Ch 10, Smooth muscle Slides & Pictures (copy)
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
Do smooth muscle cells have sarcomeres?
No
What is the arrangement of thick and thin filaments in smooth muscle?
They overlap, like skeletal muscle
What are dense bodies in smooth muscle?
Where the thin filaments connect to
What connects the dense bodies in smooth muscle?
Intermediate filaments
Where are dense bodies attached?
To the sarcolemma (cell membrane)
What part of the nervous system controls smooth muscle?
The autonomic nervous system (involuntary)
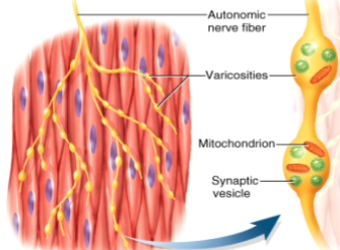
What are varicosities in smooth muscle innervation?
Where neurotransmitters are released in smooth muscle
Where do varicosities form in smooth muscle?
In diffuse junctions
How are smooth muscle cells usually arranged?
Connected to each other in sheets
What allows signals to move between cells quickly?
Gap junctions
How do smooth muscle cells typically contract?
As a single unit
Smooth muscle contractions are _______ to start, but last longer than skeletal muscle contractions:
Slower
Chemicals released from nerve signals such as _________ and ________ can stimulate smooth muscle:
ACh and Norepinephrine
Some _______ can signal smooth muscles to tighten (like during childbirth):
hormones
_________, a chemical released during allergies or inflammation can cause smooth muscle contractions:
Histamine
What is the most common type of smooth muscle?
Single-unit smooth muscle (visceral muscle)
In what places can single-unit smooth muscle be found?
The digestive tract, uterus, bladder
Single-unit smooth muscle works together as a unit, which means…
When one contracts, the others follow
Because of _______ cells, single-unit smooth muscle can often contract rhythmically on their own, even without nerves:
Pacemaker cells
What kind of smooth muscle is found in large airways of lungs, large arteries, and internal iris muscles (muscles controlling the iris)?
Multi-unit smooth muscle
How do the cells work structurally in Multi-unit smooth muscle?
Independently
How is single-cell smooth muscle similar to multi-cell smooth muscle?
They both are involuntary
What hormone helps build muscle?
Testosterone
Why do men generally have more muscle mass than women?
Because testosterone increases muscle growth.
What percentage of a man’s body weight is typically muscle?
About 42%
What percentage of a woman’s body weight is typically muscle?
About 36%
What is sarcopenia?
The gradual loss of muscle mass due to aging
At what age does sarcopenia usually begin?
Around age 30
What can minimize sarcopenia?
Exercise
Most muscles attach to how many bones?
Two, one at each end
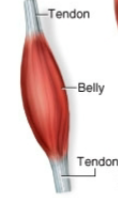
What is the relatively stationary end of a muscle that doesn’t move much during contraction called?
The origin
What is the thick, fleshy midregion of a muscle called?
The belly
What is the more mobile end of a muscle that moves during contraction called?
Insertion
What determines the strength and direction of a muscle's pull?
Fascicle arrangement
Which fascicle arrangement is thick in the middle and tapered at both ends?
Fusiform
Name this fascicle arrangement:
Fusiform
What are fusiform arrangements designed for?
Strength
Which fascicle type has uniform width and straight, parallel fibers?
Parallel
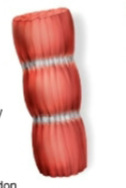
Name this fascicle arrangement:
Parallel
Which fascicle arrangements have parallel fascicles?
Fusiform and parallel
Which fascicle arrangement is fan-shaped with a broad origin and narrow insertion?
Convergent
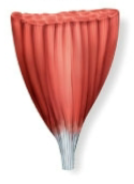
Name this fascicle arrangement:
Convergent
What does it mean for a muscle to have parallel fascicles?
The individual muscle fibers run in the same direction
In which type of pennate muscle do all fascicles insert from one side?
Unipennate
Which pennate type has fascicles inserting from two sides of the tendon?
Bipennate
Which type of pennate muscle has multiple feather-like fascicle arrangements?
Multipennate

Name this fascicle arrangement:
Unipennate

Name this fascicle arrangement:
Bipennate

Name this fascicle arrangement:
Multipennate

What kind of fascicle arrangement forms a ring around an opening?
Circular muscles (sphincters)
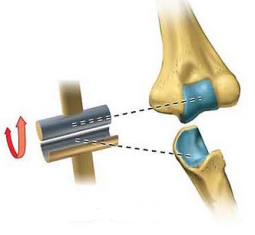
Name this joint
Hinge Joint
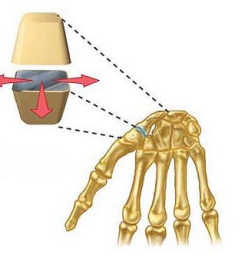
Name this joint
Plane Joint
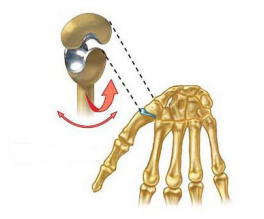
Name this joint
Saddle Joint
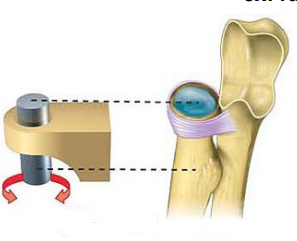
Name this joint
Pivot Joint
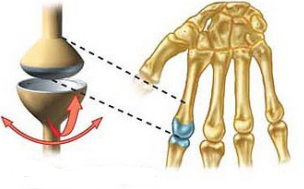
Name this joint
Condyloid Joint
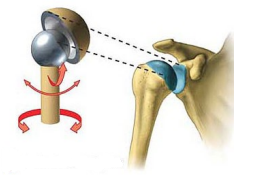
Name this joint
Ball and Socket Joint

Name this movement
Abduction
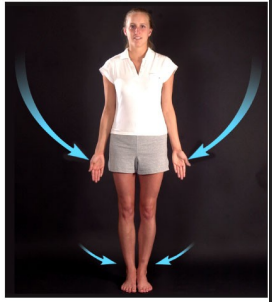
Name this movement
Adduction

Name this movement
Circumduction

Name this movement
Medial Internal Rotation

Name this movement
Medial External Rotation
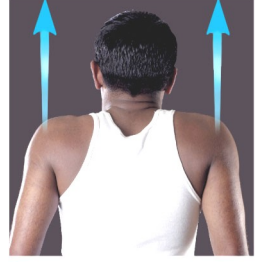
Name this movement
Elevation
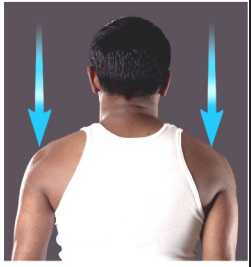
Name this movement
Depression
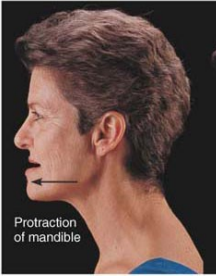
Name this movement
Protraction
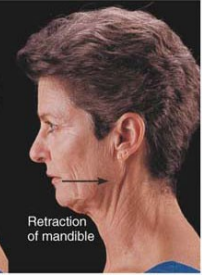
Name this movement
Retraction
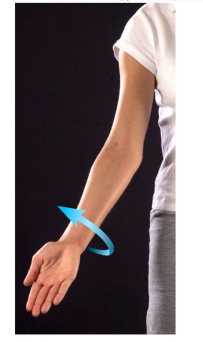
Name this movement
Supination
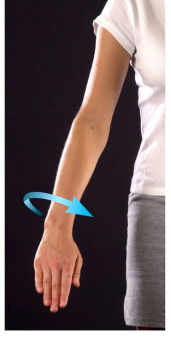
Name this movement
Pronation

Name this movement
Radial Flexion

Name this movement
Ulnar Flexion

Name this movement
Abduction of fingers

Name this movement
Abduction of thumb

Name this movement
Opposition of thumb
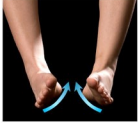
Name this movement
Inversion
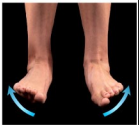
Name this movement
Eversion
What type of tissue is affected in a sprain?
Ligaments are stretched or torn in a sprain.
Why do partial ligament tears heal slowly?
Because ligaments have poor blood supply.
What is usually required for a full ligament tear to heal properly?
Prompt surgery is usually required for the best outcome.
Can cartilage damage typically heal on its own?
No, cartilage damage is usually not self-repairing.
What might be necessary when cartilage is damaged and does not heal?
The damaged cartilage may need to be surgically removed.
What is a dislocation (luxation)?
A condition where bones are forced out of alignment.
What is a subluxation?
A partial dislocation.
What is the treatment for a dislocated joint?
It needs to be reduced—bone ends must be returned to their proper position.
What tissue is often stretched during a dislocation?
Ligaments are often stretched during a dislocation.
What are bursitis and tendonitis?
They are inflammatory conditions affecting bursae and tendons.
What is arthritis?
Arthritis refers to over 100 types of inflammatory or degenerative joint diseases.
What are four common symptoms of arthritis?
Pain, stiffness, swelling, and loss of range of motion or mobility.
What is the most common chronic form of arthritis?
Osteoarthritis
What is osteoarthritis also called?
"Wear-and-tear" arthritis.
What causes osteoarthritis?
Joint overuse leads to cartilage breakdown.
What type of disorder is rheumatoid arthritis?
A chronic inflammatory autoimmune disorder.
What happens to the joints in rheumatoid arthritis?
The body's immune cells attack joint components.
How does rheumatoid arthritis compare to osteoarthritis in severity?
It is usually more severe.
What causes joint inflammation in gouty arthritis?
Uric acid crystals in the joint tissue.
What leads to uric acid buildup in gout?
Either too much uric acid production or too little excretion.
Who is more commonly affected by gout?
Men.
What can happen if gout is not treated?
Bone ends can fuse, causing joint immobilization.
What are common treatments or lifestyle changes for gout?
Medications, drinking water, avoiding alcohol and purine-rich foods.