AQA Physics Waves
Transverse Wave
A wave for which the oscillations are perpendicular to the direction of energy transfer.
Longitudinal Wave
A wave for which the oscillations are parallel to the direction of energy transfer.
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards for AQA Physics GCSE 4.6.1 - Waves in air, fluids and solids
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Transverse Wave
A wave for which the oscillations are perpendicular to the direction of energy transfer.
Longitudinal Wave
A wave for which the oscillations are parallel to the direction of energy transfer.
Examples of Transverse Waves
Electromagnetic waves and Seismic s-waves
Examples of Longitudinal Waves
Sound waves and Seismic p-waves
Parts of a Longitudinal Wave
Compressions and rarefactions.
Wave's Amplitude
The maximum displacement of a point on a wave from its undisturbed position.
Wavelength
The distance from a point on a wave to the same position on the adjacent wave, commonly peak to peak or trough to trough.
Frequency of a Wave
The number of waves that pass a given point each second.
Unit for Frequency
Hertz, Hz
Frequency of 200Hz
200 waves pass a given point each second.
Wave Speed
The speed at which the wave moves or at which energy is transferred through a medium.
What a Wave Transfers
Energy
Equation to Calculate Wave Speed
Wave Speed = Frequency x Wavelength; Speed (m/s), Frequency (Hz), Wavelength (m)
Wave Bouncing off a Surface
Reflection
How Sound Waves Travel Through a Solid
The particles in the solid vibrate and transfer kinetic energy through the material.
Frequency Range of Human Hearing (Higher)
20 Hz - 20kHz (1kHz = 1000 Hz)
Ultrasound Waves (Higher)
Waves which have a frequency higher than the upper limit of human hearing (20kHz).
Example Use for Ultrasound Waves (Higher)
Medical or industrial imaging.
Natural Event that Causes Seismic Waves (Higher)
Earthquakes; They produce both P-waves and S-waves
Difference Between Mediums of P and S Waves (Higher)
P-waves travel through both solids and liquids, S-waves only travel through solids (not liquids)
Technique to Detect Objects in Deep Water (Higher)
Echo sounding; High frequency sound waves are emitted, reflected and detected; Time difference between emission and detection, alongside wave speed, are used to calculate distances
What type of spectrum do electromagnetic waves form?
A continuous spectrum
Order the types of electromagnetic radiation from lowest to highest frequency.
● Radio waves ● Microwaves ● Infrared ● Visible Light ● Ultraviolet ● X-rays ● Gamma Rays
How do the speeds of EM radiation differ in a vacuum and in air?
Electromagnetic waves all travel at the same speed in a vacuum and in air.
What property of waves in different mediums causes refraction? (Higher)
●Velocity ●Wave speed is slower in denser materials, causing refraction
In which direction (relative to the normal) do waves refract when entering a denser medium?
●They bend towards the normal ●The angle of refraction is less than the angle of incidence
What type of waves can be produced by oscillations in an electrical circuit? (Higher)
Radio waves.
How can radio waves create an alternating current in a circuit? (Higher)
When radio waves are absorbed, they can induce oscillations in a circuit with the same frequency as the waves themselves.
Where do gamma rays originate from?
They originate from changes in the nuclei of atoms
What health effects can ultraviolet waves cause?
●They can cause the skin to age prematurely ●The can increase the risk of developing skin cancer
What health effects can X-rays and Gamma rays cause?
●They are ionising radiation so can cause mutations in genes ●They can lead to increased risk of developing various cancers
Give three practical uses for infrared radiation.
1. Electrical heaters 2. Cooking food 3. Infrared cameras
Give two practical uses for microwave radiation
1. Satellite communications
2. Cooking food
Give two practical uses for radio waves.
1. Television transmission 2. Radio transmission
What wave phenomenon is used by lenses to form an image? (Physics only)
Refraction.
How does a convex lens form an image? (Physics only
Parallel rays of light are refracted and brought together at a point known as the principal focus
What is meant by the focal length of a lens? (Physics only)
The distance from the lens to the principal focus.
What is the difference between the image produced by a convex and a concave lens? (Physics only)
●Convex lenses can produce real or virtual images ●Concave lenses can only produce virtual images
Why does magnification not have a unit? (Physics only)
● It is the ratio between image height and object height ●Ratios do not require units
What symbol is used to represent a convex lens in a ray diagram? (Physics only)
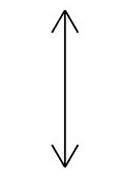
What symbol is used to represent a concave lens in a ray diagram? (Physics only)

What determines the colour of visible light waves? (Physics only)
The wavelength and frequency of the light waves.
What colour of visible light has the highest frequency? (Physics only)
Blue
What colour of visible light has the largest wavelength? (Physics only)
Red
What is meant by the term ‘specular reflection’? (Physics only)
Reflection from a smooth surface in a single direction.
What is meant by the term ‘diffuse reflection’? (Physics only)
Reflection from a rough surface which causes scattering
How does a red colour filter work? (Physics only)
●A red filter absorbs all wavelengths of light other than those in the red range of the spectrum
●This means only red light passes through the filter
What determines the colour of an opaque object? (Physics only)
●Different objects reflect different wavelengths of light by different amounts ●The wavelengths that are most strongly reflected determine the colour
What happens to the wavelengths of light that aren’t reflected by an opaque object? (Physics only)
Any wavelengths that aren’t reflected are absorbed by the object.
What colour does an object appear if all wavelengths are reflected by equal amounts? (Physics only)
White
What colour does an object appear if all wavelengths are absorbed? (Physics only)
Black
What do all bodies (objects) emit and absorb?
Infrared radiation.
What happens to the quantity of infrared radiation emitted by an object as temperature increases?
The hotter the object, the more infrared radiation it will emit
What is a perfect black body?
An object that absorbs all of the radiation that is incident upon it.
How much radiation does a perfect black body reflect or transmit?
None
Why is a perfect black body the best possible emitter of radiation?
● It is a perfect absorber since it absorbs all radiation incident on it
●A perfect absorber is also a perfect emitter
Other than the intensity of radiation emitted, how does increasing the temperature of an object affect its emissions?
The wavelength distribution of any emission is dependent on the object’s temperature.
What can be said about the rates of emission and absorption for a body at constant temperature? (Higher)
The body is absorbing and emitting radiation at the same rate.
What can be said about the rates of emission and absorption for a body increasing in temperature? (Higher)
The body is absorbing radiation faster than it is emitting it.
Give two factors that affect the temperature of the Earth. (Higher)
1. The Earth’s rate of absorption and emission of radiation
2. The amount of reflection of radiation into space