Intro to pharmacology
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What are drugs
Chemicals that produce biological effects
Define pharmacodynamics
What the drug does to the body, its mechanism of action
Define pharmacokinetics
What the body does to the drug, how it is absorbed, distributed, metabolised, excreted (ADME)
Describe the pharmacodynamics (mechanism of action) of aspirin. Primary, Secondary and research uses
Primary
analgesic (pain killer)
anti-pyretic (reduce fever)
anti-inflammatory (reduce immune response)
Secondary
anti-platelet aggregation in low doses (¯ formation of blood clots)
Research
possible actions of reducing cancer of colon and rectum?
delays onset of Alzheimer’s disease?
Describe the pharmacodynamics of aspirin
Inhibits an enzyme called cyclooxygenase (COX)
COX catalyses the conversion of arachidonic acid into prostaglandins (PGs) and thromboxanes
List the actions of prostaglandins
Sensitising pain nerve endings
Dilating blood vessels - redness
Increasing blood vessel permeability - swelling
Setting body temperature during fever
Thromboxanes cause platelet aggregation
What are the actions of aspirin
analgesic, anti-inflammatory, anti-pyretic and anti-platelet aggregation
Describe the pharmacokinetics of aspirin
Routes of administration – oral (other routes IV, IM, SC)
Readily absorbed from stomach and intestine
Broken down in liver by esterases, some excreted unchanged – half-life of 4 hours in low doses
Excreted in urine – need kidney function
Important in deciding the dose / how often administrated
What are the adverse effects of aspirin
Gastrointestinal irritation and bleeding, might be severe in some individuals (side effect)
Kidney dysfunction
Tinnitus, vertigo, nausea and vomiting – high doses (side effect)
Should be avoided in asthmatics – stimulate attack (this is a potential contraindication)
May cause Reye’s syndrome in children which can be fatal – do not give to young children (contraindication)
What are the properties of drugs
Tissue selective: adrenaline acts on the heart, blood vessels, lungs but not skeletal muscle
Chemical selectivity: small changes in structure greatly alter action of a drug
Amplification of action: drugs work at very low concentrations
What must receptors have for drugs to function
Expressed in selective tissues
Have the correct chemical structure to bind the drug
Linked to amplification of signals
What is a drug receptor
A receptor is a cellular molecule (often a protein) that a drug binds to. Binding of drug to receptor couples to a change in cellular effects
e.g. adrenaline binding to ß-adrenoceptors in the heart leads to an increase in heart rate
List the types of drug targets (receptors) and give examples
Receptors - Adrenaline acting at β-adrenoceptors
Enzymes - Aspirin acting at cycloxygenase
Carrier molecules - Fluoxetine acting at serotonin uptake carrier
Ion channels - Lignocaine acting at Na+ channels
What is an agonist
A drug which binds to a receptor to produce a biological cellular response
E.g. adrenaline increases heart rate
What is an antagonist
A drug which binds to a receptor (same as an agonist) but does not produce a biological effect. Antagonist bind to receptors to prevent agonists producing effects
E.g. Atenolol blocks adrenaline-mediated increases in heart rate
define drug affinity
The strength of the interaction between a drug and its target receptor.
It indicates how tightly a drug binds to a receptor, influencing its effectiveness and potency.
define drug efficacy
refers to the ability of a drug to produce the desired therapeutic effect when administered at a specified dose.
(only agonists produce a cellular response)
List the types of weak/reversible drug bondings
Hydrogen bonding
Ionic bonding
Van der Waal’s forces
List the types of strong/irreversible drug bondings
Covalent bonding
What is Reversible binding of an agonist to a receptor is governed by
Law of Mass Action
describe the law of mass action
The rate of a chemical reaction is proportional to the concentrations of the reactants
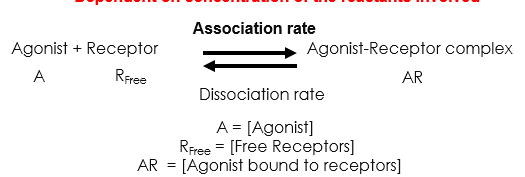
What determines affinity
Law of mass action
A + R ⇌ AR (Agonist + Receptor ⇌ Agonist Receptor complex)
Low [A] - lots of Rfree - few AR interactions
As we increase [A] - more AR interactions - reaction reaches maximum as numbers of receptors is finite
What is equilibrium constant of a drug (KA)
When 50% of receptors are free and 50% are bound to agonist
KA is the [A] at equilibrium, e.g. KA of 50 nM means that at this agonist concentration 50% of receptors will be occupied
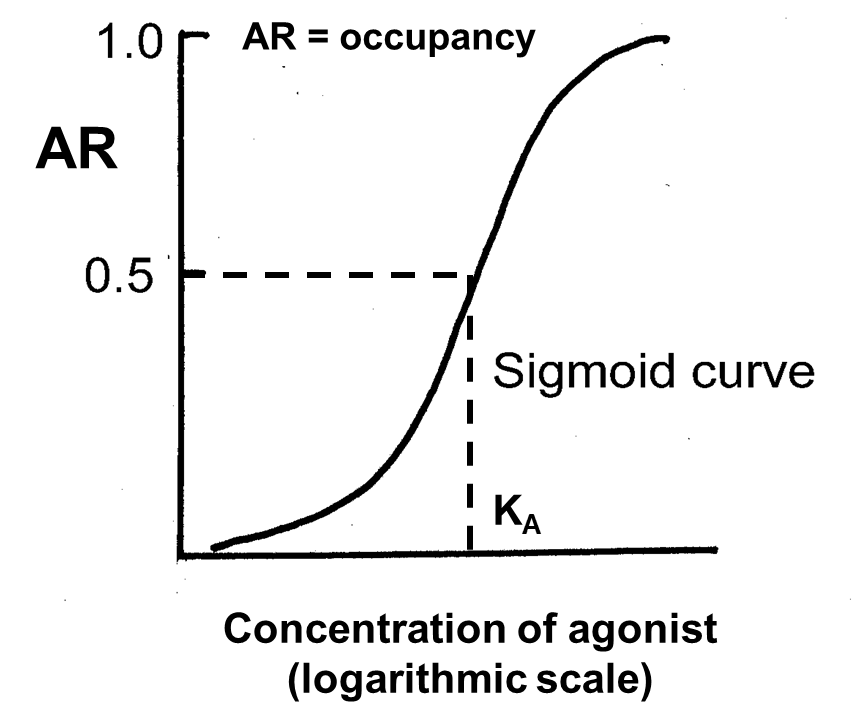
What does a smaller KA mean
Smaller KA (e.g. 5 nM) means agonist has a greater AFFINITY for receptor (it binds more) than a drug with a higher KA value (e.g. 50 nM)
Define affinity and efficacy
Affinity – occupancy, binding of drug to receptor
Efficacy – biological effect, e.g. increase in heart rate
Describe EC50
Effective concentration giving 50% biological response
Describe Partial agonists
E.g. Buprenorphine for opioid addiction
Present at receptors – high affinity, but less efficacy
Reduces withdrawal effects
Reduces additive ‘highs’
Heroin-induced highs (full agonist) are reduced in presence of partial agonist
describe Competitive Antagonism
Receptors only bind either Agonist (A) or Antagonist (Ant)
A and Ant compete for the same binding site
A and Ant both bind reversibly
Reaction now dependent on two equilibrium constants, KA and Kant
If KAnt < KA, then Ant has greater affinity for Receptor than A
[A] must increase to overcome Ant binding to Receptor
Describe Non-competitive antagonism
Ant binds to a different site to that of the agonist
e.g. ketamine (anaesthetic) blocking glutamate NMDA receptor in brain
Describe Irreversible antagonism
Ant binds irreversibly to either agonist- or non-agonist binding sites on the receptor through covalent bonds
Reduces number of receptors the agonist can bind to
e.g. aspirin – acetylates COX enzyme