BIOL 233 Week 2 Lecture Notes: Tissues and Integumentary System (Exam 1)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/72
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:51 PM on 9/23/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
1
New cards
Tissues
Groups of cells with a common structure and function.
2
New cards
Histology
Study of tissues
3
New cards
epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous
the four types of tissues are _______, _______, _______, and _______.
4
New cards
Epithelial
This type of tissue covers
5
New cards
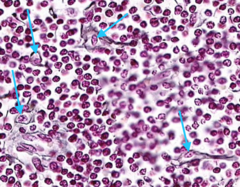
Connective
This type of tissues supports. Most abundant in the body.
6
New cards
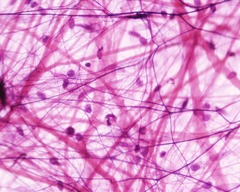
Muscle
The type of tissue allows movement
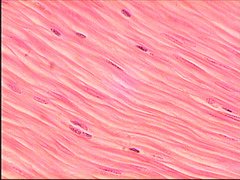
7
New cards
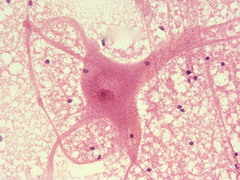
Nerve
This type of tissue controls. In the brain, spinal cord, and nerves.
8
New cards
Protection, absorption, filtration, secretion/excretion, sensory perception
Functions of epithelial tissue
9
New cards
Polarity
One end is in a different shape than the other end
10
New cards
Apical
The side exposed to the exterior
11
New cards
Basal
The side attached to a surface. Contains adhesive surface
12
New cards
Specialized contacts, connective tissue support, avascular but innervated, regeneration
The four characteristics of epithelial tissue
13
New cards
Squamos
Flattened and scale-like cells
14
New cards
Cuboidal
Boxlike, round nucleus cells
15
New cards
Columnar
Tall, column shaped cells, elongated nucleus
16
New cards
Simple Epithelial
Single layer of cells that absorb, secrete, and filtrate.
17
New cards
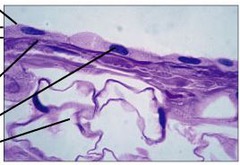
Simple squamous
Single layer of flat cells, on areas with rapid diffusion. Low protection. In kidneys, lungs, and serosae
18
New cards
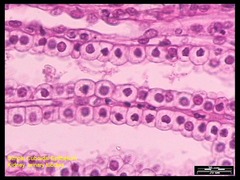
Simple cuboidal
Single layer of cube shaped cells, secrete and absorb, gland ducts. In kidney tubules
19
New cards
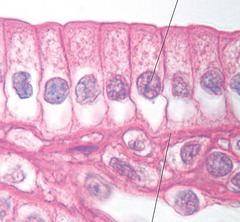
Simple columnar
Single layer of tall cells, absorb and secrete mucus, enzymes, and more, conciliated. Found in gallbladder and digestive tract.
20
New cards
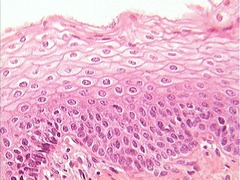
Stratified Epithelial
Multiple layers of cells, more durable, for protection
21
New cards
Stratified Squamous
Multiple layers of flat cells, handle wear and tear, keratinized in skin, nonkeratinizd in mouth, esophagus, and vagina.
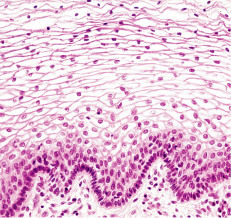
22
New cards
Stratified Cuboidal
Usually two layers thick, in sweat and mammry glands.
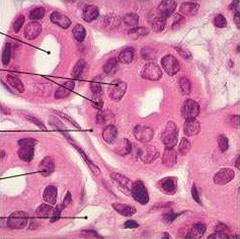
23
New cards
Stratified columnar
For secretion and protection, very rare, in eye conjunction
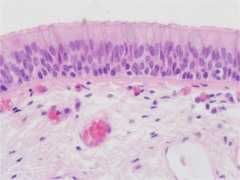
24
New cards
Transitional
Multiple layers thick. Can flatten out from cuboidal/columnar to squamous. Stretches, in interior or urinary organs.
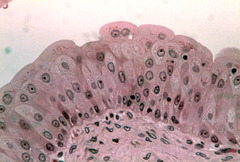
25
New cards
Psuedostratified columnar
Tall cells with varying lengths, mixture of stratified and simple, secretes substances, conciliated or ciliated.
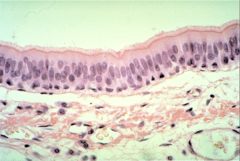
26
New cards
Gland
One or more cells that secrete fluids with enzymes, molecules, or hormones
27
New cards
Endocrine
Ductless glands, secrete hormones that travel through blood or lymphatic system to target organs.
28
New cards
Exocrine
Glands with ducts, secrets onto body surfaces or cavities.
29
New cards
Connective tissue proper, cartilage, bone, blood
The four categories of connective tissue
30
New cards
Binding/support, protection, insulation, storing reserve fuel, transport
The major functions of connective tissue
31
New cards
Embryonic tissue
This type of connective tissue is the original tissue source.
32
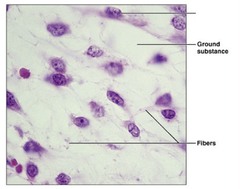
New cards
Ground substance, fibers, cells
The three elements of connective tissue
33
New cards
Areolar connective
Loosely binds organs; holds tissue fluids. Contains cartilage, and ground substance. Most widely distributed, under epithelia, and packages organs.
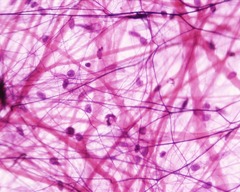
34
New cards
Support, water retention, defends from infection, stores fat
Roles of areolar connective tissue
35
New cards
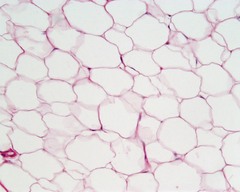
Adipose
Also called fat tissue; specialized tissue that stores lipids
36
New cards
White fat, brown fat
The two types of adipose tissue
37
New cards
White fat
This adipose tissue has nurtrient support, offers protection, insulation, and energy storage.
38
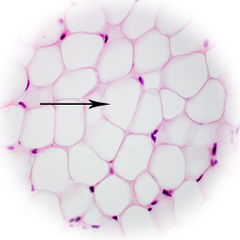
New cards
Adipocyte
Cell that stores fat
39
New cards
Brown fat
This adipose tissue decreases with age, and is thermogenic (releases heat)
40
New cards
Abdomen, breasts, around eyes and kidneys
Some locations of adipose tissue
41
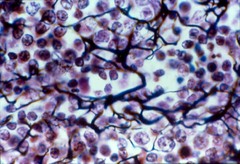
New cards
Reticular connective
Forms the framework for organs like the liver or spleen; contains reticular cells, in lymphoid organs.
42
New cards
Dense regular connective
This connective tissue consists of bundles of parallel collagen fibers, resits pulling, few cells, poorly vascularized. Contains fibroblast cells. In tendons and ligaments.

43
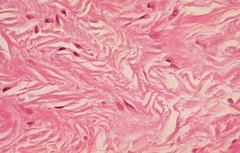
New cards
Dense irregular connective
This connective tissue and tough, fibers are thick, irregularly arranged, resists tension from many directions. Contains fibroblast cells and collagen. Found in fibrous capsules of organs, joints, and dermis.
44
New cards
Cartilage
A connective tissue that is more flexible than bone and that protects the ends of bones and keeps them from rubbing together. Up to 80% water
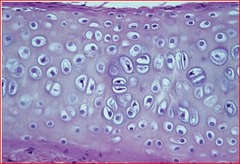
45
New cards
Fibroblasts
In connective tissue, cells that secrete the proteins of the fibers.
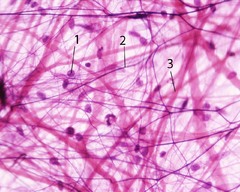
46
New cards
Proteoglycans
Proteins with carbohydrates attached to them
47
New cards
Hyaline, elastic, fibrocartilage
The three types of cartilage
48
New cards
Hyaline
Most common type of cartilage. Protects and cushions, gelatinous ground substance. Contains collagen fibers and proteoglycans. On ends of bones
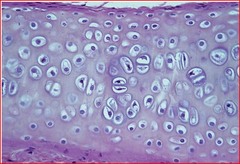
49
New cards
Elastic
This cartilage is supple, gives some support. Contains elastic fibers, collagen, and proetoglycans. In external ear and larynx
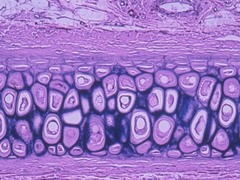
50
New cards
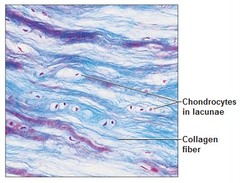
Fibrocartilage
This cartilage is very tough, some elasticity, and may replace damaged hyaline. Contains parallel collagen fibers and chondrocytes. Forms cushioning pads between vertebrae and in insertion points of tendons and ligaments.
51
New cards
Bones
Supports and protects organs, stores fat, synthesizes blood, contains cartilage and contains cartilage.
52
New cards
Blood
This tissue is for transport, full of red and white blood cells.
53
New cards
Erythrocytes
Another name for red blood cells
54
New cards
Leukocytes
Another name for white blood cells
55
New cards
Skeletal, cardiac, smooth
The 3 types of muscle tissue
56
New cards
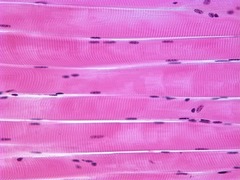
Skeletal
This muscle tissue is voluntary
57
New cards
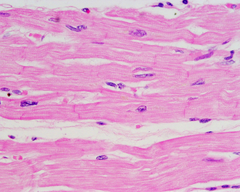
Cardiac
This muscle tissue is in walls of the heart, involuntary
58
New cards
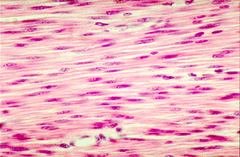
Smooth
This muscle tissue is found in walls of hollow organs other than the heart
59
New cards
Neurons
Generate nerve signals
60
New cards
Neuroglia
Support and insulate nerves
61
New cards
Skin, sub skin
Skin is divides into two parts
62
New cards
Epidermis, dermis
Makes up the skin
63
New cards
Hypodermis
Makes up the sub skin. Under the dermis, stores fat and anchors skin to the muscles below.
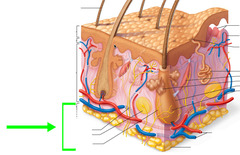
64
New cards
Epidermis
Outermost layer of skin, or epithelial cells
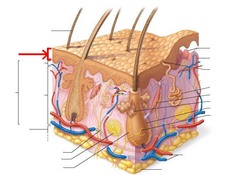
65
New cards
Dermis
Inner layer of skin made or areolar connective tissue
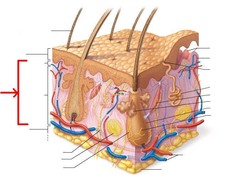
66
New cards
4-5, cuboidal, keratinized cells
How many layers does epidermis have? What kind of cells are the bottom layers? What do the upper layers contain?
67
New cards
Stratum basale
Deepest layer of epidermis. Has a single row of stem cells. Contains melanocytes.
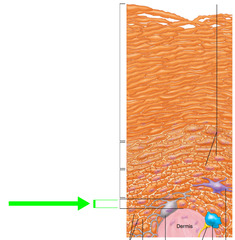
68
New cards
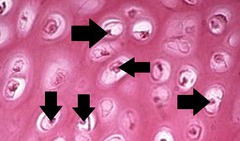
Chondrocytes
Mature cartilage cells
69
New cards
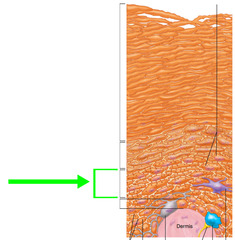
Stratum spinosum
"Prickly layer" made of layers of cuboidal cells. Contains lots of desmosomes and pro keratin.
70
New cards
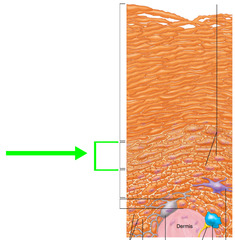
Stratum granulosum
This layer of skin has flat cells and nuclei. Has protein filled granules, and makes keratin. Layers above this are dead.
71
New cards
Stratum Lucidum
A layer of the epidermis found only in the thick skin of the fingers, palms, and soles. Transparent, made of dead cells
72
New cards
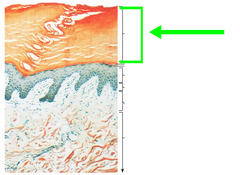
Stratum corneum
20-30 layers of dead acidic cells, water proof, repels environment agent, resists microbial growth. Cells constantly shed.
73
New cards
Reticular cells
These cells produce reticular fiber stroma that supports other cells in lymphoid organs