Bonding and structure
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/32
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
1
New cards
Define ionic bonding
Electrostatic attraction between two oppositely charged ions
2
New cards
Describe the effects that ionic radius and ionic charge have on the strength of ionic bonding
The shorter the distance between oppositely charged ions and the higher the charges, the stronger the electrostatic forces between them.
3
New cards
How are ions formed
Positive ions from through the loss of electrons and negative ions form through the gain of electrons
4
New cards
Describe the trend of ionic radii down the groups
The radii increases as there are more shells
5
New cards
Describe the trend of ionic radii with isoelectronic ions
The greater the number of protons the smaller the atomic radii as the electrons are pulled more closely to the nucleus
6
New cards
Describe the evidence for the existence of ions
This is shown through x-ray diffraction as the electron density maps show the likelihood of finding electrons in a region
7
New cards
Define covalent bond
Strong electrostatic attraction between two nuclei and the shared pair of electrons between them
8
New cards
Describe the relationship between bond length and strength
Generally, the shorter the bond, the stronger it is
9
New cards
How is the shape of a simple molecule determined?
This occurs by electron pair repulsion
10
New cards
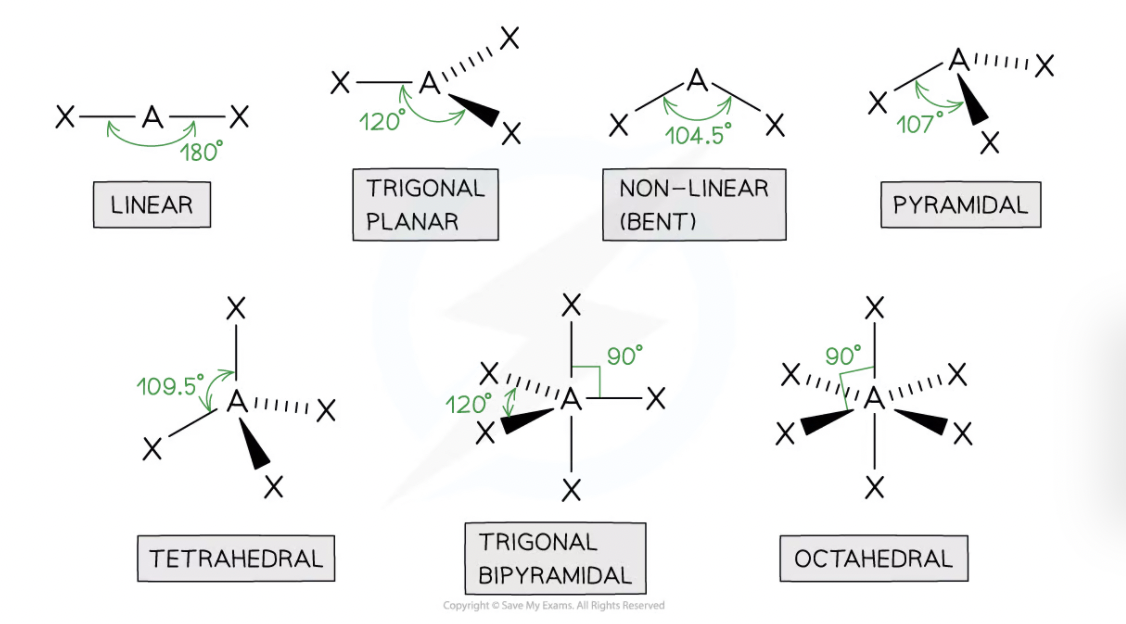
State the main shapes of molecules and their angles
Little - 180°
TurniPs - 120°
Never - 104.5°
Punch - 107°
Tiny - 109.5°
TriBes - 90° and 120°
Over - 90°
TurniPs - 120°
Never - 104.5°
Punch - 107°
Tiny - 109.5°
TriBes - 90° and 120°
Over - 90°
11
New cards
How do lone pairs affect bond angles
Each lone pair will reduce the bond angle by 2.5°
12
New cards
Define elctronegativity
The ability of an atom to attract the bonding electrons in a covalent bond
13
New cards
State the ranges of the electronegativity scale and the bonding it corresponds to
0 - 0.4 = non-polar covalent
0\.4 - 1.7 = polar covalent (permanent dipole)
1\.7 - 4 = ionic bond
0\.4 - 1.7 = polar covalent (permanent dipole)
1\.7 - 4 = ionic bond
14
New cards
When will molecules be non polar
When they have an electronegativity between 0 and 0.4 and are symmetrical
15
New cards
Describe London forces
\
forces
forces
16
New cards
Describe permanent dipole forces
1\. Occurs between polar molecules
2\. It is stronger than London forces, so have higher b.p
3\. They occur in asymmetrical molecules and have a bond with significant difference in electronegativity
2\. It is stronger than London forces, so have higher b.p
3\. They occur in asymmetrical molecules and have a bond with significant difference in electronegativity
17
New cards
Describe hydrogen bonding
1\. Occurs with an H and a N/O/F which are the most electronegative and have a lone pair of electrons
2\. There is a 180° between two molecules bonded by hydrogen bonds
3\. Occurs in addition to London forces
2\. There is a 180° between two molecules bonded by hydrogen bonds
3\. Occurs in addition to London forces
18
New cards
Describe H2O, NH3 and HF in terms of their hydrogen bonds
1
19
New cards
Explain the two anomalous properties of water
1\. High m.p and b.p- have both London (dipole-dipole) and hydrogen bonds
2\. Ice has a lower density that water- when the hydrogen bonds are broken as the **ice** melts, the **water** molecules get closer together
2\. Ice has a lower density that water- when the hydrogen bonds are broken as the **ice** melts, the **water** molecules get closer together
20
New cards
Explain the trends in boiling temperatures of the hydrogen halides
HF → HI → HBR → HCl
This is due to the increasing electronegativity, meaning that HF can form hydrogen bonds while the others can’t
This is due to the increasing electronegativity, meaning that HF can form hydrogen bonds while the others can’t
21
New cards
Where are giant lattices present
1\. Ionic solids (giant ionic lattices)
2\. Covalently bonded solids (giant covalent lattices)
3\. Solid metals (giant metallic lattices)
2\. Covalently bonded solids (giant covalent lattices)
3\. Solid metals (giant metallic lattices)
22
New cards
What is the structure of iodine and water
They are simple molecular
23
New cards
Describe the structure of graphite
1\. It is macromolecular
2\. 3 covalent bonds per atom
3\. Delocalised electrons between layers
2\. 3 covalent bonds per atom
3\. Delocalised electrons between layers
24
New cards
Describe the structure of diamonds
1\. Macromolecular
2\. Tetrahedral structure
3\. 4 covalent bonds per atom
2\. Tetrahedral structure
3\. 4 covalent bonds per atom
25
New cards
Describe the structure of graphene
1\. One layer of graphite
2\. 3 covalent bonds per atom
2\. 3 covalent bonds per atom
26
New cards
Define enthalpy change of formation
Enthalpy change when 1 mole of ==substance== is formed from its ==constituent elements== in their standard states under standard conditions
27
New cards
Define 1st ionisation energies
Heat energy required to %%remove 1 mole of electrons%% from 1 mole of gaseous atoms to form 1 mole of %%gaseous +1 ions%%
28
New cards
Define 2nd ionisation energies
Heat energy required to %%remove 1 mole of electrons%% from 1 mole of gaseous +1 ions to form 1 mole of %%gaseous +2 ions%%
29
New cards
Define lattice formation energy
The enthalpy change when one mole of an @@ionic lattice@@ is formed from its @@isolated gaseous ions@@
30
New cards
Define enthalpy of atomisation
The enthalpy change when one mole of atoms is formed from its its element in its standard state under standard conditions
31
New cards
Define 1st electron affinity
The enthalpy change when one mole of gaseous atoms ^^acquires one mole of electrons^^ to form one mole of gaseous negative ions (^^EXO^^)
32
New cards
Define 2nd electron affinity
The enthalpy change when one mole of gaseous negative ions ^^acquires one mole of electrons^^ to form one mole of gaseous ^^2- ions^^ (^^ENDO^^)
33
New cards
State the steps of the Born-Haber process
1\. Atomise metal
2\. Ionise metal
3\. Atomise non metal
4\. Electron affinitise non metal
5\. Lattice
f==At== @@Ion@@ At %%E%%a^^L^^ing
2\. Ionise metal
3\. Atomise non metal
4\. Electron affinitise non metal
5\. Lattice
f==At== @@Ion@@ At %%E%%a^^L^^ing