Cone Beam Computed Tomography Introduction
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
May 13
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
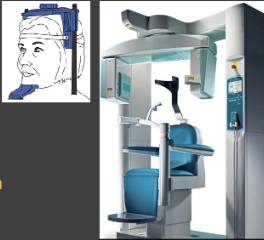
How should a patient be positioned when taking a CBCT?
They sit, stand or lay with their head between x-ray source and detector (head stabilization/immobilization is key)
How does a CBCT rotate?
There is a rotating gantry with x-ray source and reciprocating detector. There is a single rotation around a single fixed axis or rotation center

How does a CBCT capture images?
There are many sequential planar (2D) projection images captured. All several hundred of these basis/fram/raw images constitute the projection data
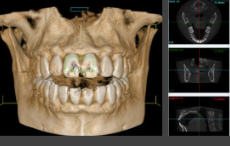
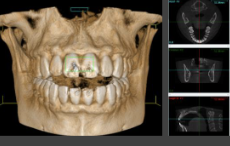
How do CBCTs get their image generated?
A computer algorithm generates image volume (volumetric data set). They take images by secondary reconstruction into orthogonal planes (axial, sagittal, coronal)
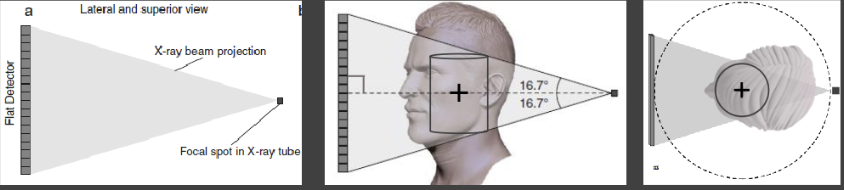
How are x-rays generated in beam geometry
They are transmitted from the central ray of an x-ray beam at a perpendicular angle
Non-central rays are incident on detector at non-perpendicular angles
Image quality is optimal at the center of the beam
Anatomy positioned at the beam center will be images best
Position region of interest (ex. tooth #8) at center of scan volume/field of view (ex. anterior maxilla)
Quality decreases toward the edges as beam diverges
X-ray generation
The fundamental concepts of x-ray production in CBCT are the same as PAs:
The beam is filtered and collimated
Parameters depend on machine-specific, variably adjustable presets
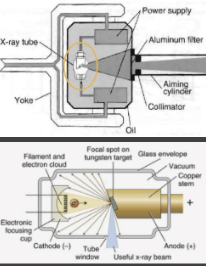
Define focal spot
Area on anode struck by elections from cathode
How can you adjust focal spot?
Fixed/non-adjustable
What is the impact of adjusting focal spot?
Decrease spot size will increase image sharpness
Define tube voltage (kVp)
Voltage applied between anode and cathode
How do you adjust tube voltage? (kVp)?
Preset/adjustable
What is the impact of adjusting tube voltage (kVp)?
Increase kVp = increase beam energy and penetrability
Decrease image contrast, x-ray exposure inversely proportional to kVp2
Define tube current mA
Current applied to the cathode filament
How do you adjust mA?
Preset/adjust
What is the impact of adjusting tube current (mA)?
Increasing the mA increases the number of x-rays
Increases image low-contrast resolution
Decreases image noise
Define exposure time (s)
Duration of the current applied to the filament
How do you adjust exposure time (s)?
Present/adjustable
What is the impact of adjusting exposure time (s)?
Increase exposure time = increase the number of x-rays
Expressed with mA as mA*s
x-ray exposure is inversely proportional to mAs
In field of view, what do dimensions depend on?
Detector size/shape
Beam projection geometry
Beam collimation
How is the beam collimated in field of view?
To cover the region of interest —> it limits radiation exposure (dose reduction of 25 to 66%)
What does a smaller field of view mean?
It is associated with better image quality
Reduced scattered radiation per detector area
Less beam divergence at scan edges (cone beam effect)
Increase image resolution (smaller voxel size)
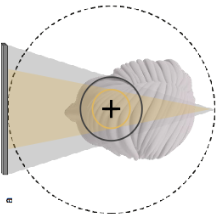
What are the scan parameters for trajectory arc?
180 to 360 degrees. Combined panoramic units often have arcs <360
Sometimes it is adjustable
Limited arc is associated with
Decreased scan time
Decreased radiation dose
Decreased projection data (fewer basis images)
Decrease image quality (increased noise and artifact)
What are the parameters for scan time?
Limiting scan time helps reduce motion artifact
Reduced scan time is associated with
Decreased projection data
Decreased image quality
How are x-ray signals collected in their detector function?
They record photon attenuation for each basis/projection image
How do x-rays read out?
They send a signal for each basis/projection image to the computer
What is the detector frame rate?
The number of basis images acquired per second. It is limited by detector capacity, not directly selectable or controllable by operator. A high frame rate is associated with
Increased projection data
Increased image quality (increased signal-to-noise ratio and decreased artifact)
Increased radiation dose
Increased image/volume reconstruction time
Increasing frame rate could be used to reduce scan time
More data (x-rays) =
Better image quality