The Ultimate Biology Reviewer Part 2
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What is the breakdown (oxidation) of food substances with the release of energy in living cells?
Respiration
What are the two types of Respiration?
Aerobic Respiration
Anaerobic Respiration
What is the breakdown of food substances in the presence of oxygen with the release of large amount of energy?
Aerobic Respiration
What is the process of Aerobic Respiration?
Carbohydrates→Sugar→O2→Energy
C6H12O6 +6 O2(Glucose)→6CO2+6H2O+Energy(Products)
What is the breakdown food substances in the absence of oxygen that releases less energy than aerobic respiration?
Anaerobic Respiration
Which type of respiration is mainly used by microorganisms?
Anaerobic Respiration
What is the process of breaking down sugar molecules in the absence of oxygen?
Fermentation
What are the two types of Fermentation?
Alcoholic Fermentation
Lactic Fermentation
What type of fermentation describes this, NADH transfers its electrons directly to pyruvate, generating lactate as a byproduct?
Lactic Fermentation
What is the process of Lactic Fermentation?
C6H12O6(Glucose)→2 C3H6O3 + Energy(Lactic Acid)
(No Oxygen Involved)
Which type of fermentation describes this, NADH transfers its electrons to acetaldehyde producing ethanol?
Alcoholic Fermentation
What is the process of Alcoholic Fermentation?
C6H12O6(Glucose)→2 C2H5OH + 2C02+ Energy(Ethanol)
(No Oxygen Involved)
What is the organ system in an organism’s body responsible for gas exchange?
Respiratory System
What is exchange of gases between an organism and the environment?
Gas Exchange
What are the components of the Respiratory System?
Nose
Trachea
Bronchi
Bronchioles
Lungs
Alveoli
Diaphragm
What is the prominent structure on the face that serves as the entrance point of the air in the body?
Nose
What does the nasal cavity contain that trap dust particles in the air?
Fringe of Hairs
What serves as the main passageway of air to lung which is also called a windpipe?
Trachea
What supports the trachea?
C-shaped rings of cartilages
What is the lumen of Trachea surrounded of?
Epithelium made of two types of cells:
gland and ciliated cells
What is the extension of trachea that shuttles air to and from the lungs?
Bronchi
What are the smaller branches from bronchi that enter in each lungs and is connected to each air sacs?
Bronchioles
What are the pair of air-filled organs that contains numerous air sacs responsible for gas exchange?
Lungs
What are the parts of the lung?
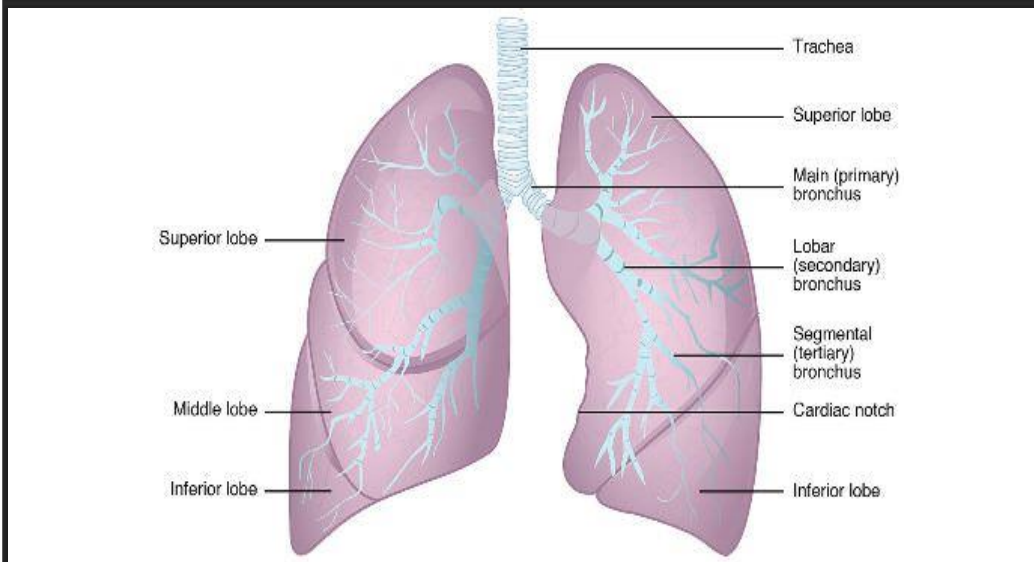
What are the air sacs inside the lungs where gas exchange occurs?
Alveoli
What is the dome-shaped sheet that separates the thorax from the abdomen?
Diaphragm
What are the muscular contractions and movements of the ribs which result in air moving in and out of the lungs?
Breathing
What are the two types of breathing?
Inspiration/Inhalation
Expiration/Exhalation
Process of Inhalation
• Diaphragm contracts and flattens.
• External intercostal muscles contract; internal intercostal muscles relaxes.
• Ribs move upwards and outwards, and sternum moves upward and forward. • Volume of thoracic cavity increases.
• Lungs expand and volume increases due to decrease of air pressure inside.
Process of Exhalation
• Diaphragm relaxes and arches upwards.
• Internal intercostal muscles contract; External intercostal muscles relaxes.
• Ribs move downwards and inwards, and sternum moves downwards and inwards.
• Volume of thoracic cavity decreases.
• Lungs compress and volume decreases due to increase of air pressure inside.