Electric Fields AQA A Level Physics
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
how to work out the number of electrons from the charge?
Q / e
where e = 1.6 x 10^-19
What do any two charged objects exert?
equal and opposite forces on each other without being directly in contact
what surrounds a charged object?
an electric field
When a small positive force is placed as a test charge near a body with a much larger positive charge, if the test charge is free to move, what happens?
it follows a path away from the body with the larger charge
-- this path is called a line or force or a field line
In which direction are field lines?
from positive to negative as this is the path a positive test charge would follow
What is the electric field strength, E, at a point in the field defined as?
the force per unit charge on a positive test charge placed at that point
Unit of electric field strength?
Newton / Coulomb (NC^-1) or Volt / Metre (Vm^-1)
Electric field strength, E =
Force / Charge
F / Q
What is the field pattern for two oppositely charged flat plates?
The field lines are:
parallel to each other
at right angles to the plates
from the positive plate to the negative plate
Electric field strength, E =
(in terms of voltage)
V / d
where V = voltage
d = distance between the plates
How to prove E = V / d
the force F on a small charge Q in the field is given by F = QE
if the charge is moved from +ve to -ve plate, the work done by the field on Q is W = Fd = QEd
V = W / Q so = QEd / Q
-> V = Ed rearrange for E = V / d
How is the strength of the electric field affected by the charge?
The greater the charge on the body, the stronger the electric field is.
Also the more concentrated the charge is on the surface, the stronger the electric field is above the surface
What is the permittivity of free space?
ε0 - (Epsilon naught)
8.85 x 10^-12 farads per metre (Fm^-1)
What is a farad?
1 coulomb per volt
Define the electric potential at a certain position in any electric field
the work done per unit positive charge on a positive test charge when it is moved from infinity to that point.
Unit of electric potential
volt = 1JC^-1
Electric Potential, V =
Ep / Q
Where Ep = electric potential energy
Q = charge
If a test charge +Q is moved in an electric field from one position where the electric potential is V1 to another where it is V2, then what is the ΔW given by?
ΔW = Q(V2 - V1)
What are Equipotential surfaces?
surfaces of constant potential.
A test charge moving along an equipotential has constant potential energy so no work is done by the electric field on the test charge
Why is not work done by the electric field on a test charge along an equipotential surface?
because the force due to the field is at right angles to the equipotential
What is the potential gradient at any position in an electric field?
the change of potential per unit change of distance in a given direction
If the field is non-uniform, how does the potential gradient vary with respect to?
position and direction
The closer the equipotentials are, the greater the potential gradient is a right angles to the equipotentials
If the field is uniform, what is the shape of the equipotentials between the plates?
equally spaced lines parallel to the plates
The potential gradient has what three factors?
(in a uniform field)
constant
the potential increases in the opposite direction to the electric field
is equal to V / d
What is the negative of the potential gradient equal to?
the electric field strength
In a non uniform field, is the electric field strength = negative of the potential gradient?
yes!
however its given by ΔV / Δx
where ΔV is the change in potential between two closly spaced points at distance apart Δx
Electric field strength E =
(in terms of potential)
ΔV / Δx
What is force F proportional to?
1 / r^2
where r = distance between two charges
What is Coulomb's Law?
F = k Q1 Q2 / r^2
where F = force between two point charges
r = distance between the charges
k = constant of proportionality
constant of proportionality, k =
1 / 4πε0
= 9.0 x 10^9 mF^-1
using Coulomb's Law, what is another equation for the Electric field strength?
E = F / Q = kQ / r^2
where r = distance from Q
For forces acting in the same direction, what is the resultant electric field strength?
E = E1 + E2
For forces acting in opposite directions, what is the resultant electric field strength?
E = E1 - E2
For forces acting at right angles to each other, what is the resultant electric field strength?
E^2 = E1^2 + E2^2
Why is the curve of how E varies with r an inverse square law?
because E is proportional to 1 / r^2
Electric potential, V =
(at distance r from Q)
kQ / r
What does a negative value for the electric field strength indicate?
a field that acts towards a negative charge
Why can the electric potential in the electric field near a point charge be positive or negative?
because it depends on the charge and that can be either positive or negative
What is the change in electric potential equal to on a graph?
the area under an electric field strength by distance graph
What does a graph of electric field strength against distance show?
how the force per unit charge on a +ve test charge varies with distance
the area under the graph gives the work done per unit charge (change in potential) when a +ve charge is moved through that distance.
Coulomb's law equation
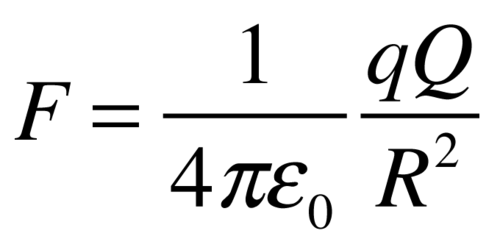
What is Coulomb's law (description)
Coulomb's law states that the electrical force between two charged objects is directly proportional to the product of the quantity of charge on the objects and inversely proportional to the square of the separation distance between the two objects
In what way is Coulomb's law similar to Newton's law of gravitation?
They are both inverse square laws - force is inversely proportional to square of the distance between two masses/charges.
force between two like charges
repulsive. F is positive
force between two opposite charges
attractive. F is negative
What does ε0 represent?
Permittivity of free space
Define electric field strength
force per unit charge
acting on a positive charge
electric field strength unit
N C-1
or V m-1
Define electric potential at a point in an electric field
work done per unit charge on a small positive test charge required to move it from that point to infinity in the field
Electric field strength is a vector - in which direction does it act?
In the direction of the force acting on a positive charge
How can the direction of an electric field be represented in a diagram?
Electric field lines
Electric Field Strength equation
E = F/Q
What is the value of the electric potential at infinity?
zero
What is the electrical potential difference between one point and another?
The work done per unit charge to move an object between these points.
What is the equation for electrical potential difference between one point and another?
∆W=Q∆V
W= work done
Q= charge being moved
V= electric potential difference
equation for the magnitude of electric potential in a radial field
V=1/(4πε0 ) x Q/r
V= electric potential
Q= charge
r= radius
Field lines on a positive charge
field lines on a negative charge
Describe the path of an electron entering a uniform electric field at right angles to the field lines
It feels a constant force parallel to the electric field lines in the opposite direction as the field lines.
this makes the particle accelerate at right angles to the particle's original motion so it follows a curved path
(path Z on picture)
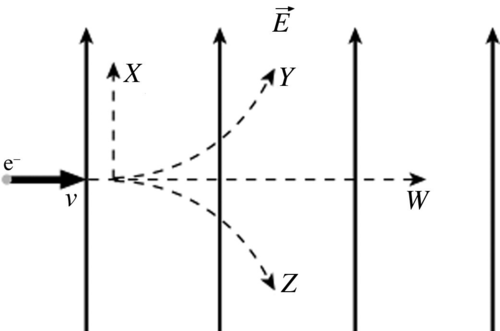
What is absolute electric potential?
the electric potential energy that a unit positive charge has at that point in the electric field
graph of absolute electric potential against distance for a positive charge

graph of absolute electric potential against distance for a negative charge

on a graph of E against r what does the area under the curve represent?
the change in absolute electric potential
What shape are equipotentials in the electric field of a point charge
spherical
Is electric field strength a vector or scalar quantity?
vector
what happens to a charge moving along an equipotential
no work is done
-no movement in direction of force
-kinetic energy is constant
-potential energy is constant
potential gradient
at a point in a field is the change of potential per unit change of distance along the field line at that point.
The potential gradient = - the field strength at any point