Biology Unit 6 - Evolution
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Evolution
The process of biological change that makes descendants differ from their ancestors
The two types of evolution
Microevolution and Macroevolution
Microevolution
Evolution occurring on a small scale affecting a single population
Macroevolution
Evolution occurring on a large scale affecting changes in species across populations
What evolution is driven by
Natural selection
Natural selection
Organisms with better traits will survive and reproduce more
The 4 mechanisms of natural selection
Variation, overproduction, adaptation, and descent with modification
Variation
The differences in traits of organisms
Overproduction
Too much offspring for the environment, struggle for existence of resources
Adaptation
beneficial traits with higher chance for survival
Descent with modification
Change in gene frequency over time, organisms with better traits survive and inherit them to their offspring
The 3 mechanisms of microevolution
Genetic drift, gene flow, and sexual selection
Genetic drift
Random change in allele frequency over time
Gene flow
genes moving in and out of a population
The 7 mechanisms of macroevolution
Speciation, extinction, gradualism, punctuated equilibrium, divergent evolution (adaptive radiation), convergent evolution, and coevolution
Sexual selection
Choosing a specific other to mate with specific traits
Speciation
a new forming species from a pre-existing species
Extinction
a disappearance of a species
Gradualism
Slow change over a long period of time
Punctuated equilibrium
Change separated by bursts over a long time
Divergent evolution
Species sharing a common ancestor
Convergent evolution
Two unrelated species developing similar characteristics
Coevolution
Two organisms change in response to each other
Evidence of evolution
Anatomy, biogeography, embryology, paleontology and biochemistry
Anatomy
study of the structures of organisms
Biogeography
Where living things are located
Embryology
The study of organisms' embryos
Paleontology
The study of prehistoric life
Biochemistry
The study of chemical processes in an organism
Biochemistry helps create...
Phylogenetic trees
3 types of structures that provide evidence for anatomy
Homologous structures, analogous structures, and vestigial structures
Homologous structures and analogous structures result from...
Divergent evolution (adaptive radiation)
Analogous structures
Similar function, different structures, different ancestor
Vestigial structures
Structures that were useful to ancestors but not anymore to descendants
Homologous structures
Similar structure, same ancestor, different function
What do vestigial structures result from
Convergent evolution
Directional Selection
increases the abnormal trait in a population
(ex: darker moths survive more than lighter moths when they are able to blend in easier with tree bark = more dark color genes)
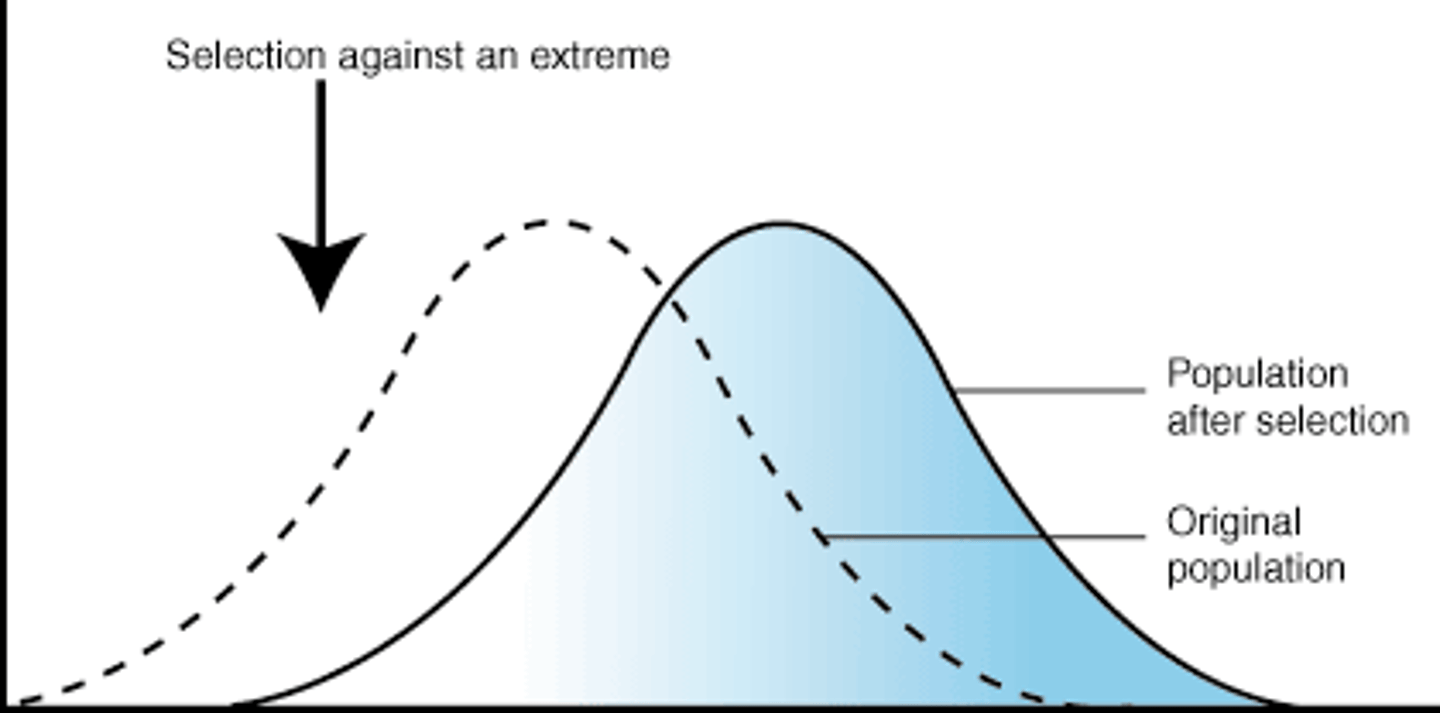
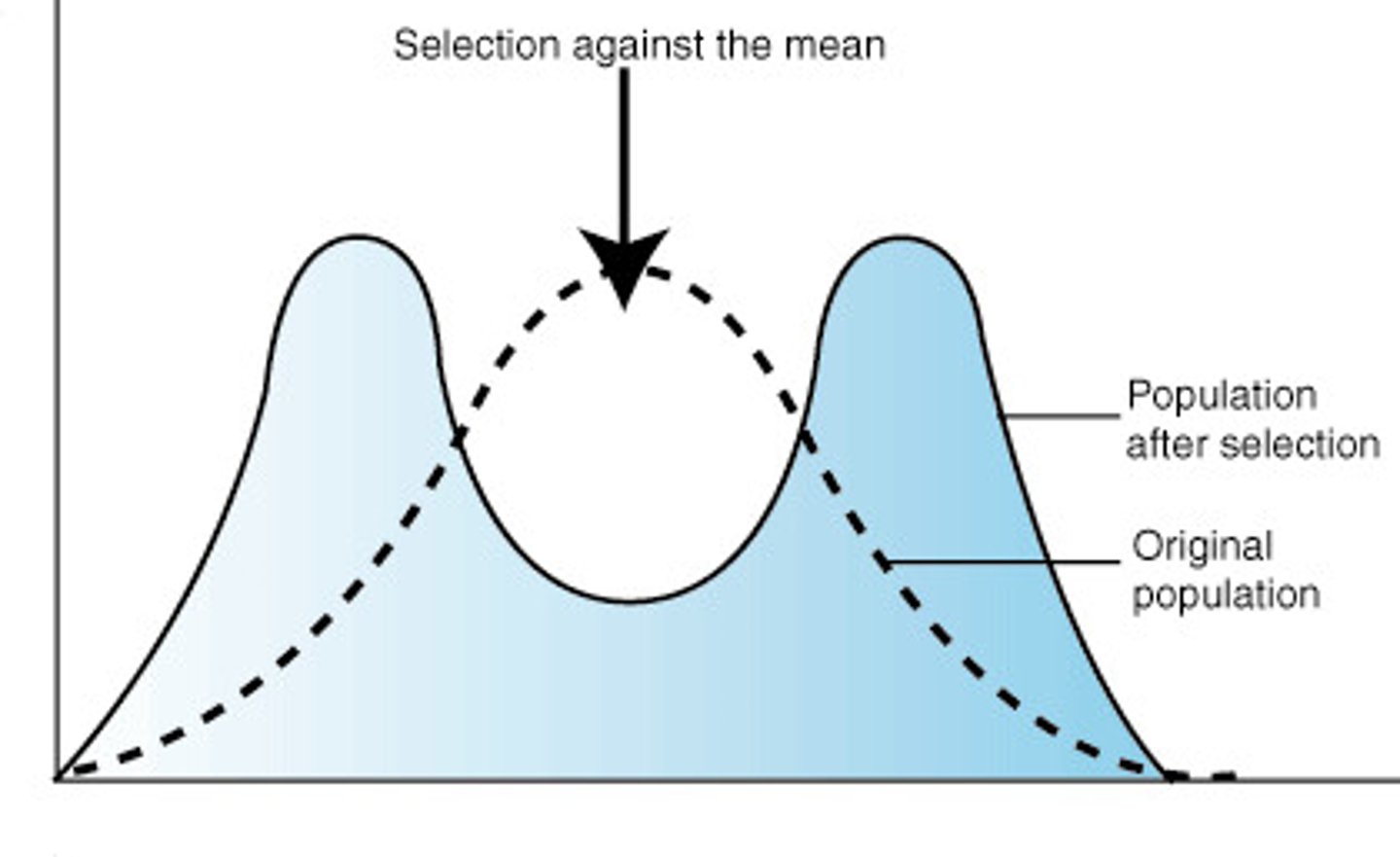
Disruptive Selection
removing average traits and favoring abnormal traits
(ex: gray snakes blend in with rocks, green snakes blend in with grass, normal colored snakes have a disadvantage because they are more visible to predators)
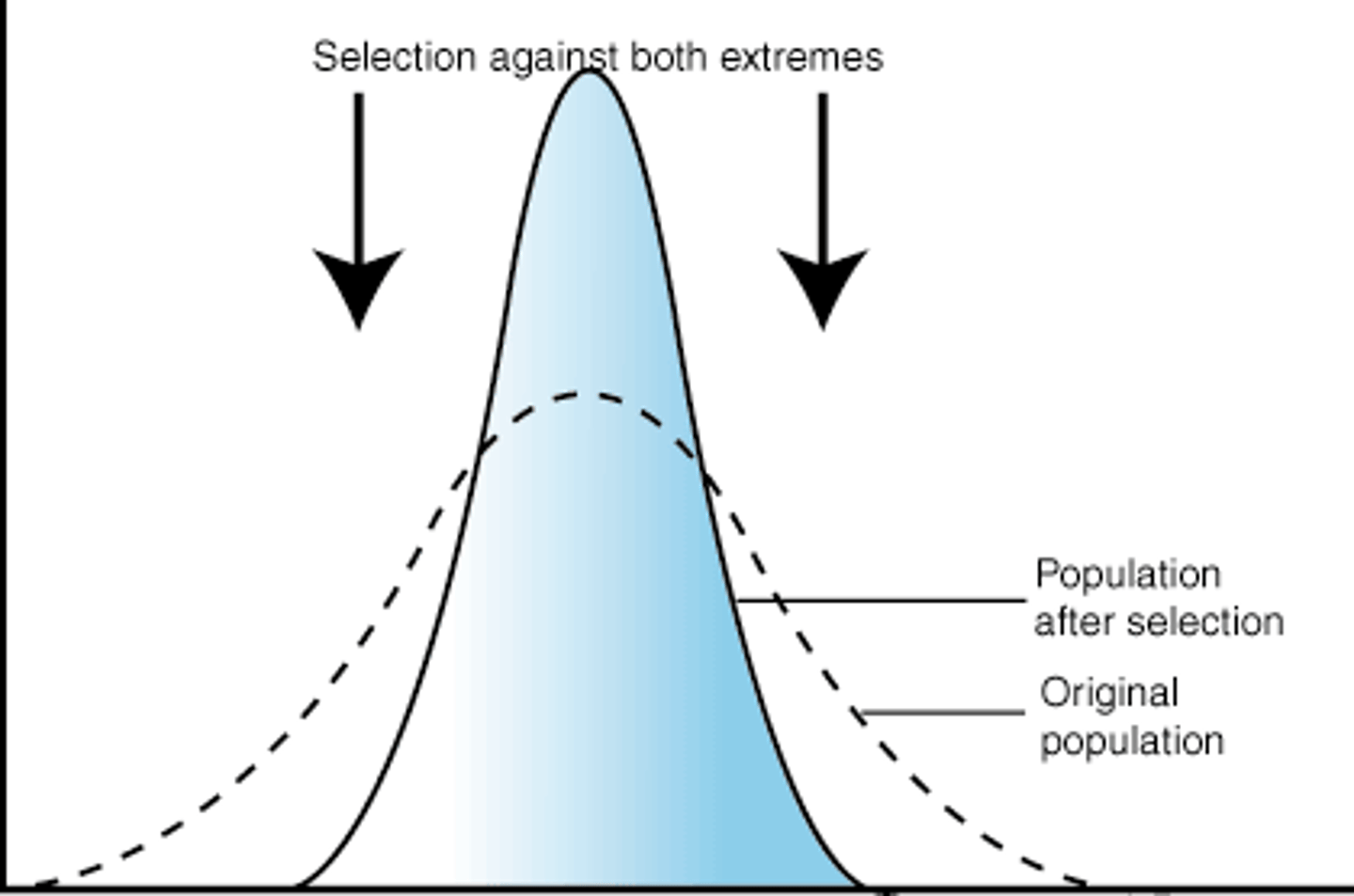
Stabilizing Selection
eliminating abnormal traits when the normal traits become more common
(ex: below-average and above-average baby weights have lower chances of survival than normal baby weights = little variation in birth weight)
Purpose of Hardy-Weinberg principle
Used to calculate allele frequencies for the dominant allele (p) and the recessive allele (q)
Formula to calculate the frequency of genotypes in a population
p² + 2pq + q² = 1
p² = homozygous dominant (AA)
2pq = heterozygous (Aa)
q² = homozygous recessive (aa)
Carolus Linnaeus
created binomial nomenclature
Charles Darwin
discovered the natural selection of evolution
Thomas Malthus
discovered the struggle for existence
Georges Cuvier
discovered catastrophism
James Hutton
discovered gradualism
Charles Lyell
discovered uniformitarianism, proposed Earth was more than thousands of years old
Jean Baptiste Lemark
discovered acquired trait inheritance
Aristotle
proposed organisms are perfectly adapted to the world and a Creator made everything
Gregor Mendel
created the concept of genetic