Computer networks question 1 and 2
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms



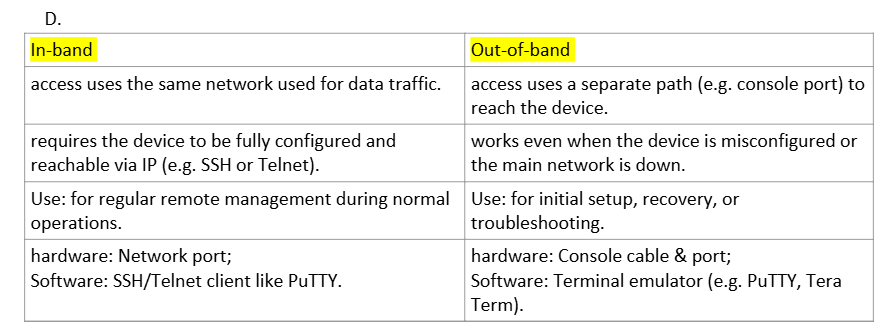
Configuring switch/router - A console cable and a computer with terminal software (e.g. PuTTY or Tera Term) are required to configure a new managed switch or router.
The computer connects directly to the console port on the device using the cable.
This allows access to the device’s CLI (Command Line Interface) for initial setup before network connectivity exists.
This method is called out-of-band management because it uses a separate path from the network traffic.

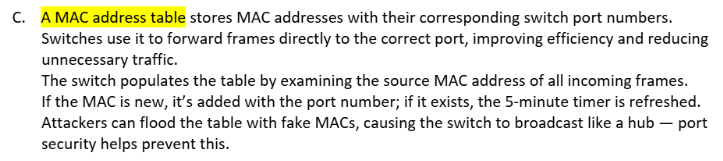












MAC addresses identify devices at Layer 2; IP addresses are used at Layer 3.
MAC is needed for local delivery; IP is needed for routing across networks.
ARP is used to find the MAC address from a known IP address.
Host sends ARP Request (“Who has IP X?”); the target replies with its MAC.
This info is stored in the ARP table for future communication.
Both addresses are essential to move data from app to physical transmission.

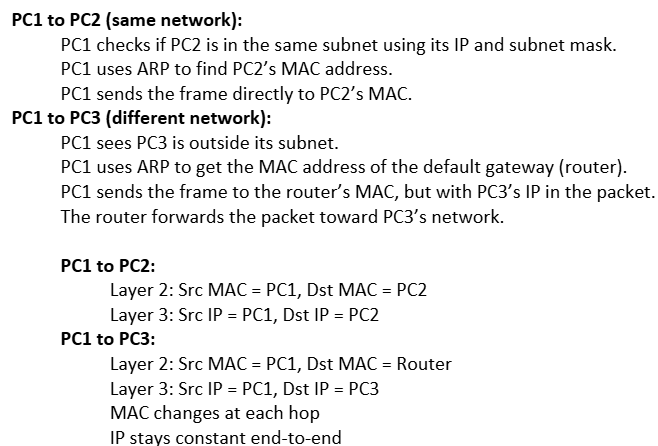
The gateway is the router that connects the LAN to external networks.
Host uses subnet mask to check if destination IP is in the same subnet.
If not, the host forwards data to the default gateway.
If yes, it sends data directly to the local device’s MAC address.
The default gateway’s MAC is resolved using ARP.
Without a gateway, communication outside the subnet fails.

