opportunity costs such as forgone time and forgone income
27
New cards
Three economic questions
1. What goods and services should be produced?
2. How should these goods and services by produced?
3. Who consumes these goods and services?
2. How should these goods and services by produced?
3. Who consumes these goods and services?
28
New cards
economic system
the method used by a society to produce and distribute goods and services
29
New cards
4 factors of production
1. Land
2. Labor
3. Capital
4. Entrepreneurship
2. Labor
3. Capital
4. Entrepreneurship
30
New cards
Land
all natural resources that are used to produce goods and services. Anything that comes from "mother nature" (Water, sun, oil)
31
New cards
Labor
any effort a person devotes to a task for which that person is paid (lawyers, doctors, teachers)
32
New cards
Two types of capitals
1. Physical: any human-made resource that is used to create other goods and services (tools, tractors)
2. Human capital: any skills or knowledge gained by a worker through education and experience (college, degrees, vocational training
2. Human capital: any skills or knowledge gained by a worker through education and experience (college, degrees, vocational training
33
New cards
entrepreneurship
ambitious leaders that combine the other factors of production to create goods and services (bill gates, henry ford)
34
New cards
Entrepreneurs
1. Take the initiative
2. Innovate
3. Act as the Risk brearers
So they can obtain PROFIT
2. Innovate
3. Act as the Risk brearers
So they can obtain PROFIT
35
New cards
profit
revenue - costs
36
New cards
you will continue to consume until
Marginal Benefit = Marginal Cost
37
New cards
Utility maximizing rule
the consumer's money should be spent so that the marginal utility per dollar of each good equals each other. it always assumes that you always consume where MU/ for each product is equal
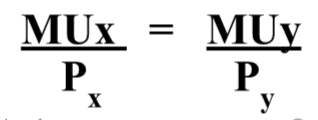
38
New cards
the product market
the "place" where goods and services produced by businesses are sold to households
39
New cards
the resource (factor) markey
the "place" where resources (land, labor, capital, and ent.) are sold to businesses
40
New cards
circular flow model
see image
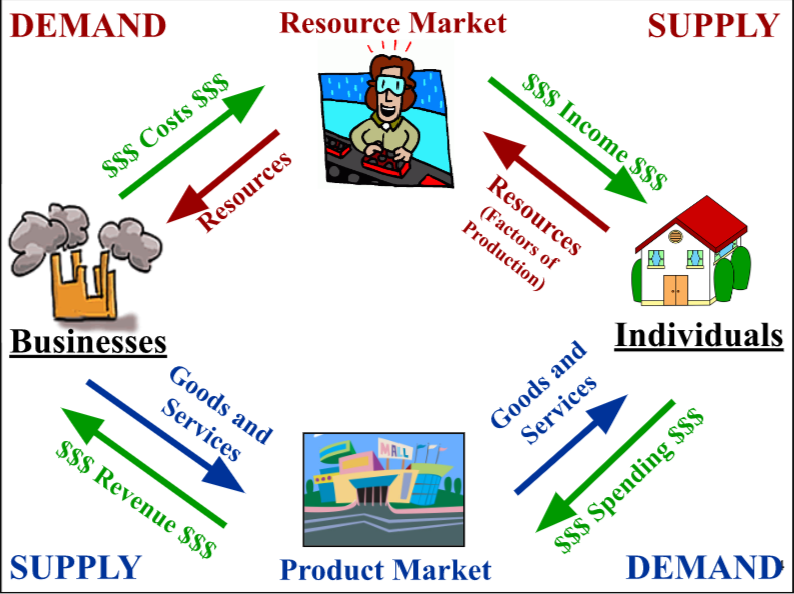
41
New cards
scarcity means there is not enough for everyone
government must step in to help allocate resources
42
New cards
economic systems
1. Centrally-Planned (Command) Economy
2. Free Market Economy
3. Mixed Economy
2. Free Market Economy
3. Mixed Economy
43
New cards
Centrally-Planned of Command Economies (aka communism)
1. owns all the resources
2. answers the three economic questions
NO PROFIT MEANS NO INCENTIVE TO WORK HARDER
2. answers the three economic questions
NO PROFIT MEANS NO INCENTIVE TO WORK HARDER
44
New cards
Free Market System (aka Capitalism)
1. Little government involvement in the economy
2. Individuals OWN resources and answer the three economic questions
3. The opportunity to make PROFIT gives people INCENTIVE to produce quality items efficiently
4. Wide variety of goods available to consumers
5. Competition and Self-Interest work together to regulate the economy (keep prices down and quality up)
2. Individuals OWN resources and answer the three economic questions
3. The opportunity to make PROFIT gives people INCENTIVE to produce quality items efficiently
4. Wide variety of goods available to consumers
5. Competition and Self-Interest work together to regulate the economy (keep prices down and quality up)
45
New cards
The invisible hand (adam smith)
the concept that society's goals will be met as individuals seek their own self-interest. competition and self-interest act as an INVISIBLE HAND that regulars the free market
46
New cards
ROLL
READ the entire question first
ORGANIZE your answer
LIST your answers like the question
LABEL everything
ORGANIZE your answer
LIST your answers like the question
LABEL everything
47
New cards
the production possibilities curve (PPC)
a model that shows alternative ways that an economy can use its scarce resources. it graphically demonstrates scarcity, trade-offs, opportunity costs, and efficiency
48
New cards
4 key assumptions
Only two goods can be produced
Full employment of resources
Fixed Resources
Fixed Technology
Full employment of resources
Fixed Resources
Fixed Technology
49
New cards
constant opportunity cost
resources are easily adaptable for producing either good. result is a straight line PPC (not common)
50
New cards
law of increasing opportunity cost
as you produce more of any good, the opportunity cost (forgone production of another good) will increase. Why? resources are NOT easily adaptable to producing both goods
51
New cards
how much each marginal unit costs
opportunity cost/units gained
52
New cards
productive efficiency
- Products are being produced in the least costly way
- There is any point ON the PPC
- There is any point ON the PPC
53
New cards
allocative efficiency
- The products being produced are the ones most desired by society
- This optimal point on the PPC depends on the desires of society
- This optimal point on the PPC depends on the desires of society
54
New cards
3 shifters of the PPC
1. Change in resource quantity or quality
2. Change in Technology
3. Change in Trade
2. Change in Technology
3. Change in Trade
55
New cards
capital goods and future growth
Countries that produce more capital goods will have more growth in the future.
56
New cards
per unit opportunity cost review
opportunity cost / units gained
57
New cards
absolute advantage
the producer that can produce the most output OR requires the least amount of inputs (resources)
58
New cards
comparative advantage
the producer with the lowest opportunity cost
59
New cards
output questions
other goes over
60
New cards
input questions
other goes under