DPT 642: Gait Cycle & Clinical Implications
1/172
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
173 Terms
Locomotion
way in which an animal moves about, e.g., swimming, flying, crawling, or climbing, among others.
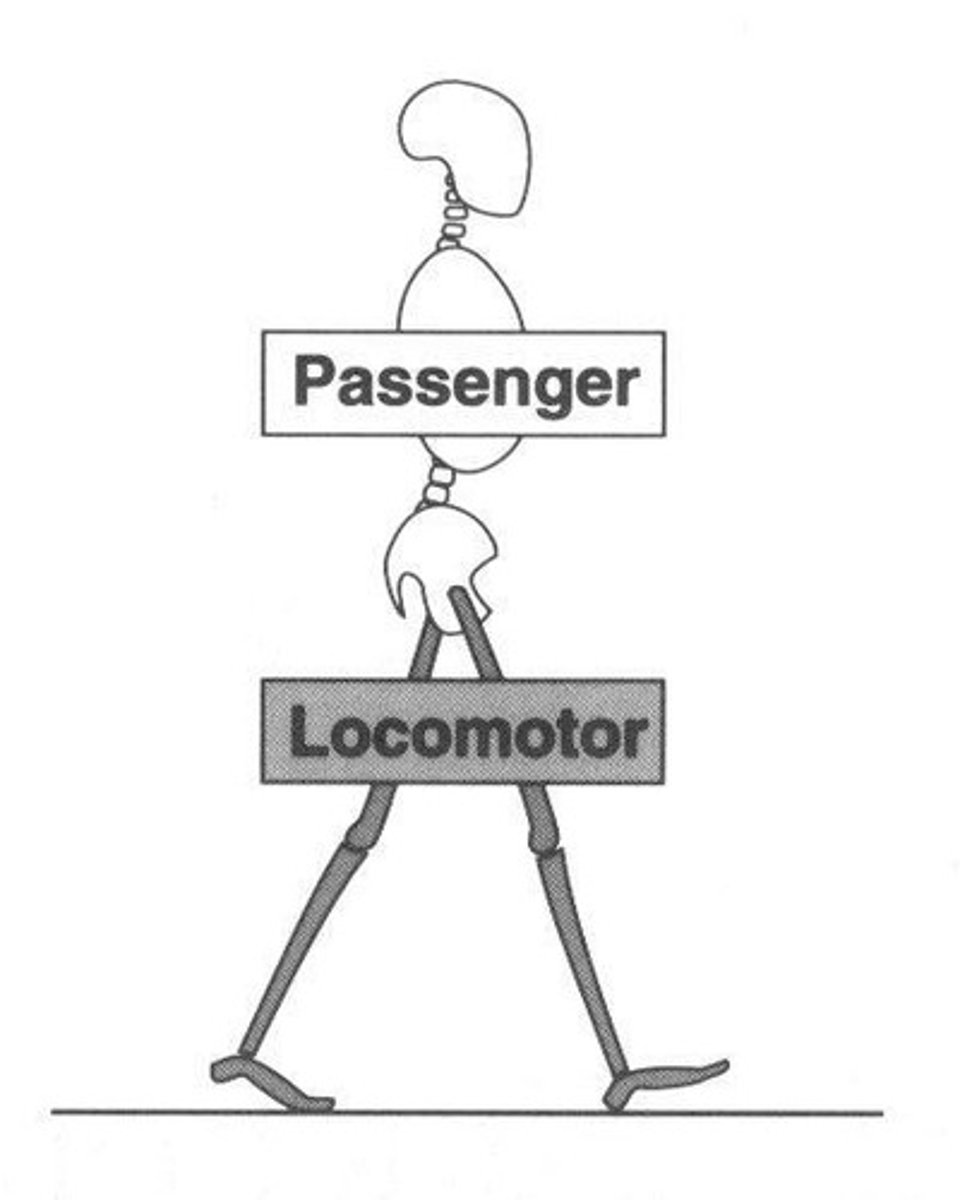
Gait
a particular way or manner of moving on foot: can take many forms such as running, skipping, or marching, but the most commonly employed is walking.
Walking
characterized by symmetrical, alternating movement of the two lower limbs with a phase lag of 0.5.
Ambulation
To walk from place to place; move about. Specific to PT - also includes wheeling/driving oneself by wheelchair.
Progression
movement in the desired direction.
Stability
not falling down.
Adaptation
accommodating or avoiding obstacles.
Normal gait
the result of highly efficient motor control responses, programmed at the spinal cord level.
Gait efficiency
depends on the amount of available joint mobility & muscle activity that is selective in timing & intensity.
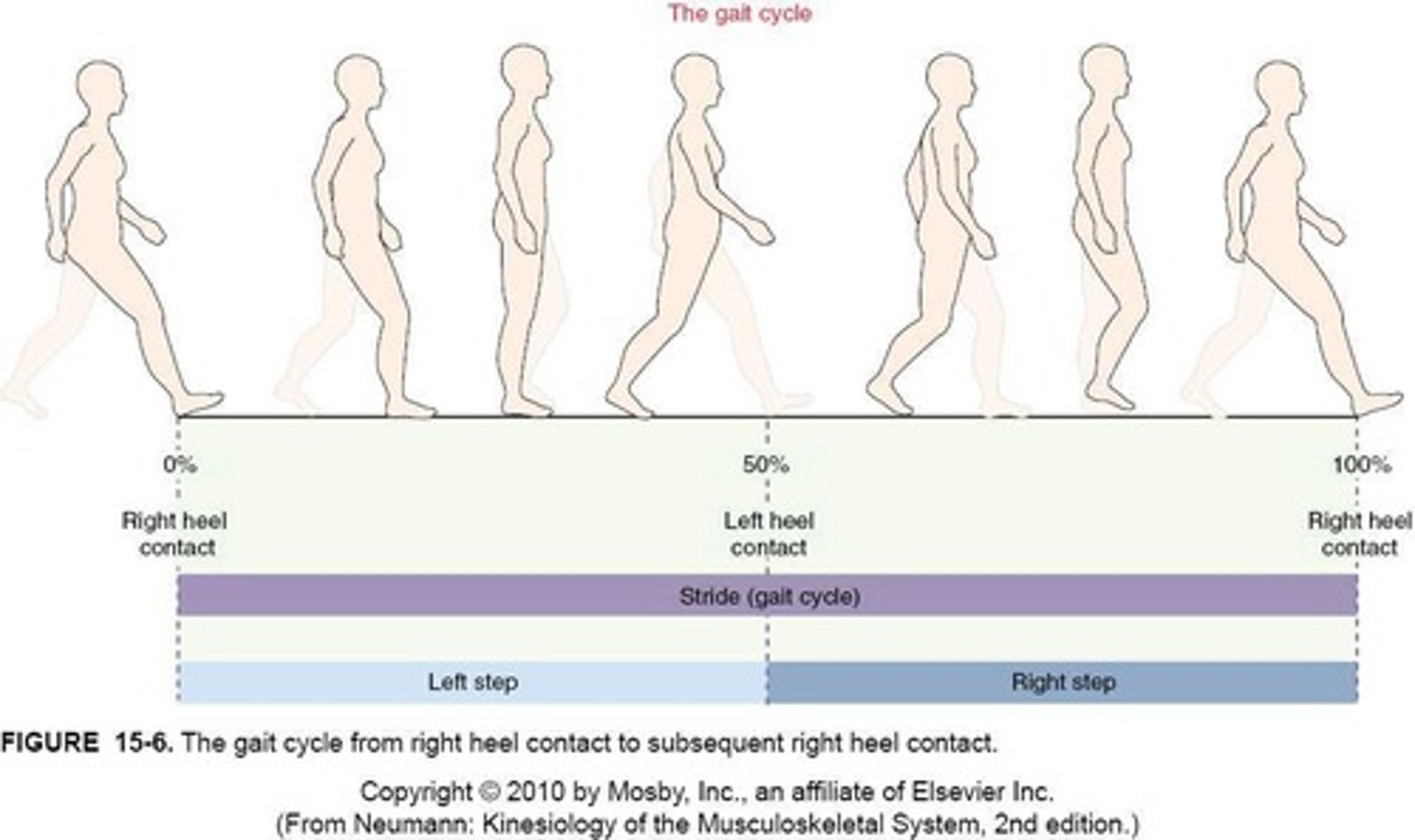
Stride
initial contact of 1 foot to initial contact of same foot.
Step
completion of a right or left step (e.g., heel strike R to heel strike L).
Stride length
distance (AP) b/w successive heel contacts of same foot. avg = 144 cm (4.5').
Step length
distance (AP) b/w successive heel contacts of the opposite feet; avg= 72 cm (28"); Normal range: 70-80 cm.
Step width
lateral distance b/w feet, measured (ML) b/w two heel centers; avg = 8-10 cm.
Foot angle
Angle b/w long axis of foot (heel center to 2nd MT) & line of forward progression of body. Avg = 5°-7°.
Cadence
# of steps per minute. Normal range: 1.87 steps/sec; 110 steps/min.
Stride time
time (s) for a full gait cycle: from initial contact of 1 foot to initial contact of same foot. Usually takes slightly > 1 sec.
Step time
time (s) for the completion of a right or left step (e.g., heel strike R to heel strike L).
Speed
distance/time (in m/s). Most spatial, temporal, kinetic & kinematic variables depend on speed.
Normal gait speed
1.37 m/s (3 mph). Reported as the best functional measure of one's ability to walk.
Velocity
change in position (displacement)/time (in m/s). Has magnitude & direction.
Gait Speed
step length * cadence
Gait Cycle
Begins with heel contact of 1 limb (0% of cycle) & ends with next heel contact of that same limb (100%).
Stance Phase
Period of time when foot is touching the ground (60% of gait cycle).
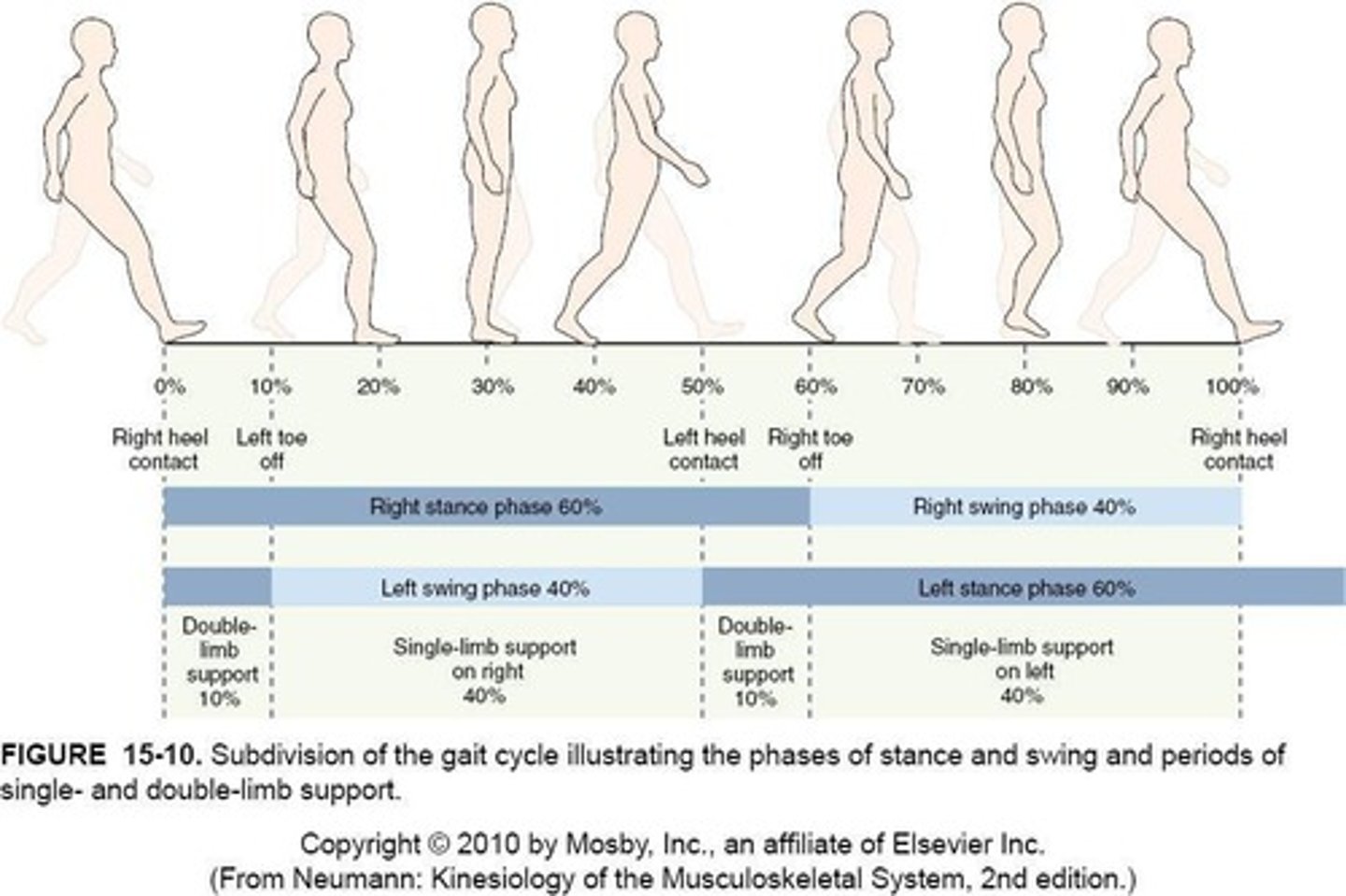
Swing Phase
Period of time when foot is swinging forward and not touching the ground (40% of gait cycle).
Single-limb Support
Time when only 1 foot is in contact with the ground: 80% of cycle.
Double-limb Support
Time when both feet are in contact with the ground simultaneously (20% of cycle).
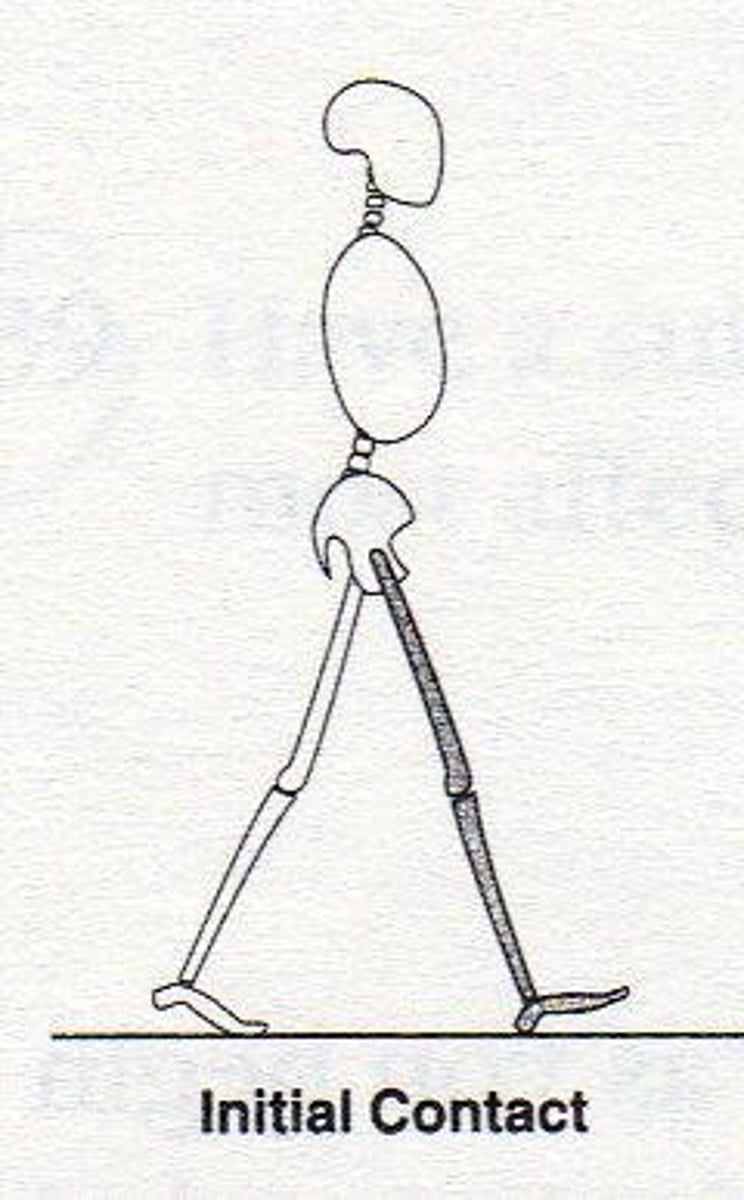
Heel-strike (Initial Contact)
Instant heel comes in contact with ground; begins period of double limb support. (0%)
Foot Flat (FF)
Instant entire plantar surface of foot comes in contact with ground. (8%)
Loading Response
Period of weight acceptance by LE, initiating contact with ground. Body mass transferred from 1 limb to other. (0 - 10%)
Contralateral Toe Off
At 10% - instant of opposite toe off; begins single limb support phase.
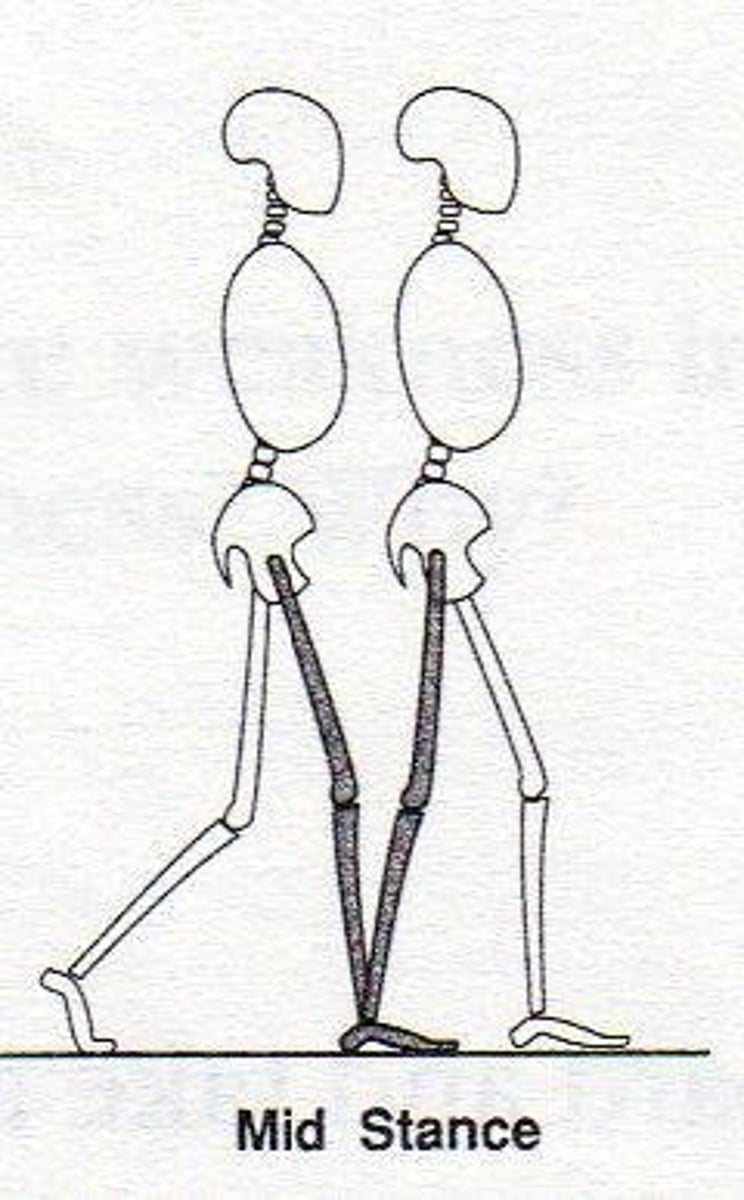
Mid-stance (MS)
Instant COM passes directly in line with supporting limb - GT is vertically above midpoint of supporting foot in sagittal plane.
Heel-off (HO)
Instant heel comes off ground. (40%)
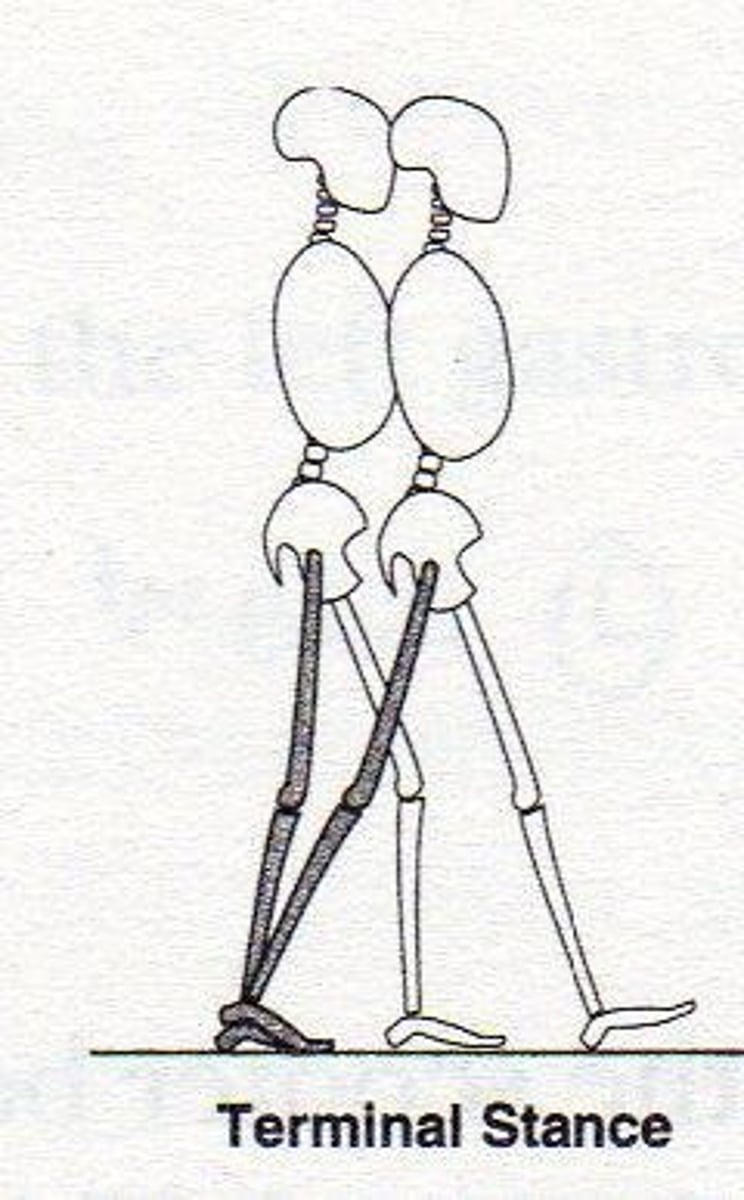
Terminal Stance
Period - begins when heel rises, ends at contra-lateral HC. (40 - 50%)
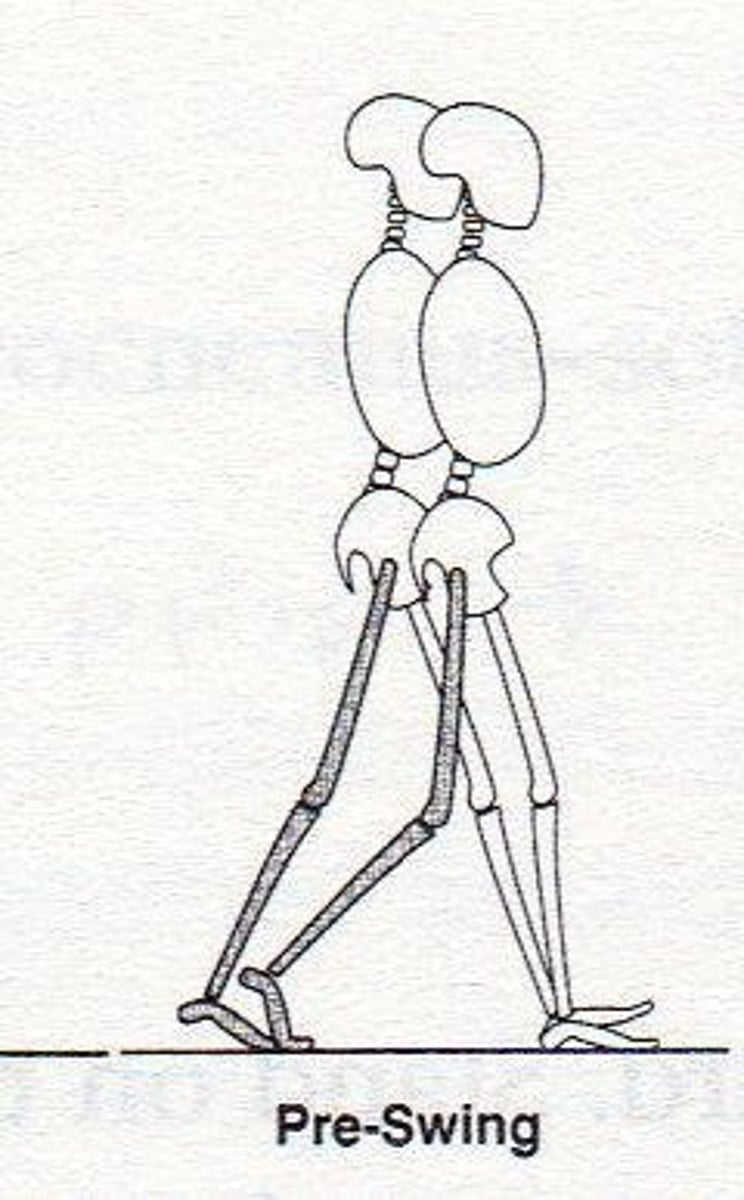
Pre-swing
Period from foot contact of contralateral limb to toe-off of ipsilateral foot; corresponds to 2nd double limb support. (50-60%)
Toe-off (TO)
Instant toes come off the ground. (60%)
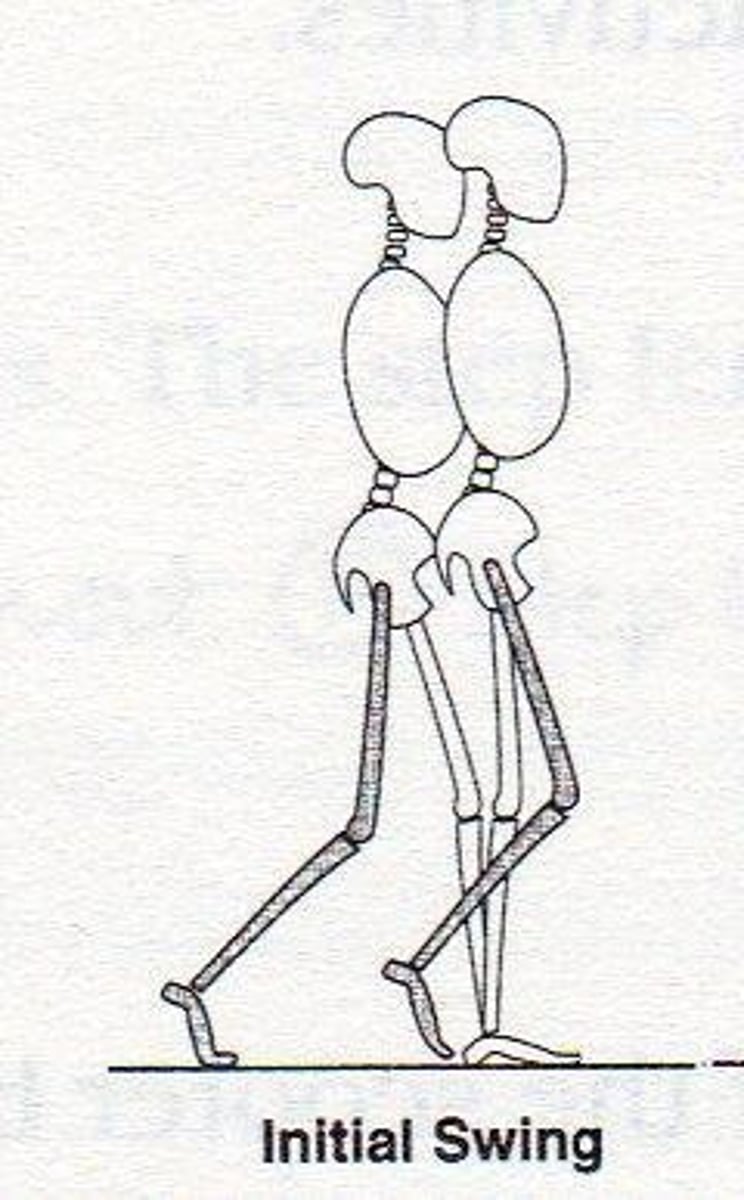
Early or Initial Swing
Immediately after toe-off to mid-swing. (60%-75%)
Mid-swing
Midstance event of opposite LE; foot of the swing leg passes next to the foot of the stance leg. (75%-85%).
Late or Terminal Swing
From mid-swing to just prior to initial contact with the ground. (85%-100%)
HAT
(head, arms, trunk)
HAT Functions
1. postural stability 2. HAT alignment determines what muscle actions occur throughout the system.
Lower Limb & Pelvic Functions
1. provides propulsive force
Lower Limb & Pelvic Functions
Provides propulsive force, maintains upright stability, shock absorption, and energy conservation.
Center of Mass (COM)
Is approximately anterior to S2 vertebrae.
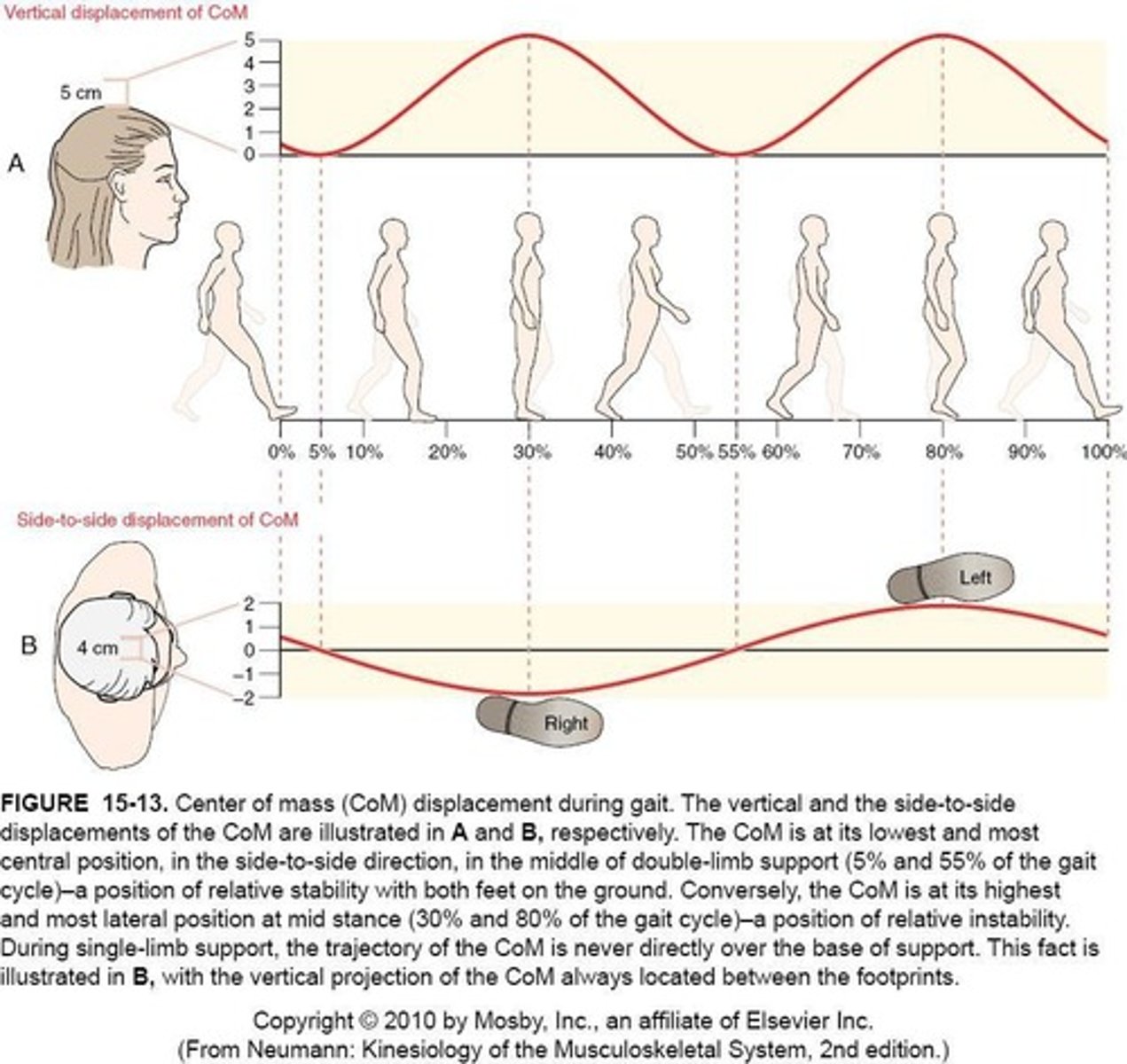
Vertical Displacement of COM
Is approximately 5 cm during gait.
Medial-Lateral Displacement
Is approximately 4 cm, with the foot placed slightly lateral to COM to control side-to-side movement.
Acceleration
Change in velocity/time, measured in m/s².
Deceleration
The reduction of velocity of COM from heel strike to mid stance.
Potential Energy at Mid-Stance
Is highest, while kinetic energy is lowest.
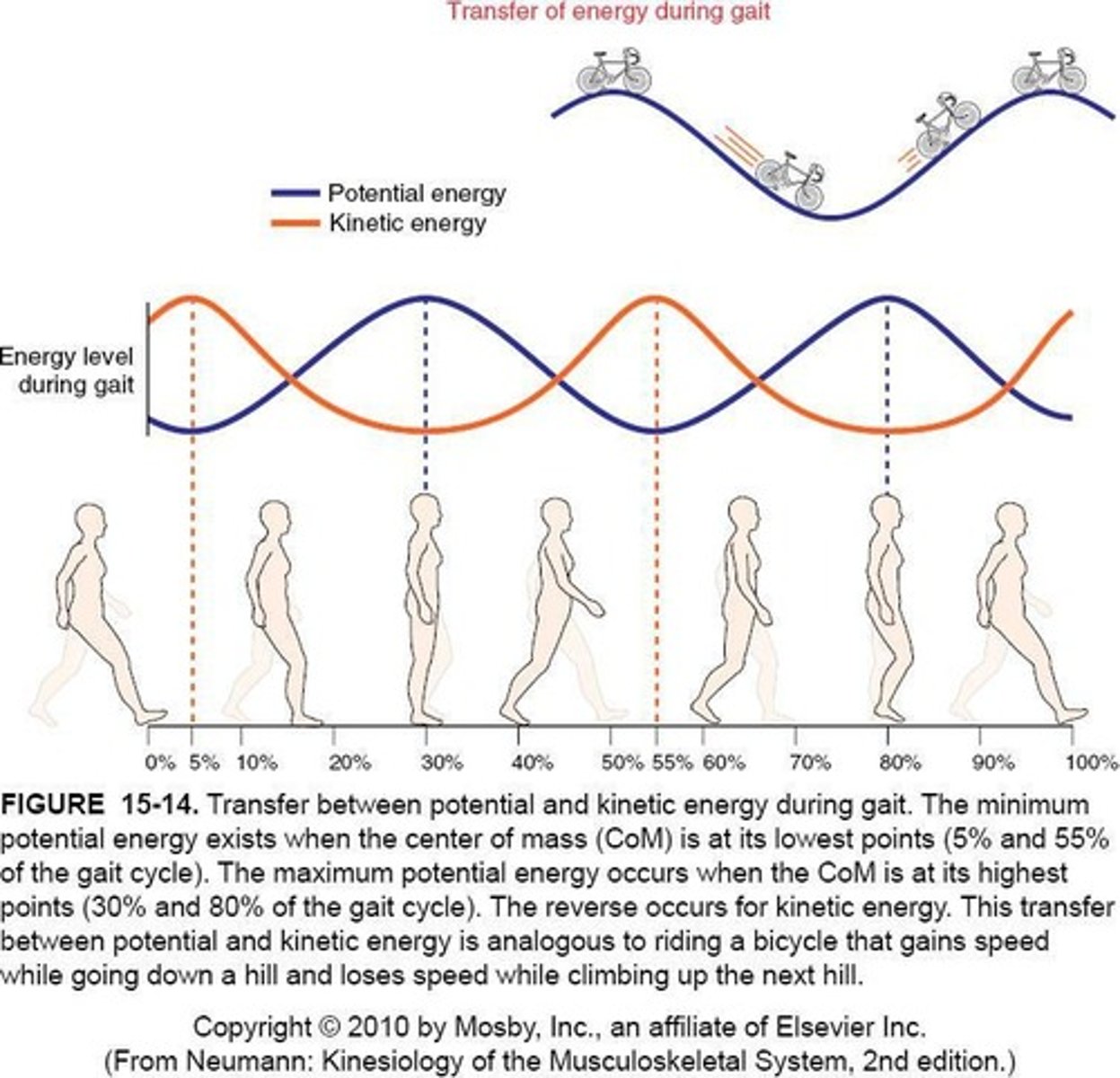
Kinetic Energy during Double Limb Support
Is highest, while potential energy is lowest.
Initial Contact (Heel Strike)
Moment foot strikes the ground.
Hip ROM at Initial Contact
Is 25-30° flexion, maintained from terminal swing.
Pelvic ROM at Initial Contact
Is nearly neutral tilt with ipsilateral anterior rotation.
Ground Reaction Force (GRF) at Initial Contact (Hip)
Is anterior.
Muscle Activity at Initial Contact (Hip)
Glut max and hamstrings decelerate forward limb, preventing 'jackknifing'.
Knee ROM at Initial Contact
Is initially 5° flexion.
GRF at Initial Contact (Knee)
Is posterior.
Muscle Activity at Initial Contact (Knee)
Quads concentrically contract to extend the knee, with hamstrings co-activation for stability.
Ankle ROM at Initial Contact
Is neutral or slight plantarflexion (0°-5°) with slight STJ supination (2°-3° inversion).
GRF at Initial Contact (Ankle)
Is posterior.
Muscle Activity at Initial Contact (Ankle)
Dorsiflexors eccentrically contract to decelerate passive ankle plantarflexion.
Hip ROM at Loading Response
Is 25° flexion, starting to extend and adduct.
Pelvic ROM at Loading Response
Is slight posterior tilt with left pelvis dropping and right pelvis elevating.
GRF at Loading Response (Hip)
Is anterior.
Muscle Activity at Loading Response (Hip)
Glut max and hamstrings eccentrically control flexion torque, then begin to concentrically extend the hip.
Glut medius, minimus, TFL
Eccentrically control pelvic drop on swing side.
Hip ER's
Eccentrically control IR of the lower limb in early stance.
Knee ROM
15°-20° flexion, then begins to extend.
Knee GRF
Posterior.
Knee External torque
Rapid flexion torque caused by body being behind foot.
Knee Muscle activity
Major burst of quadriceps activity eccentrically controls knee flexion in 1st 10% of gait cycle.
Knee Co-contraction
HS co-contract with quads to stabilize the knee.
Ankle ROM
5°-10° of rapid plantarflexion.
Ankle GRF
Posterior.
Ankle External torque
Plantarflexor torque forces the foot to the floor.
Ankle Muscle activity
Dorsiflexors (tib anterior) counteract PF torque.
Tib posterior
Decelerates foot pronation.
Fibularis longus & brevis
Contribute to PF & counteract strong inversion created by tib posterior and deep posterior muscles.
Midstance
Point at which the body passes over the supporting limb.
Hip ROM in Midstance
Hip extends to neutral (0°).
Pelvic ROM in Midstance
Ipsilat pelvis starts to rotate posteriorly, anteriorly tilt, L pelvic drop reaches maximum.
Hip Muscle activity in Midstance
Glut max extends the hip until end of midstance.
Knee ROM in Midstance
Knee continues to extend (0°).
Knee GRF in Midstance
Anterior.
Knee External torque in Midstance
Extensor torque created by muscle activity and forward momentum of the contralateral limb.
Knee Muscle activity in Midstance
Quadriceps contract concentrically to extend the knee and support body weight.
Ankle ROM in Midstance
5° dorsiflexion as body glides over the stable foot.
Ankle GRF in Midstance
Anterior.
Ankle External torque in Midstance
Marked dorsiflexion torque.
Terminal Stance Hip ROM
15°-20° extension.
Terminal Stance Pelvic ROM
5° backward (posterior) rotation and slight anterior tilt.
Terminal Stance Knee ROM
Knee reaches maximal extension (0°).
Terminal Stance Knee GRF
Anterior.
Terminal Stance Ankle ROM
10° dorsiflexion (at max when knee is extended).
Tib anterior & plantarflexors
Supinate (invert) foot; controlled by fibularis longus & brevis.
Fibularis longus
Holds 1st MT rigidly to ground so foot can act as rigid lever.
Tib posterior
Supinates foot.
Intrinsics
Stabilize foot, raise MLA.
EDL & EDH
Co-contract with PF's for stability (PF activity at this time = 70% of MVIC!).
PRE-SWING
Phase known as 'push-off'.