24. Trauma of the chest wall and lungs. Neoplasia of the lungs. Pneumothorax. Diagnosis and therapy. Lobectomy. Thoracic drainage. Thoracocentesis.
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
13 (9 true ribs attached to the sternum)
Which organs are found in the thorax?
GIT (oesophagus)
Cardiovascular (heart, aorta, pulmonary arteries, vena cava, pulmonary vein)
Respiratory (trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, lungs)
How does the aorta travel from the heart?
From the left ventricle, it arches dorsally and travels caudally
Two (cranial and caudal)
Four (cranial, middle, caudal, and accessory)
Drugs that cause hypoventilation. Use butorphanol + acepromazine
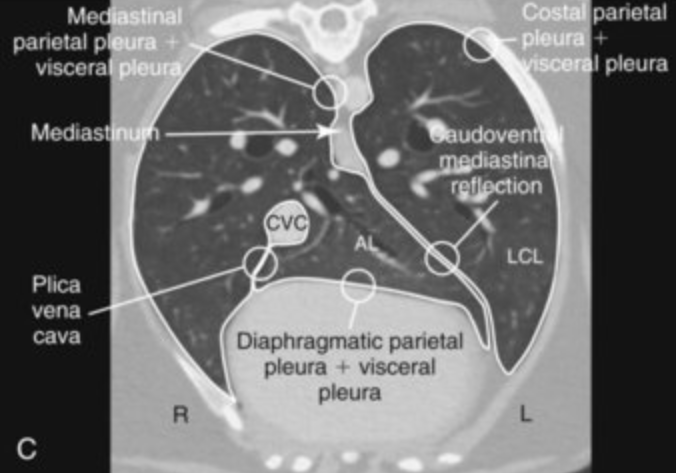
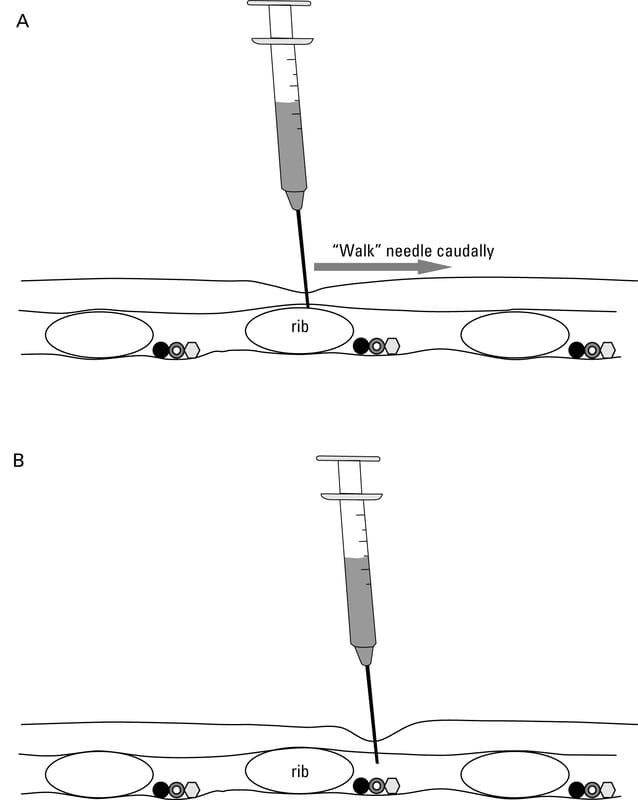
Insert needle on dorsal surface of rib, keeping as caudal as possible, till you hit bone surface. Then direct caudally along surface of rib until it reaches soft tissue. 2-3 intercostal nerves are blocked before & after planned target area
Traffic accidents, bites, gunshot wounds, falls, kicks, blunt force → pneumothorax, fractured rib, wounds of pleura/lungs
Dyspnoea, pain, shock, emphysema, pneumothorax, haemothorax
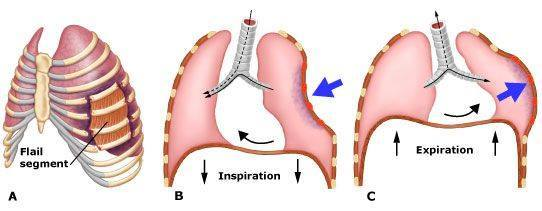
Animals should be evaluated for flail chest, pulmonary contusions or lacerations & diaphragmatic rupture.
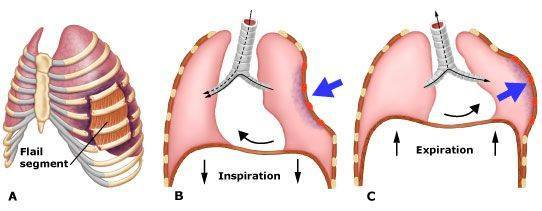
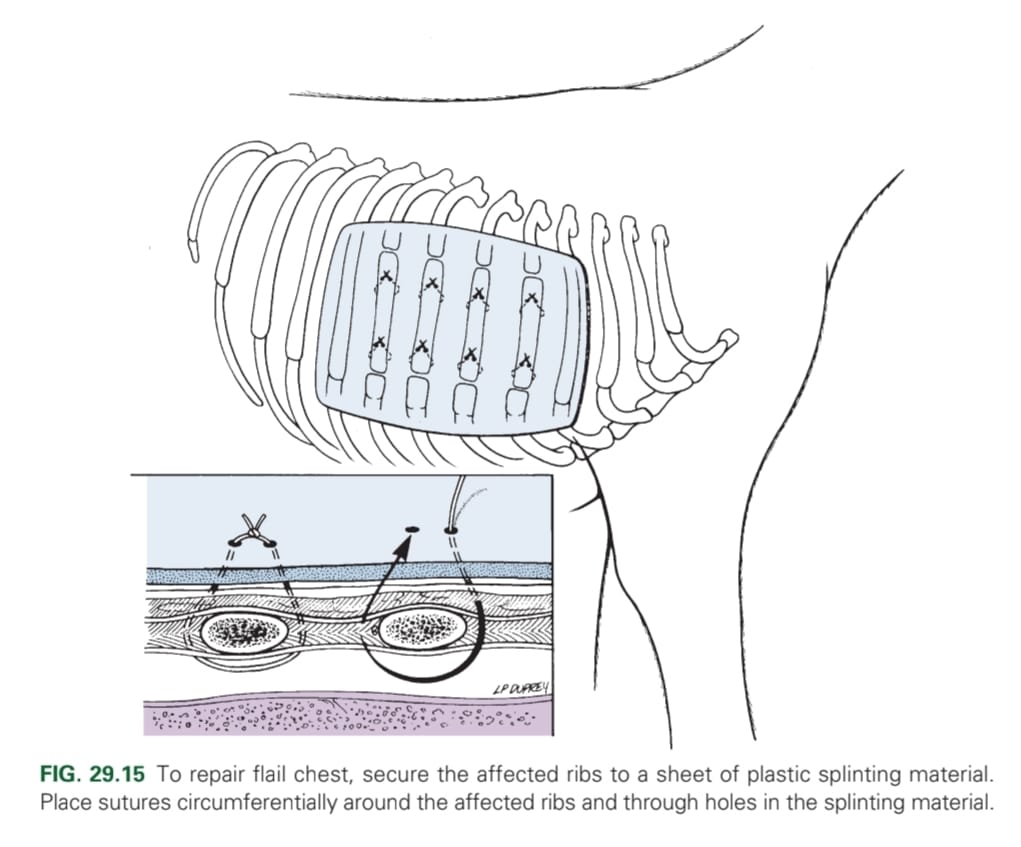
Multiple segmental rib fractures resulting in a free-floating segment of the thoracic wall → severe respiratory distress, pain & hypoventilation
What lab finding from a thoracocentesis suggests internal bleeding?
> 5 g/dl protein
What is the radiological finding of pneumothorax?
Heart is elevated from the sternum
Stabilisation (fluids, oxygen, compress bleeding, cover wounds), thoracocentesis, blood transfusion, analgesia (fentanyl, buprenorphine)
Debridement
Rib fracture repair (pins, cerclage wire)
Flail chest stabilisation (external splints for 4 weeks; fastened with percutaneous sutures and aluminium frame)
What is a crucial initial step before further clinical exam if pneumothorax is suspected?
One-way valve effect trapping air in the pleural space → decreases ventilation and venous return → a life-threatening emergency
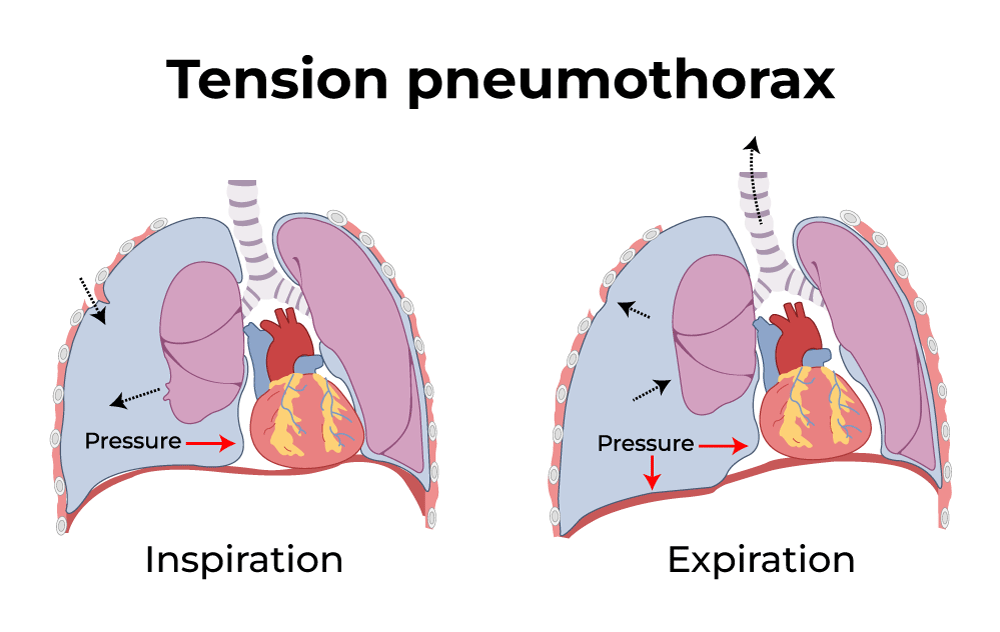
What is the result of pneumothorax?
Compromise intrapleural pressure → partial lung collapse → low tidal volume → hypoxia, hypercapnia & CV compromise
Respiratory distress, shallow, rapid breathing, cyanosis, tachycardia, dull/absent lung sounds
What are differential diagnoses of lung neoplasia?
Pneumonia, bronchitis, brochiectasis, pulmonary fibrosis, congestive heart failure
What are examples of surgical procedures of the thorax?
Lobectomy
Thoracic drainage/thoracostomy tube
Thoracocentesis
(Thoracotomy)
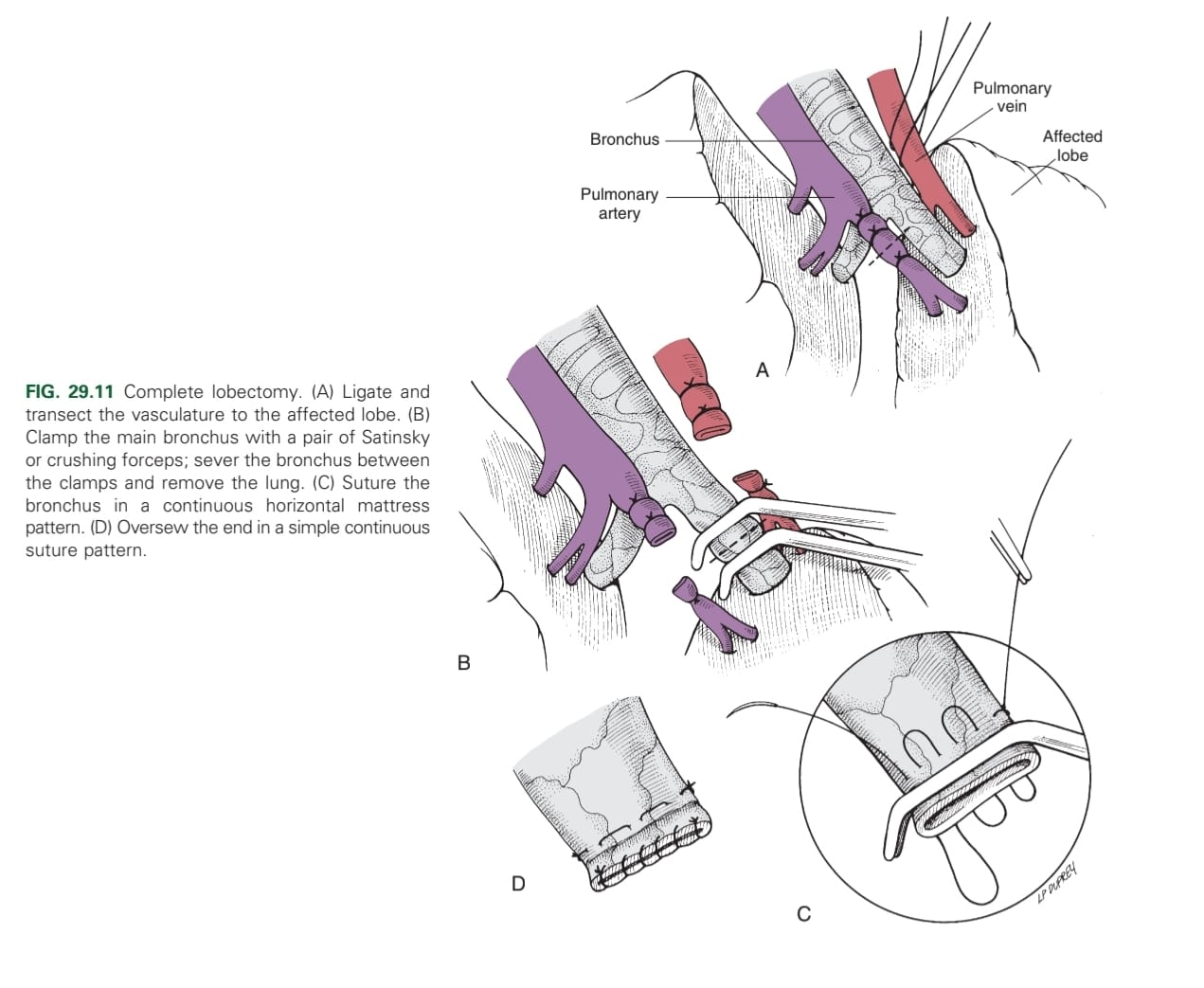
Surgical removal of a whole or part of a lung lobe via intercostal thoracotomy or median thoracotomy
1. Clamp it: place two crushing forceps proximal to lesion
2. Suture it: Place continuous, overlapping suture pattern proximal to each forceps
3. Cut it: between the clamp and suture.
4. Over-sew the lung in a simple continuous pattern
1. Ligate & transect the vasculature to the affected lobe
2. Clamp the main bronchus with crushing forceps
3. Sever the bronchus between the clamps & remove the lung
4. Suture the bronchus in a continuous horizontal pattern
5. Over-sew the bronchus end in a simple continuous pattern
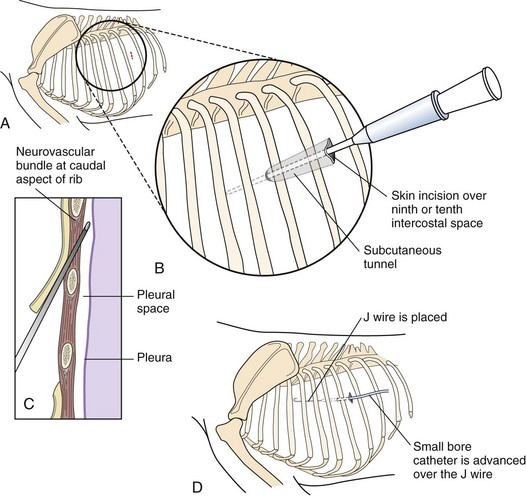
Allows intermittent or continuous pleural drainage
What is the procedure for putting in a thoracostomy tube?
Intercostal nerve blocks at 7th-9th ICS
Skin incision in 9th/10th ICS
Make subcutaneous tunnel from 10th to 8th ICS, inserting tube through 8th ICS towards opposite shoulder
Suture drain to skin with Chinese finger trap
When is thoracocentesis indicated?
Should be performed on any animal that has evidence of pleural effusion on physical examination or thoracic radiograph
What is the procedure for a thoracocentesis?
Insert needle at cranial portion of rib (avoids vessels and nerves at the caudal portion), just below the rib-cartilage junction. More dorsally if pneumothorax, more ventrally if fluid is suspected in pleural space.
Advance needle in 45 degree angle, downwards, parallel to body wall (avoids stabbing the lung)
While entering the body, have a small amount of negative pressure in the syringe as the needle passes the thoracic wall – when in pleural space sucks in the air in the syringe and you know that you are in the right place (the pleural cavity).
Aspirate fluid/air. Stopcock allows for removal of fluid w/o possibility to let air get sucked into the cavity through the tube
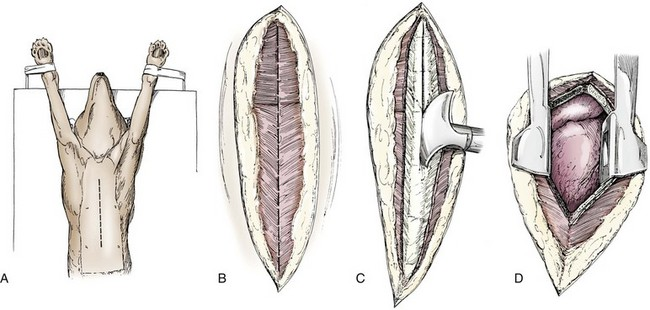
Transect sternebrae longitudinally on the midline with a sternal saw, chisel and osteotome, or bone cutters
Add drainage tube subcostal & lateral to midline before closure.
Closure: depend on animal size; close with wires or heavy sutures places around sternebrae
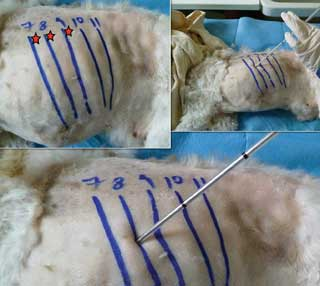
Cranial oesophagus (3rd-4th)
Heart (4th-5th)
Lungs (5th-6th)
Thoracocentesis (6th-8th)
Caudal oesophagus (7th-9th)
Thoracostomy tube (10th-12th)
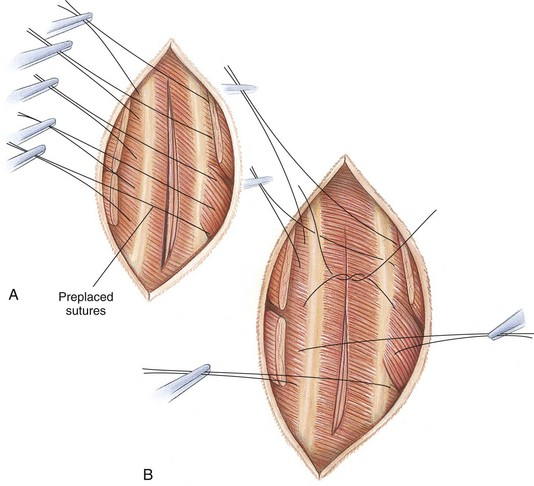
Preplace 4-8 sutures around two ribs either side of the incision, criss-cross arrangement for easy organisation of sutures, tied during inspiration. Start from centre suture.
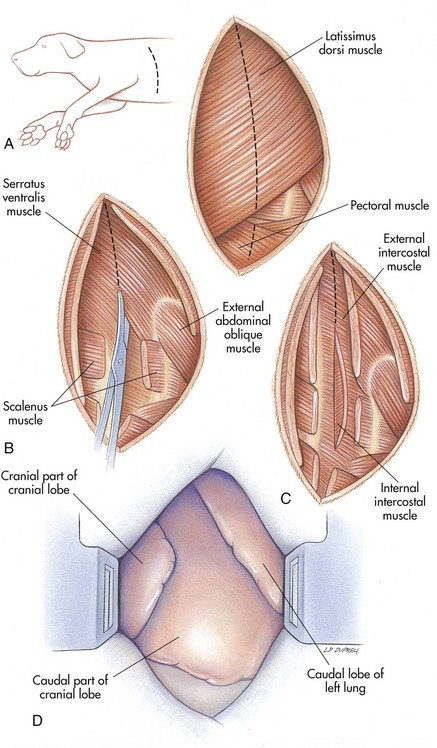
All except the intercostal muscles
What is the final step after closure of the chest cavity?
Thoracocentesis
Is a thoracotomy painful, and what should be given?
Yes, opioids.