Structure of eukaryotic, prokaryotic cells and viruses
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
5 Terms
The structure of eukaryotic cells, restricted to the structure and function of:
cell-surface membrane
nucleus(containing chromosomes, consisting of protein-bound, linear DNA, and one or more nucleoli)
mitochondria
chloroplasts(in plants and algae)
Golgi apparatus and Golgi vesicles
lysosomes (a membrane-bound organelle that releases hydrolytic enzymes)
ribosomes
rough endoplasmic reticulum and smooth endoplasmic reticulum
cell wall (in plants, algae and fungi)
cell vacuole (in plants).
are eurkaryotic cells or prokaryotic cells bigger?
eukaryotic cells are bigger, prokaryotic cells are smaller
what do prokaryotic cells also differ from eukaryotic cells in having:
cytoplasm that lacks membrane-bound organelles
smaller ribosomes
no nucleus; instead they have a single circular DNA molecule that is free in the cytoplasm and is not associated with proteins
a cell wall that contains murein, a glycoprotein.
In addition, many prokaryotic cells have:
one or more plasmids
a capsule surrounding the cell
one or more flagella.
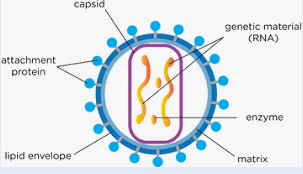
what is a virus described as?
acellular and non-living.
what does the structure of a virus look like?