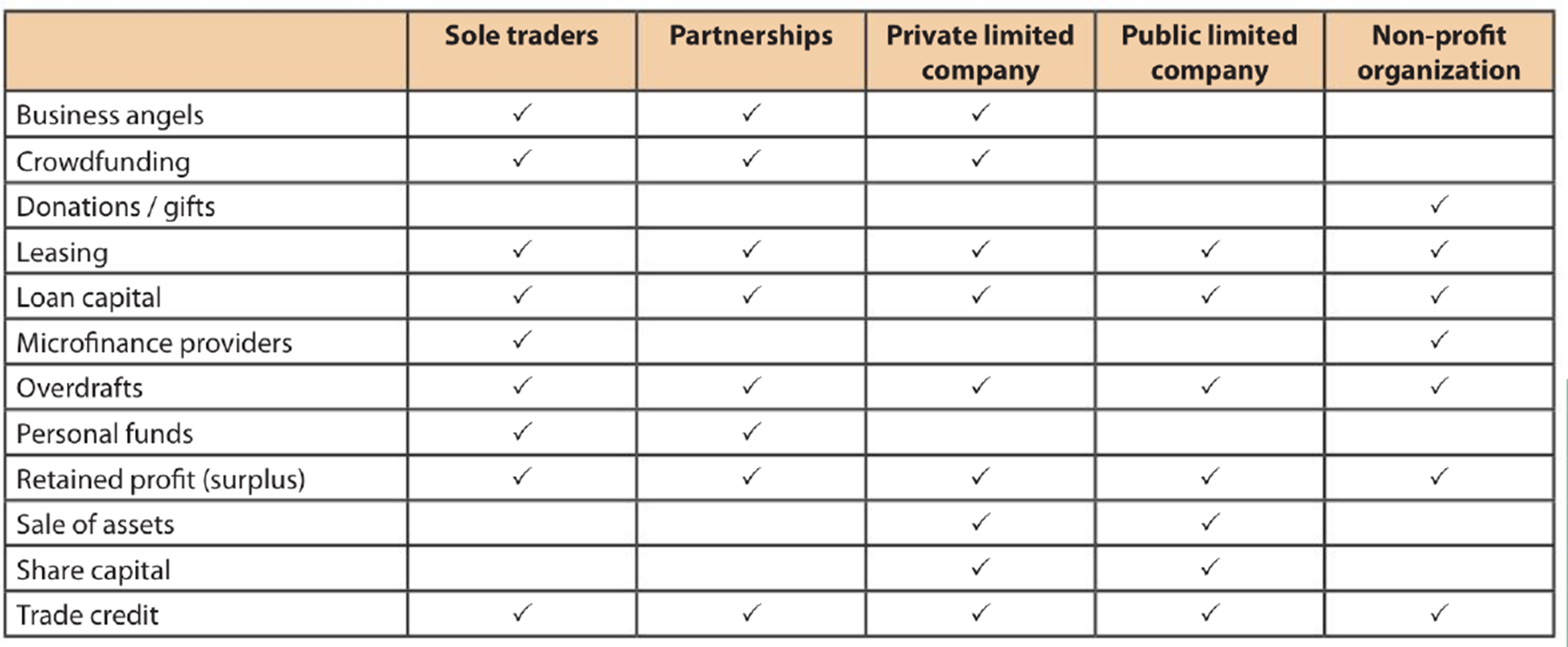
3.2 Sources of Finance
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
External sources of finance
Share Capital, Loan Capital, Overdraft, Trade of Credit, Crowdfunding, Leasing, Microfinance Providers, Business Angels
Internal sources of finance
Personal Funds, Retained Profit, Sales of Assets
Personal Funds
Main source of finance for sole traders and partnerships. •Sole traders
•Partnerships
•Disadvantage – unlimited liability (for sole traders and partnerships)
Retained profits
Profit that remains after paying corporate taxes and dividends. It is then reinvested in the company for growth.
+no interest rate charges
Sale of Assets
Selling things the business owns (like machines, buildings, or vehicles) to get cash. Internal.
+raise money quickly
+no direct cost
+no risk of losing control
-not available for all companies
-might slow down business growth
exam tip
profitable business is cash rich – and that it can use all of its profits as a source of finance for future projects. In practice, profits are often ‘tied up’ in money owed to the business by debtors or have been used to finance increased stocks or replace equipment.
Do not make the mistake of suggesting that selling shares is a form of internal finance for companies. Although the shareholders own the business, the company is a separate legal unit, and therefore, the shareholders are ‘outside’ it.
selling shares = external
Share capital
available to public limited & private limited companies. Money a business raises by selling shares (ownership parts) to investors.
+Permanent source of finance
+not repay
+no interest charged
-dividends have to be paid
-might be expensive
-takes time
long term bank loans
a loan for 10 years or more.
advantages include it being quick to arrange, flexible repayment, discount rates available if large amount is borrowed, interest is paid before profit is taxed.
while disadvantages are having to repay the loans, interest must be paid, interest rate has to be variable which adds risk, Collateral or security is often required.
Debentures
long term loans not secured by any collaterals and has fixed rate of interest.
+interest is fixed
+debenture holders do not own a part of company
+long term financing
-pay interest
-repay at maturity (so exactly on time)
Medium term bank loan
advantages include it being quick to arrange, flexible repayment, discount rates available if large amount is borrowed, interest is paid before profit is taxed.
while disadvantages are having to repay the loans, interest must be paid, interest rate has to be variable which adds risk, Collateral or security is often required.
Hire Purchase
Buying something (like equipment) by paying in small installments over time instead of all at once. The buyer owns it fully after the last payment.
+Enables businesses to buy assets when they have little cash available
+ No collateral required
+ Useful for businesses that have limited finance options.
-A large cash deposit may be required.
-Interest rates are generally higher than bank loans.
-Failure to make a payment may result in the asset being taken back by the HP company.
Leasing
Renting an asset (like a car or machine) instead of buying it. The business pays regularly but doesn’t own it.
+Firms can make use of assets without the need for large sums of money.
+Firm’s money to be used elsewhere in the business (helps cash flows).
+Gives the firm flexibility. It can lease assets only when it needs to use them (reduces costs).
+The care and maintenance of the asset is the responsibility of the leasing company.
+Assets are kept up to date (ideal for computers and other equipment that become obsolete quickly).
-at the end of the contract, hirer has to return the goods
-in the long run, it costs more than buying the asset
Sell and lease back
Business raise money by selling assets they need and then lease them back.
+Immediate Cash Flow
+ Company still uses the asset without owning it.
+ No Maintenance Costs
-Loss of Ownership
-In long term it costs mor
-Dependence on the Lessor
-must continue paying lease fees
Bank overdraft
Allows businesses to spend more than they have in their bank account up to a set limit
+help in settling short-term debts.
+flexible
+quick access to funds
-high interest rates
-short term
-penalties if overdraft limit is exceeded
-bank can cancel any time
Trade credit
when a business delays paying its suppliers for an agreed period of time.
+decreases the strain on a business finances
+allows business to sell goods before paying for them
- suppliers may refuse supplying if they are not paid for long
- firm cannot usually obtain a discount for paying the supplier quickly.
- Is generally limited to a period no longer than 60 days.
Debt Factoring
when a business sells its unpaid customer invoices to a factoring company at a discount to get quick cash.
+business receives most of the money immediately
+The risk of non-payment is taken on by the Factor.
-The business gets less money than the original invoice value.
Grants
money, usually give by governments to assist firms.
+do not need to be repaid
+assist firms with paying for important expenditures
-have strings attached such as firms must create a certain number of jobs or purchase sth specific
Subsidies
payments made by governments to keep business operational.
+money doesnt have to be returned
+no interest
-only available for businesses in certain industries
Crowdfunding
way of raising money from large number of people
+access to many investors
+fast
-risk of having project idea stolen
-if target amount isnt reached money goes back to the investors & business is left with nothing
Microfinance providers
financial services aimed at small organizations and vulnerble groups. Companies or organizations that give small loans to people or businesses that can’t get loans from big banks, often in developing countries.
+access to finance
+promote entrepreunship
-limited accessibility
-limited finance
Venture capital
Money from investors who fund startups or small businesses with high growth potential in exchange for part ownership.
Business angels
Are wealthy entrepreneurs who risk their own money by investing in small to medium-sized businesses that have high growth potential.
They provide finance and expertise to small business start-ups, such as organizing networking opportunities.
– owner loses some control to the BA
VC VS BA
VC invests more than BC. VC gets more ownership. BA offers advice and guidance.
Criteria for VC and BA
•Return on investment – business has to have good potential to be highly profitable.
•The business plan – should outline the LT aim and purpose of the business venture.
•People – must have good team of people.
Track record – Investors will assess the past track record of the business and its management before investing any capital
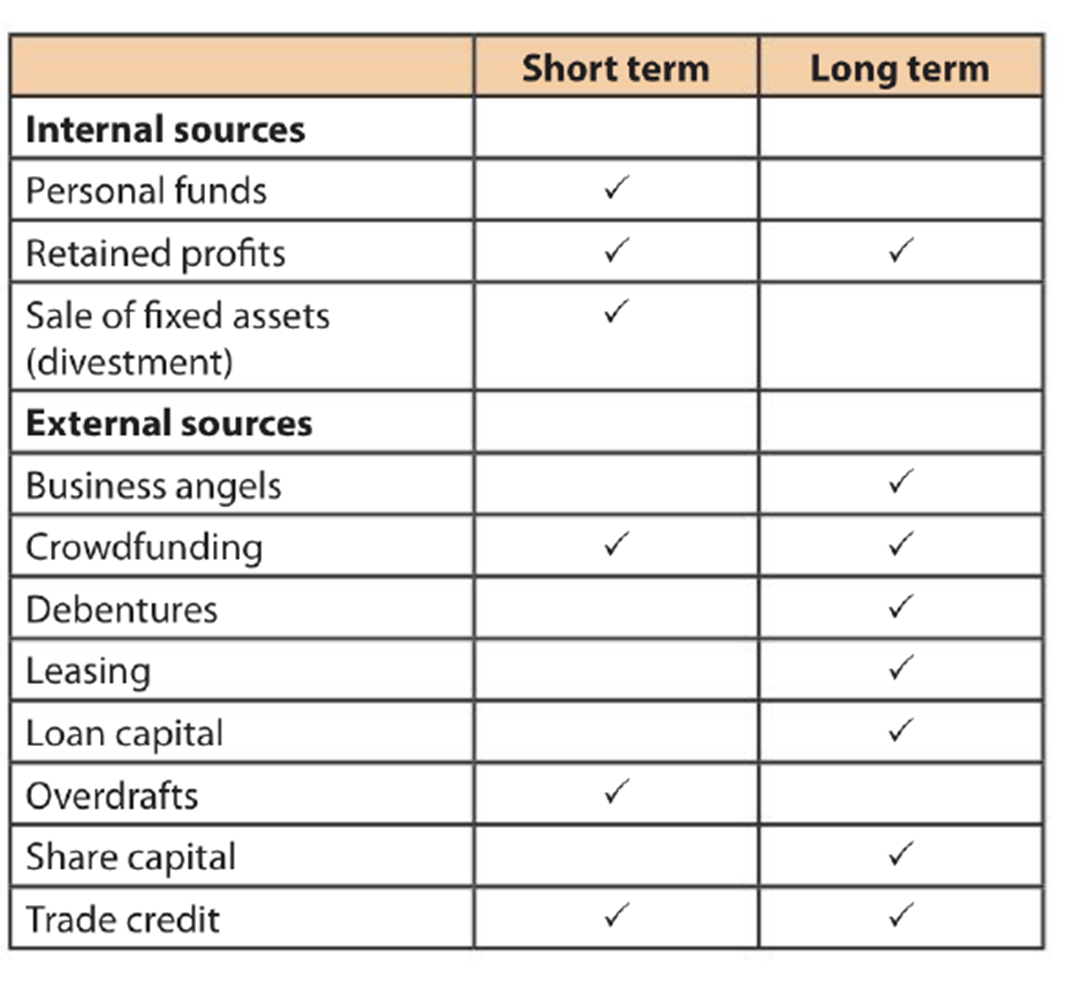
funding types
short or long term
Revenue Expenditure
money spent on salaries and wages
Owner’s capital
sources of finance that come from internal stakeholders, e.g., personal funds (for sole traders) and shareholders’ funds