Concept 13.3: Meiosis reduces the number of chromosome sets from diploid to haploid
1/16
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Meiosis
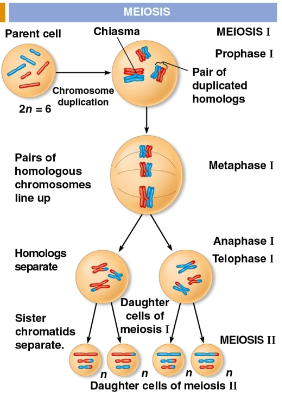
A method of cellular reproduction preceded by the replication of chromosomes, taking place in two stages
Results in four daughter cells with half as many chromosomes as the parent cell
Reduces the number of chromosome sets from two (diploid) to one (haploid), producing four genetically differing cells

Mitosis
A method of cellular reproduction that conserves the number of chromosome sets
Produces two cells genetically identical to the parent cell
Sister chromatid cohesion
The close association of sister chromatids as chromosomes duplicate before meiosis and sorting
Cohesins are cleaved at the end of metaphase in mitosis
Cohesins are cleaved along the chromosome arms in anaphase I (separation of homologs) and at the centromeres in anaphase II (separation of sister chromatids)

Cohesins
Proteins that hold together sister chromatids after interphase
Nonsister chromatids are broken at precisely matching points
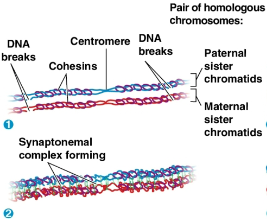
Synaptonemal complex
A zipper-like structure that holds the homologs together tightly in prophase I
Synapsis
Process where DNA breaks are repaired and DNA is joined from one nonsister chromatid to the corresponding segment of another
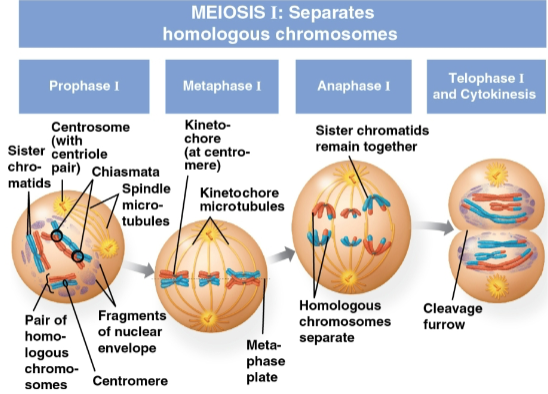
Meiosis I
The first stage of meiosis with four phases:
Prophase I
Metaphase I
Anaphase I
Telophase I and cytokinesis
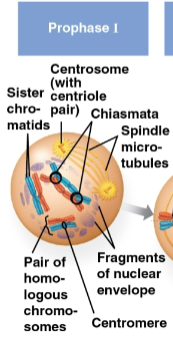
Prophase I
First stage of meiosis I where each chromosome pairs with its homolog and crossing over occurs at chiasmata
Crossing over occurs for each sister chromatid within each chromosome, resulting in genetic variation for all four
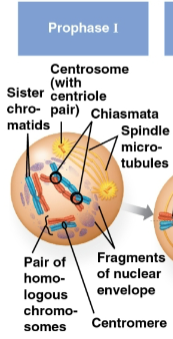
Chiasmata
X-shaped regions on chromosomes where crossovers occur
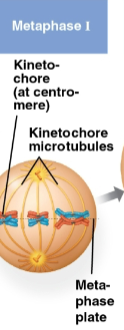
Metaphase I
Second stage of meiosis I where pairs of homologs line up at the metaphase plate, one chromosome facing each pole
Microtubules from the poles are attached to the kinetochore of each chromosome
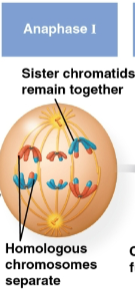
Anaphase I
Third stage of meiosis I where pairs of homologs separate as one chromosome of each pair moves towards opposite poles
Sister chromatids remain attached at the centromere and move as one unit toward the pole
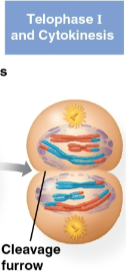
Telophase I
Fourth and last stage of meiosis I where each half of the cell has a haploid set of duplicated chromosomes
Each chromosome still consists of two sister chromatids
Cytokinesis occurs simultaneously with this, forming two haploid daughter cells with either a cleavage furrow or cell plate forming
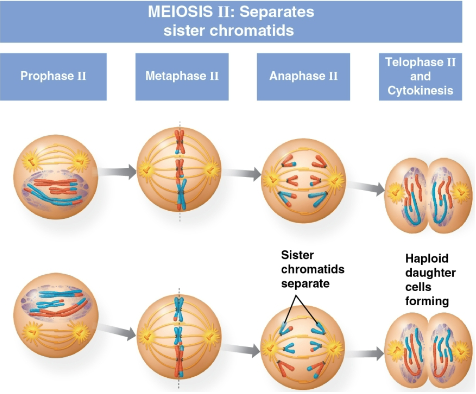
Meiosis II
The second stage of meiosis with four phases:
Prophase II
Metaphase II
Anaphase II
Telophase II and cytokinesis
Is very similar to mitosis
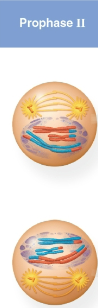
Prophase II
First stage of meiosis II where a spindle apparatus forms
Chromatid pairs move toward the metaphase plate later in this stage

Metaphase II
Second stage of meiosis II where the sister chromatids are arranged at the metaphase plate
Crossing over in meiosis I means the two sister chromatids are no longer genetically identical
Kinetochores attach to microtubules extending from opposite poles

Anaphase II
Third state of meiosis II where the sister chromatids separate
Each sister chromatid now moves as two newly individual chromosomes toward opposite poles

Telophase II
Fourth and last stage of meiosis II where the chromosomes arrive at opposite poles
Cytokinesis occurs shortly after as nuclei form and chromosomes decondense