Cog: Problem-Solving & Creativity
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Problem
When there is an obstacle btwn a present state & goal
What do problems need?
Problem needs to be identified before they can be solved.
Well-defined probs are easy to identify and solve
Ill-defined probs are hard to identify and solve
Problem Representation
The way a problem is translated/represented in our mind
T or F: a problem may be represented to us in the same way
True.
We may represent problems differently, resulting in different approaches to solve the problem
Problem Reconstructing
Process of changing a problems representation
Problem can be solved by changing how it is represented
Insight
Sudden realization of a solution to a problem
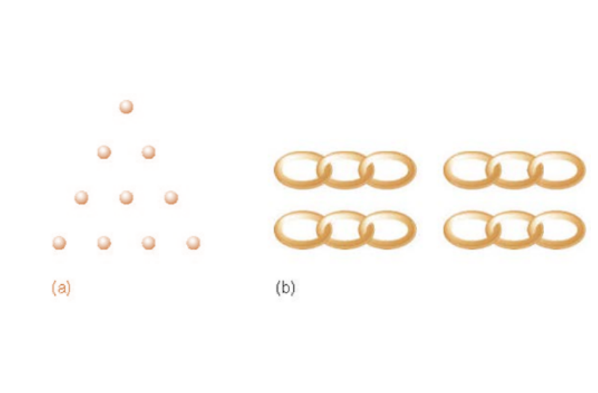
Is this an example of a insight or non-insight problem?
Insight problem
a non-insight problem is more numerical Ex. (1/5)x+10=25
Functional Fixedness
Tendency to focus on similar functions or uses of objects
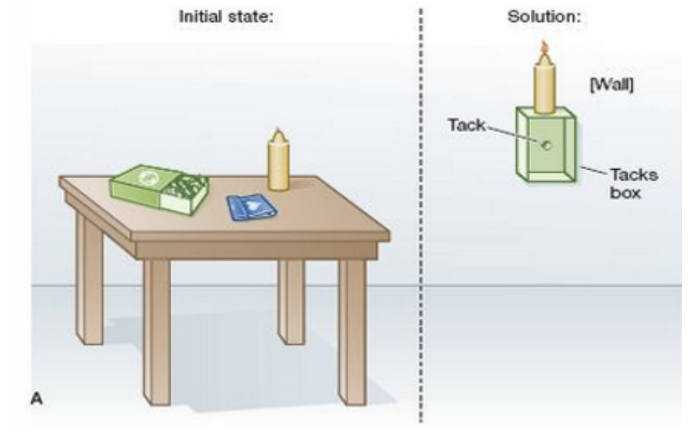
What is the solution to the candle problem?
The solution requires thinking of the match box as a platform, not a container
When is it easier to overcome functional fixedness?
It is easier to overcome functional fixedness when tasks are presented outside the box
Mental Set
Preconceived notion about how to approach a problem
What do prior examples inhibit in a mental set?
Prior examples can establish a mental set that inhibits participants from using simpler solutions later on
Information Processing Approach
Problem solving is a search between the posing of a problem and its solution
Initial State
Conditions at the beginning of a problem
Intermediate State
Conditions after each step is made toward solving a problem
Goal State
Solution to the problem
Problem Space
All possible states that can occur when solving a problem
Operators
Actions that take the problem from 1 state to another
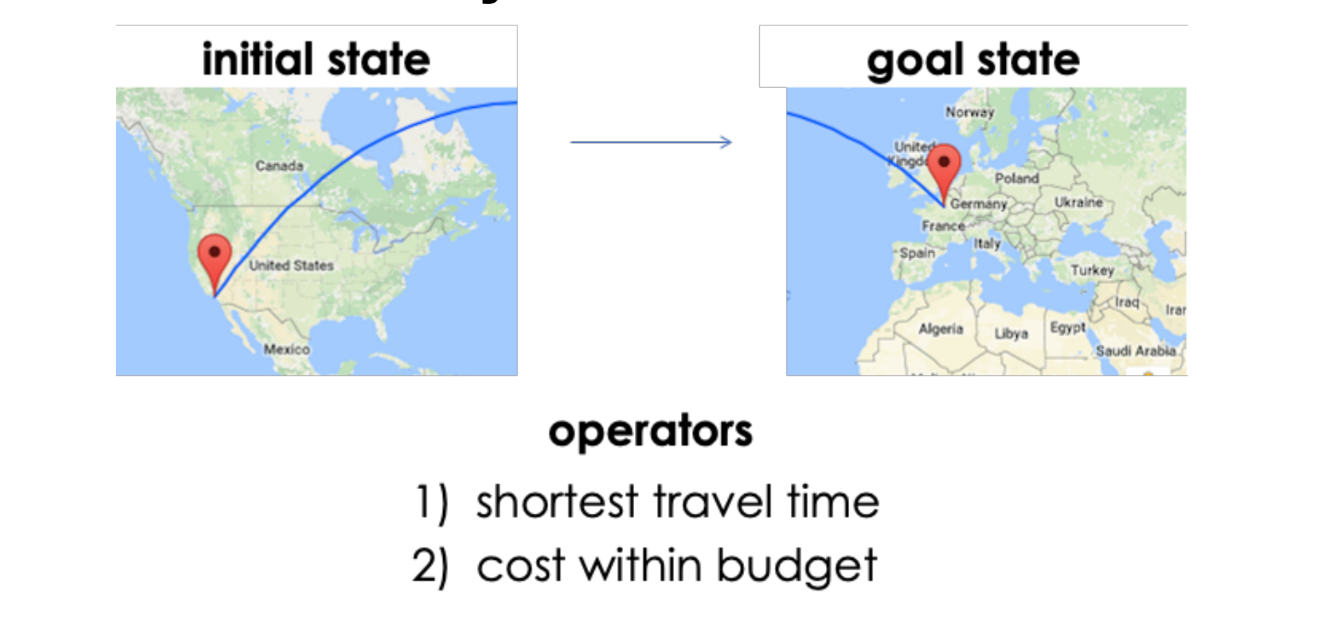
Means End Analysis
Reduce the differences btwn the initial and goals states by creating sub-goals
Analogical Problem Solving
Attempting to solve a problem using the solution to a similar problem
Ex. The Russian Marriage problem can be used to solve the mutilated checkerboard problem
Analogical Transfer
Experience solving 1 problem is transferred to another problem
Target Problem
Problem you’re trying to solve
Source Problem
Another problem that’s similar to & may illustrate a way to solve the target problem
What does analogical transfer require you to do?
Notice, map, and apply the analogy
Analogical Paradox
It can be difficult to apple analogues in the lab, but we routinely use analogies in real world settings
Expert
Someone who is knowledgeable or skilled in a particular field
T or F: Experts solve problem in their field more quickly & often than beginners
True
Experts possess more knowledge about their field
Experts organize their knowledge differently than novices
Creativity
The use of imagination or original ideas
Creative problem-solving is a process
Divergent Thinking
Thinking that is open-minded & involves a large number of potential “solutions”
Creative Cognition
Technique to train ppl to think creatively
Daydreaming
Purposeful mind-wandering
Solitude
Avoiding distractions; giving the mind space and time to make new connections and find meaning
Mindfulness
Pay attention to what is happening in our mind and in environment