VET 215 - Laboratory Animal Medicine: Rabbits
1/70
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards for VET 215 - Laboratory Animal Medicine: Rabbits
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
Scientific name for the domestic rabbit
Oryctolagus cuniculus
Order of rabbits
Lagomorpha
Most popular rabbit breed used in research
New Zealand White (NZW)
2nd popular rabbit breed used in research
Dutch
Californian
Large size
Meat production
White, colored nose, ears, tail, and feet
Large rabbit breed occasionally used for research
Flemish Giant
Common pet rabbit breeds
American chinchilla, Angora, Satin, Rex, Silver Martin, Dutch, American Checkered Giant, Polish, Lop, Lion head
Rabbits are commonly used in ophthalmic studies due to their well-studied _
Ocular morphology
rabbits are diurnal
and are most active during the day, particularly in the mornings and late afternoons.
Scientist who did most of his work with rabies using the rabbit
Louis Pasteur
What rabbits might do when frightened or hurt
Scream
How rabbits show aggression
Stomping feet & snorting
Housing
Temperature range: 62-70 deg F
Relative humidity: 30-70%
Air changes: 10-15/hr
Light: 12-14 hrs/day
What to clean excreta trays with
Acidic solution
Nutritional content of dry pelleted commercial feed for rabbits
15% protein, 10% crude fiber, 22.5% fiber diets used to reduce obesity and prevent hairball formation
80% of a rabbit's diet should be _.
Timothy or grass hay
Type of feeders attached to front of cage for rabbits
J-type hoppers
Daily food consumption of pelleted feed for rabbits
150 grams (50g/kg)
Water consumption for rabbits
~50-150mL/kg/day
Term for eating feces and conserves water, vitamins, nitrogen
Coprophagic
Body Temp of Rabbit
101-104° F
HR of Rabbit
180-250 bpm
RR of Rabbit
30-60 bpm
Part of anatomy used for thermoregulation
Ears
Bone makes up only ____ % of total body weight
8%
High muscle/bone ratio
Dental Formula of Rabbit
2 ( I 2/1, C 0/0, P 3/2, M 3/3) = 28 teeth in total.
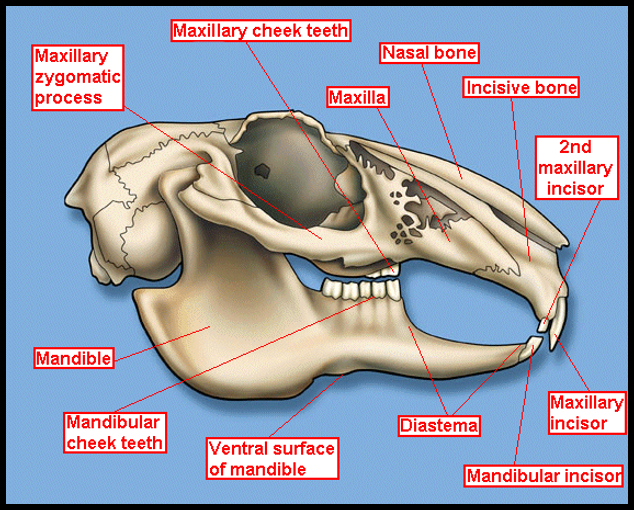
Additional pair of upper incisors in rabbits
Peg teeth
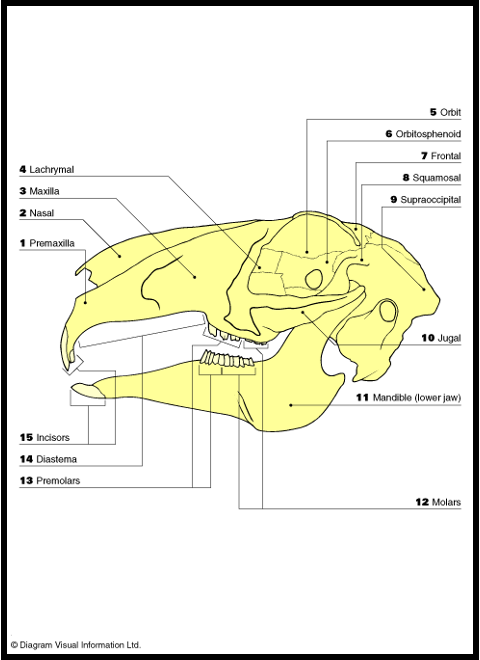
Space between incisors and premolars
Diastema
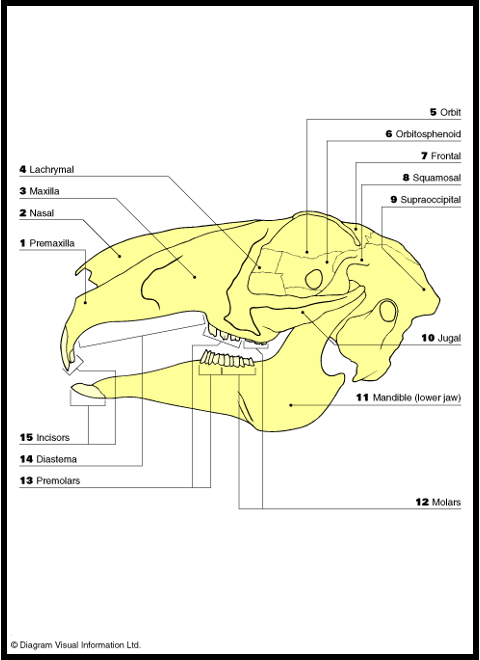
all teeth of rabbits are
“open rooted” (grow continuously)
Rabbits cannot _ like rats & horses
Cannot vomit
—The cardiac sphincter has enough tone that true vomiting is prevented
50% of lymphoid tissue in rabbit is in the ______
sacculus rotundus(end of ileum) & the appendix
Two types of feces produced
"hard pellets" and "cecotropes".
“night feces” or “soft feces”
Cecotrophs covered with mucin to protect them from acid pH of stomach usually ingested/swallowed directly from anus
Contain: high H2O content, digested bacteria (lacto bacillus is NOT common flora), nitrogen, electrolytes, volatile fatty acids(energy source) & B and K vitamins
Coprophagic
Female rabbits have a .
Double cervix
4-5 pairs of mammary glands
Only females have nipples
Mature females have prominent dewlap - females pluck hair from it to build nest
Male rabbits have open _ for life.
Inguinal canals
Age at which testes descend in male rabbits
12 weeks
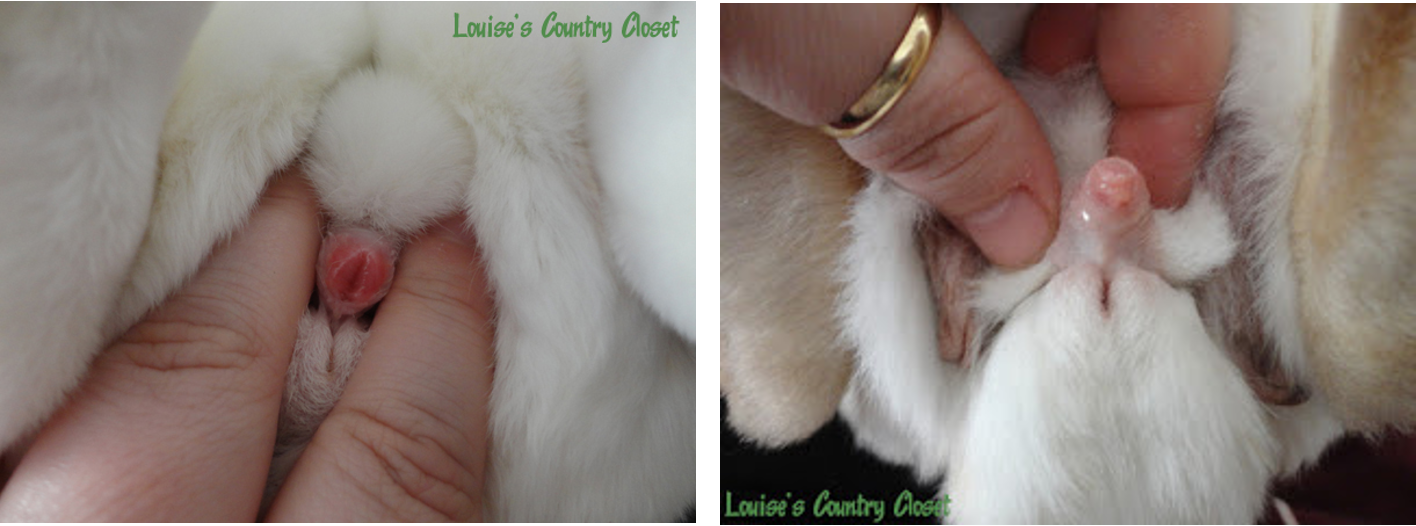
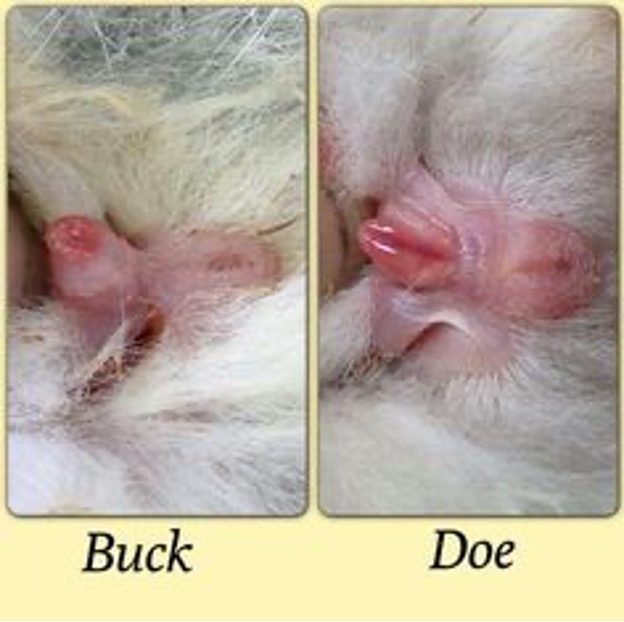
Sexing
Gently pressing skin back from genital opening:
Female has short slit like opening
Male has round opening; digital pressure will extrude the penis
Scrotal pouches in male
Female rabbits estrous cycle length _.
Induced ovulators
A male rabbit is called _.
Buck
A female rabbit is called _.
Doe
Baby rabbits are called _.
Kits
Parturition in rabbits is called _.
Kindling
Ovulation occurs ____hrs after mating
10 hrs
Kits are born
altricial
Ears open at _ days
8 days
Eyes open at _ days
10 days
Begin eating solid food at _ days
16-17 days
When handling rabbits, they can
Kick with hind limbs
Grip loose skin on back of neck; with the other hand
support their body weight or rear legs for better control.
Enzyme that hydrolyzes atropine and makes it unusable
Atropine esterase
Hypnosis
Place rabbit on its’ back and stroke the abdomen (doesn’t always work)
Blood Collection sites
Marginal ear vein
Auricular artery
Cephalic vein
Lateral saphenous
Jugular vein
Cardiac puncture (under anesthesia/terminal)
Total blood volume: 160 - 480 ml
Single sample: 20 - 40 ml
Exsanguination: 60 - 160 ml
New intubation technique that shaped to mirror the pharyngeal airway anatomical structures of rabbits and cats and prevent laryngeal and tracheal trauma
V -Gel
Lumbar in rabbits
is easily fractured
Rabbit urine
Turbid, thick or creamy due to calcium carbonate
pH > 8 alkaline urine
Pigmented
Yellow to orange or brown
Anesthesia routes
Injectable
Intranasal (not as common)
Inhalant
Caution when masking (struggle and injury)
Rabbits are known to hold their breath if not pre-medicated
Premedication allows for smoother induction
**pre-med avoids significant catecholamine release which can result in death during the procedure
Euthanasia in rabbits
Overdose of barbiturate or euthanizing agent IV/IP
Toxicology studies- anesthetize and exsanguinate
Most common post-op issue for rabbit
Hypothermia
Most common bacterial infection in rabbits
Pasteurellosis
Caused by Pasteurella multocida
Can spread to multiple locations causing a variety of disease syndromes
Lives in the upper respiratory tract
Most common form of disease in the respiratory tract
Snuffles
Caused by:
Pasteurella multocida sometimes have concurrent infection with
Bordetella brochiseptica
Transmission:
Direct contact, aerosol contamination
Clinical signs:
Sneezing, conjunctivitis, purulent discharge from nares(seen on forelimbs from wiping nose)
Other signs: multiple, large, creamy abscesses with otitis media or otitis interna causing a head tilt: torticollis (head tilt or wry neck)
Treatment:
Penicillin, chloramphenicol, enrofloxacin
Reinfection is common
Cull from herd
2nd most common health problem in rabbits
‒Enterotoxemia and Mucoid Enteropathy
Primary concern is in young rabbits 7-10 weeks old
Changes in feeding, weaning, antibiotic therapy, and concurrent infection are all stressors that allow colonization
Caused by: E. coli, Clostridium spiroforme, Clostridia perfringens, Clostridia difficile
Clinical signs: hunched posture, diarrhea, dehydration and death
Treatment: not usually successful often die within a week
Increase fiber in diet to protect against the disease, sometimes actobacillus can help normalize gut flora
*Antibiotics implicated in causing issues: Penicillin, erythromycin, clindamycin, lincomycin, streptomycin
*Safer antibiotics for use in rabbits: chloramphenicol, enrofloxacin, trimethoprim/sulfa, gentamicin, neomycin, vancomycin and metronidazole
Tyzzer’s Disease
Not common in lab rabbits
Caused by: Clostridium piliforme
Transmission: Shed in feces
Disease becomes apparent during stress, Overcrowding, Shipping, Poor ventilation, Improper nutrition
Clinical signs: Diarrhea, Dehydration, Anorexia, Death
TX: oxytetracycline
Tularemia
Francisella tularensis
“Rabbit fever”,
Rare in lab setting, primarily affects wild rabbits/hares
Transmission: direct contact, bite wound, inhalation, ingestion, arthropod vector
Causes sudden death
Zoonotic potential causes fever, lymphadenopathy and death in humans if not treated
Rabbit ear mite
Psoroptes cuniculi
Psoroptes cuniculi (rabbit ear mite)
Non-burrowing mite, feeds on epidermal skin of inner ear
Transmission: direct contact
Clinical signs: Dry crusty exudate on inner surface of ear, Head shaking and scratching of the ears
Diagnosis: otoscopic exam, or ear swab
TX: Ivermectin injections SQ; mineral oil or acaracides
Topical tx must be repeated every 2 or 3 days to kill newly hatched mites
Cuterebra
“Warbles”
Appear as lumps w/ holes
Usually found on the neck or upper extremities
TX: sx excision to remove larvae
Crushing the larvae may result in shock & death of the rabbit
Buphthalmia
Form of glaucoma
Common inherited disease of domestic rabbits especially New Zealand Whites
Hair Balls
Trichobezoars
Rabbits stop eating & drinking
Fail to pass feces, anorexia, weight loss
Caused by excessive self grooming (boredom)
Also suggested: deficiencies in copper, magnesium, some amino acids and fiber
Radiographs or palpation
L7-S1 common
Fracture or Luxation of lumbar spine
hip dysplasia
Splay leg
Slobbers
Moist Dermatitis
Sore hock or bumblefoot
Ulcerative Pododermatitis