BIOL 2160 Exam 5
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
The KIDNEY is primarily responsible for maintaining stability of _________________ volume, ________________ composition, and _________________.
It is also the main route for eliminating potentially toxic _____________________ and _____________ compounds from the body
ECF; Electrolyte; Osmolarity
Metabolic wastes; Foreign
Functions of the KIDNEY:
Maintain _______ balance in the body
Maintain proper _______________ of body fluids (BLOOD), primarily through regulating ______ balance
Regulate the quantity and concentration of most _______ ions
Maintain proper __________ volume
Help maintain proper ___________ balance in the body
Excreting (eliminating) the ______ products (wastes) of bodily metabolism
H2O
Osmolarity; H2O
ECF
Plasma
Acid-base
End
The URINARY system consists of urine forming organs like the ___________.
It also contains structures that carry urine from the kidneys to the outside for _____________ from the body like the ______________, ___________________ and __________________.
Kidney
Elimination
Ureters, urinary bladder and urethra
Ureters have a ____________ muscle-walled duct. They exit each __________ and carry urine to the ____________________.
Smooth; Kidney; Urinary Bladder
The urinary bladder temporarily stores __________. It has a hollow, distensible, ___________ muscle-walled sac. It periodically empties to the outside of the body through the ___________.
Urine; Smooth; Urethra
The urethra conveys __________ to the outside of the body.
What is it straight and short in? What is it much longer and curvy in?
The urethra has DUAL FUNCTION. What are the two functions?
Urine
Females; Males
1. Provides route for urine to leave the bladder
2. Passageway for semen from reproductive organs
The nephron has a ____________ component, ________________ component and a ___________________________ component.
Vascular, Tubular and Combined Vasculartubular
Which two processes involve trans-epithelial support?
Secretion and re-absorption
Vascular component basically means blood.
The dominant part of the vascular component of a nephron is the _______________. It is basically a ball of _______________. Water and solutes are filtered through it as _________ passes through it. It also filters a ________________ plasma into the tubular component
Glomerulus
Capillaries
Blood
Protein-free
VASCULAR COMPONENT OF A NEPHRON
Glomerulus
Afferent Arteriole - carries blood __________ the GLOMERULUS
Efferent Arteriole - carries blood ___________ the GLOMERULUS
Peritubular capillaries - supply the _________ tissue; involved in exchanges with the fluid in the tubular _________
To
Away From
Renal
Lumen
TUBULAR COMPONENT OF THE NEPHRON
Bowman's Capsule - collects the glomerular _________________
Proximal Tubule - uncontrolled _________________ and ___________ of selected substances occur here
Loop of Henle - establishes an _______________ gradient in the renal ___________ that is important in the kidney's ability to produce ___________ of varying concentration
Distal Tubule and Collecting Duct - variable, controlled reabsorption of ____ and _____ and secretion of _____ and _____ occur here; leaving the collecting duct is _________, which enters the renal ___________
Filtrate
Reabsorption and secretion
Osmotic; Medulla; Urine
Reabsorption of Na+ and H2O; Secretion of K+ and H+
Leaving duct is Urine; Renal pelvis
What is part of the combine vasculartublar component? What does it produce?
The juxtaglomerular apparatus produces substances involved in the control of kidney function.
Which component has a HOLLOW, FLUID-filled tube formed by a SINGLE layer of EPITHELIAL cells?
What does the single layer indicate?
Tubular component
Exchange happens here
Explain the four basic renal processes.
What results from these four processes?
1. Glomerular filtration - nondiscriminant filtration of a protein-free plasma from the glomerulus into the Bowman's capsule
2. Tubular reabsorption - selective movement of filtered substances from the tubular lumen to the peritubular capillaries
3. Tubular secretion - selective movement of non filtered substances from the peritubular capillaries to the tubular lumen
4. Concentration
Urine
________ % of the plasma that enters the glomerulus is filtered.
The ______% that is not filtered leaves through the ___________ arteriole.
20
80; efferent
Reabsorption is __________ to ____________.
Secretion is __________ to ____________.
Urine to blood
Blood to urine
In GLOMERULAR FILTRATION,
Fluid filtered from the glomerulus into Bowman's capsule pass through ________ layers of the glomerular membrane.
During this step, almost everything that CAN be removed from the blood _____________. __________, which will become urine, is formed in this process.
Three
Is removed
Filtrate
TUBULAR REABSORPTION is a highly ________ and ________ process. It involves _______________ transport, or transport across the epithelial cells.
Selective and variable
Trans-epithelial
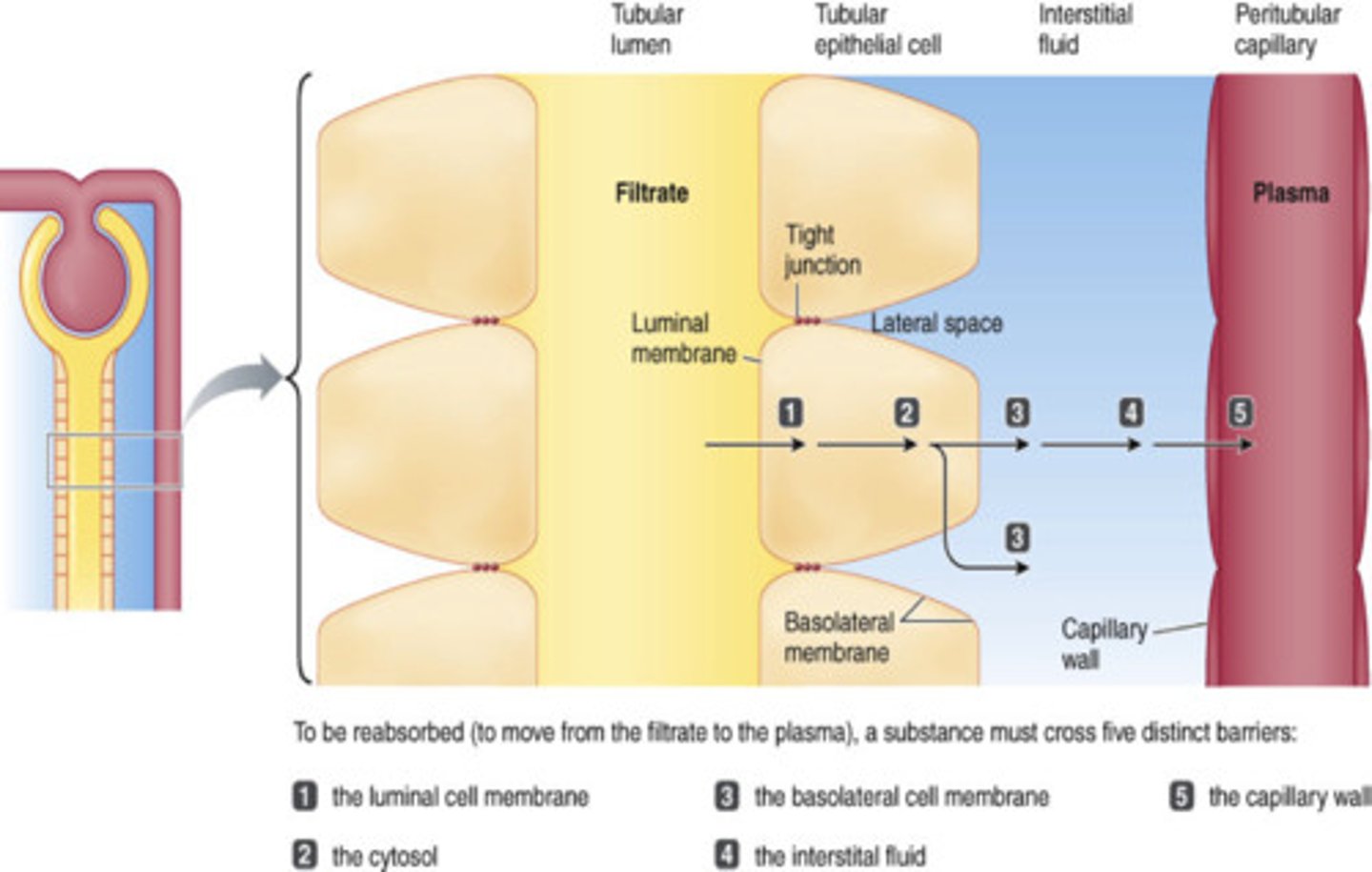
Reabsorbed substances must cross 5 barriers in tubular reabsorption.
The 5 steps are:
1. Must leave __________ fluid by crossing ___________ membrane of tubular cell
2. Must pass through _____________ from one side of tubular cell to the other
3. Must cross ______________ membrane of the tubular cell to enter ______________ fluid
4. Must diffuse through interstitial fluid
5. Must penetrate ____________ wall to enter __________ plasma
What do the tight junctions connecting the epithelial cells do?
Tubular; Luminal
Cytosol
Basolateral; Interstitial
Capillary; Blood
Make the membrane water-proof
_________ reabsorption can be an active or passive process? When is it passive? Active?
Tubular
Passive reabsorption
- No energy is required for the substance's net movement
- Moves down electrochemical or osmotic gradients
Active reabsorption
- Occurs if ANY ONE of the steps in transepithelial transport of a substance requires energy
-Movement occurs against electrochemical gradient
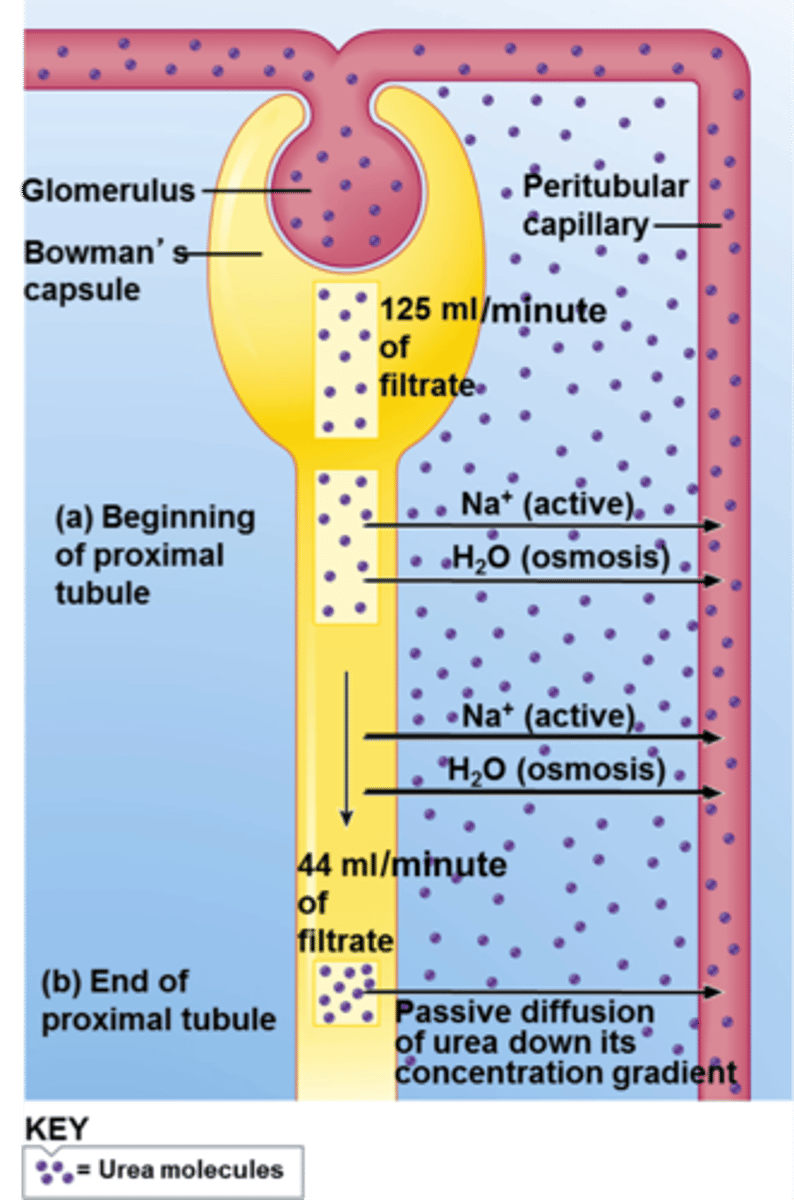
A Na+-K+ ATPase pump in ___________ membrane is essential for ____ reabsorption
Of total energy spent by kidneys, ____% is used for Na+ transport
Na+ is NOT reabsorbed (urine to blood) in the __________ limb of the loop of Henle
Water follows reabsorbed sodium by _________ which affects blood ___________ and blood ____________
Basolateral; Na+
80
Descending
Osmosis; Blood volume and blood pressure
67% of Na+ that is reabsorbed happens where? 25% where? 8% where?
Proximal tubule
Ascending limb of the loop of Henle
Distal and collecting tubules
Plays role in reabsorbing glucose, amino acids, H2O, Cl-, and urea
Proximal Tubule
Plays critical role in kidneys' ability to produce urine of varying concentrations
Ascending loop of Henle
Variable and subject to hormonal control; plays role in regulating ECF volume
Distal and collecting tubules
For sodium reabsorption, sodium going from lumen to tubular cell is _______ transport. From tubular cell to interstitial fluid is ________. From interstitial fluid to peritubular capillary is ______________.
The ATP used in the active process puts ______ into the tubular cell.
Passive; Active; Passive
K+
Urea is a __________ product.
Waste
Tubular SECRETION is that process reversed?
Tubular reabsorption
Kidney tubules can selectively add some substances to the filtrate.
In TUBULAR SECRETION, can kidney tubules selectively add some substances to the filtrate? If so, what are they?
The most important substances secreted into the tubules are?
Yes; things we have too much of
H+, K+ and organic ions
H+ is a substance important in tubular secretion.
It is important in regulating __________ balance.
It is secreted in which tubules?
Acid-base
Proximal, distal, and collecting tubules
K+ is a substance important in tubular secretion. It keeps plasma K+ concentration at appropriate level to maintain normal membrane excitability in ___________ and __________.
K+ is secreted only in which tubules?
Muscles and nerves
Distal and collecting tubules
Where are organic ions secreted?
ONLY in the proximal tubule
Is the reabsorption of sodium passive or active?
Secondary active transport
The loop of Henle is all about __________ of urine.
Descending limb is highly permeable to ______, but not to _______. As filtrate flows down, __________ leaves the tubule as the osmolarity of the _________________ increases. Loss of water increases the osmolarity of the filtrate. At the bottom of the loop, the concentration of the filtrate and the extracellular fluid is _______ (_____ mOsm).
Water, not sodium (NaCl)
Water leaves, ECF osmolarity increases
Equal (1200)
Very concentrated at bottom
The loop of Henle is all about concentration of urine.
Ascending limb is impermeable to ________, but permeable to ________. As highly concentrated filtrate flows up, NaCl _________, then is __________ transported out of the tubule. Water ___________ follow. Filtrate becomes more _________ than extracellular fluid.
Sodium (NaCl), not water
Diffuses, then actively transported out
Does not
Dilute
Very dilute at the top
Vasopresin/ ADH tells the body to ________ water.
65 percent of water re-absorption has to happen in the ___________ tubule. In the distal tubule and collecting duct it is variable, based on ____________________.
Conserve
Proximal
Secretion of ADH
Secreting vasopressin increases the permeability of the tubule cells in the distal tubule and collecting duct to water by inserting _____________.
Is the osmotic gradient for transport of water inside or outside the tubules?
Aquaporins
Outside
Where is vasopressin produced and where is it stored?
When is more of it secreted?
The release of vasopressin tells the distal tubule to _________ water.
Having excess water does what to vasopressin?
Hypothalamus; Posterior pituitary
During a water deficit
Reabsorb
Leads to less secretion of it. Mean more water in distal tubule which leads to more urination.
Alcohol _________ vasopressin. Therefore urination occurs ____________.
Inhibits; more frequently
For every ______ mLs of alcohol consumed, your body eliminates about ________ mLs of water in your urine.
This quickly dehydrates you, which is what causes the ________ the next day.
250; 1,000
Hangover
Urine stored in body is eliminated by __________.
Steps:
Urine in bladder stimulates _________ receptors
Contraction of ___________ pushes urine out of the body
The micturition reflex happens next. It is the relaxation of external _______________ sphincter muscle which allows urine to pass through _________ and out of the body.
Micturition
Stretch
Bladder
Urethral
Urethra
Micturition is under voluntary control but cannot be __________ indefinitely.
What is it called when you can't hold it any more?
Delayed
Urinary incontinence (comes with age)
The primary function of the DIGESTIVE system is to transfer nutrients, water, and electrolytes from ____________ food into body's _________ environment
What are the four functions the digestive system performs?
Ingested; Internal
1. Motility (movement)
2. Secretion
3. Digestion - chemical breakdown
4. Absorption
MOTILITY is muscular ____________ that mix and move forward the contents of the digestive tract
There are two types of digestive motilities.
Which motility pushes contents forward through the digestive tract?
Which one serves two functions? What are those functions?
Contractions
Propulsive
Mixing
1. Mixing food with digestive juices promotes digestion of foods
2. Facilitates absorption by exposing all parts of intestinal contents to the tract's absorbing surfaces
Digestive SECRETION consists of water, electrolytes and specific ___________.
Secretions are released into digestive tract ________ and are normally ___________ back into blood after digestion
Enzymes
Lumen
Reabsorbed
DIGESTION is a _____________ breakdown of structurally complex molecules into smaller, absorbable units.
It is accomplished by enzymatic _____________.
It breaks down carbs into ________________, proteins into ____________ and fats into _____________________.
Biochemical
Hydrolysis
Monosaccharides; Amino acids; Glycerol/ Fatty acids
ABSORPTION mainly occurs where? Is it complete there?
The small units resulting from digestion, along with water, vitamins, and electrolytes are transferred from digestive tract _________ into _____________
Small intestine
Lumen into blood
The digestive tract is continuous from _______ to ________.
*All of the ones listed are involved in digestion*
Name the organs where food actually enters (MPESSLA). What makes up the large intestine (CACR)?
The organs involved in digestion where food doesn't enter are called ___________________ organs. What are the 3?
What two organs make up the bilary system?
Mouth to Anus
Mouth, Pharynx, Esophagus, Stomach, Small and Large Intestine, Anus
Cecum, Appendix, Colon, Rectum
Accessory Digestive Organs
Salivary glands, exocrine pancreas and bilary system
Liver and Gallbladder
The digestive tract wall has structure from the ______________ to the _____________. State its four tissue layers from outermost to innermost.
Esophagus to anus
Serosa, muscularis externa, submucosa, mucosa
Which layer of the digestive tract lines the luminal surface and has a lot folds? What does having a lot of folds do?
Mucosa
Makes it have more surface area and more absorptive
Which layer of the digestive tract is thick with connective tissue and provides the digestive tract with elasticity? Why is elasticity beneficial?
Submucosa
Beneficial to have elastic digestive tract for storing big food or big quantities of food
What layer of the digestive tract has a major smooth muscle coat of digestive tube?
This layer consists of two main layers in most areas: circular and longitudinal.
The circular layer is the ____________ layer and its contraction decreases the ____________ of the lumen.
The longitudinal layer is the _________ layer and its contraction ____________ the tube.
Contractile activity in this layer produces ____________ and ___________ movements
Muscular externa
Inner; Diameter
Outer; Shortens
Propulsive and mixing
Which layer of the digestive tract secretes serous fluid? What two things does serous fluid do?
Serosa
1. Lubricates and prevents friction between digestive organs and surrounding viscera
2. Supports digestive organs in proper place while allowing them freedom for mixing and propulsive movements
The mouth is made up of the ______, _______, _________, ___________, ___________ and __________.
Lips, Palate, Tongue, Teeth, Saliva and Pharynx
What forms the opening of the mouth and has well-developed tactile sensation (understands TEXTURE of food)?
It helps procure, guide, and contain food in the mouth.
What forms the roof of oral cavity, which separates mouth from nasal passages?
What has taste buds and forms the floor of the oral cavity? What type of muscle is made of? What do its movements aid in?
Lips
Palate
Tongue; Skeletal; Swallowing and chewing
What is the cavity at the rear of the throat that is a common passageway for digestive and respiratory systems? What does it have on the side walls of it? What are they made of? Are they vestigial?
Pharynx
Tonsils
Lymphoid tissue
Yes
What in the mouth is responsible mastication (chewing), the first step of the digestive process?
The functions of chewing include:
Grinding and breaking food into smaller pieces to make swallowing easier and __________ food surface area on which ________ enzymes can act
Mixing food with _________
Stimulating ______ buds
Teeth
Increasing; Salivary
Saliva
Taste
Saliva, found in the mouth, produce largely by three major pairs of ___________ glands. It is _____% H2O and _____% proteins and electrolytes.
SALIVARY AMYLASE begins the digestion of ________________.
Saliva facilitates swallowing by _____________ the food. It also has antibacterial function (the ____________ destroys bacteria and saliva rinses away a possible __________ source for bacteria).
Saliva is also a solvent for molecules that stimulate _________ buds. It helps keep the mouth clean and it is RICH in ___________ buffers.
Salivary
99.5%; 0.5%
Carbohydrates
Moistening
Lysozyme; Food source
Taste; Bicarbonate
Swallowing is a motility that occurs in the __________ and ___________. It is initiated when the tongue forces food or drug to the __________. It is the most __________ reflex in the body. It can be initiated ______________ but CANNOT BE STOPPED once started.
Pharynx and esophagus
Pharynx
Complex
Involuntarily
Explain the two processes of swallowing.
The Oropharyngeal stage happens in the mouth and throat.
The Esophageal stage happens in the throat and stomach.
It moves the substances from the mouth to the pharynx and esophagus
The esophagus is a fairly __________ and __________ tube that extends between the _____________ and the _____________. It has ____________ at each end.
Which sphincter keeps the entrance closed to prevent large volumes of air from entering the esophagus and stomach during breathing?
Which one prevents reflux of gastric contents?
Straight and narrow; Pharynx and stomach
Sphincters at each end
Pharyngoesophageal sphincter
Gastroesophageal sphincter
_________ waves push food through the ESOPHAGUS.
______________ peristaltic contractions sweep bolus down the esophagus
Peristaltic waves
Ring-like
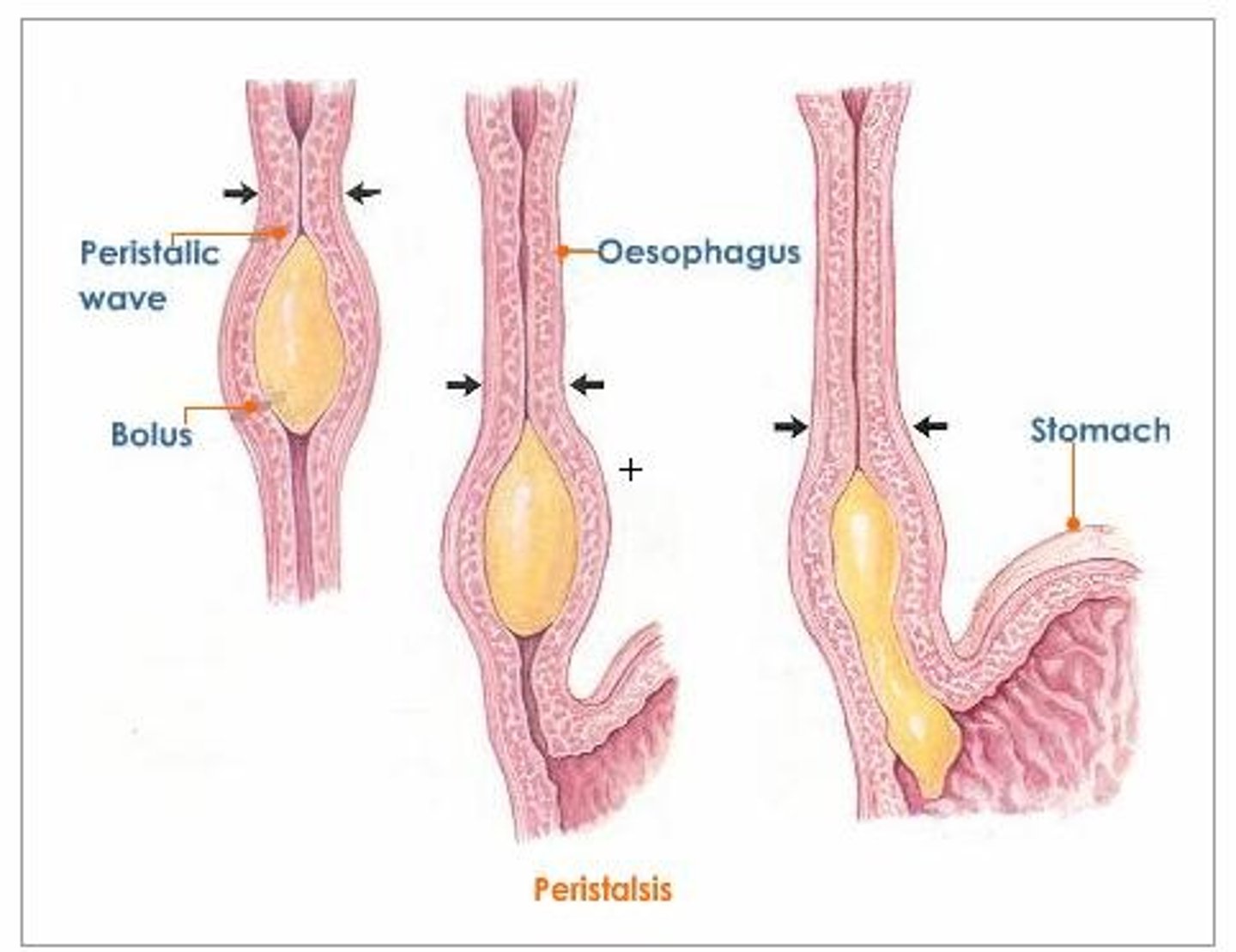
The stomach is a sac-like chamber shaped like a ______. It lies between the __________ and _____________.
J
Between esophagus and small intestine
Three sections of the stomach?
Three main functions of the stomach?
Fundus (top), body and antrum (bottom)
1. Store ingested food
2. Secretes HCl and other digestive enzymes that begin PROTEIN digestion
3. Mixing movements convert pulverized food into chyme
The __________ sphincter serves as a barrier between the stomach and small intestine.
When ___________, it blocks food to go from the stomach to small intestine. It __________ a bit at times so small portions of digested food can enter the small intestine for ____________.
Pyloric
Contracted
Relaxes
Absorption
Gastric motility (movement) has four aspects:
Filling, Storage, Mixing and Emptying
Which one occurs in the antrum of the stomach?
Which one occurs in the body of the stomach?
Which one is largely controlled by factors of the duodenum?
Mixing
Storage
Emptying
Gastric motility (movement) has four aspects:
Filling, Storage, Mixing and Emptying
____________ involves receptive relaxation. This includes the _____________ sphincter. It enhances the stomach's ability to deal with extra food by giving a little ___________ to the stomach pressure.
What is filling triggered by? What mediates it?
Filling
Gastroesophageal
Rise
Triggered by eating; Vagus nerve mediates it
What is the main factor that influences how strong a contraction is in the stomach? What is that?
The amount of chyme in the stomach
A pulpy acidic fluid that passes from the stomach to the small intestine, consisting of gastric juices and partly digested food.
Factors in the duodenum include:
Fat, pH, hypertonicity and distension
Fat digestion and reabsorption only in the __________ of the small intestine
Fat:
Further gastric emptying of additional fatty stomach contents is prevented when?
In the lumen of the small intestine
When there is already fat in the duodenum
Factors in the duodenum include:
Fat, pH, hypertonicity and dissension
pH:
Further emptying of acidic gastric contents is inhibited when? When does it resume?
Un-neutralized
When there is un-neutralized acid in the duodenum
When neutralization is accomplished
Factors in the duodenum include:
Fat, pH, hypertonicity and dissension
Hypertonicity:
Gastric emptying is inhibited when _______________ of duodenal contents starts to RISE.
Osmolarity
Factors in the duodenum include:
Fat, pH, hypertonicity and distension
Distension:
Gastric emptying is inhibited when there is too much ______________ in the duodenum.
Chyme
Sadness and fear tend to ____________ motility
Anger and aggression tend to ____________ motility
Intense pain tends to ____________ motility
Decrease; Increase; Inhibit
The four gastric secretions are:
Alkaline mucus, Pepsinogen, HCl and Intrinsic Factor
These secretions are released from _________ cells that are controlled by _________/___________ cells.
Gastric secretions are secreted where?
Secretory
Endocrine/ Paracrine
Elsewhere in the stomach and intestine
The four gastric secretions are:
Alkaline mucus, Pepsinogen, HCl and Intrinsic Factor
Which gastric secretion activates pepsinogen, breaks down CONNECTIVE tissue and kills the microorganisms that we digest?
Which gastric secretion starts protein digestion when activated?
HCl
Pepsinogen
The four gastric secretions are:
Alkaline mucus, Pepsinogen, HCl and Intrinsic Factor
Which gastric secretion facilitates re-absorption of Vitamin B12?
Which gastric secretion protects the stomach lining from other secretions (high pH)?
Intrinsic Factor
Alkaline Mucus
The three gastric hormones are secretin, gastrin and cholecystokinen (CCK).
Secretin is stimulated by the presence of _________ in the duodenum.
Its release stimulates the ___________ to release _____________ buffer.
Acidic chyme
Pancreas; Bicarbonate
The three gastric hormones are secretin, gastrin and cholecystokinen (CCK).
Gastrin is stimulated by the presence of _________ in the duodenum.
Its release stimulates the _________ and _____________ cells to secrete more __________.
Protein
Chief and parietal cells
More HCl
The three gastric hormones are secretin, gastrin and cholecystokinen (CCK).
CCK is stimulated by the presence of _________ in the duodenum.
Its release stimulates the _________ to release _______________ and _____________ enzymes.
Both fat and protein
Pancreas
Lipase (breaks down fats) and proteolytic (protein-breaking) enzymes
Gastric secretion happens over three phases:
1. During the CEPHALIC (acting in the head) phase, there is an increased secretion of ______ and ____________ in response to sensing food you're about to eat. This phase happens _______ you even eat.
2. The GASTRIC phase begins once the food does what? The presence of protein __________ gastric secretions.
3. The INTESTINAL phase is _____________. It helps shut off the flow of ___________________ as ___________ enters the small intestine.
1. HCl and Pepsinogen
Before
2. Reaches the stomach
Increases
3. Inhibitory
Gastric juices; Chyme
The pancreas is a mixture of what two types of tissues?
It is an elongated gland that is found where?
Endocrine and exocrine
Below and behind the stomach
Endocrine means entering the _____________.
Exocrine means entering the ________________.
The ENDOCRINE function of the pancreas is to:
This is done through the Islets of Lanerghans. Where are they found?
Bloodstream
Body Cavity
Secrete insulin and glucagon
Throughout the pancreas
Endocrine means entering the _____________.
Exocrine means entering the ________________.
The EXOCRINE function of the pancreas is to:
What does that consist of?
Bloodstream
Body Cavity
Secretes pancreatic juice
Pancreatic enzymes
Aqueous alkaline solution actively that line pancreatic ducts
What are the three types of enzymes found in the pancreas?
Proteolytic enzymes, Pancreatic amylase and Pancreatic Lipase
Pancreatic amylase converts ________________ to _________________.
Pancreatic lipase is the only enzyme in the digestive system that can:
Proteolytic enzymes digest protein. What are the three types?
Polysaccharides to disaccharides
Digest fat
Trypsin
Chymotrypsin
Carboxypeptidase
Bile is actively secreted by the __________ and actively diverted to the _______________ when?
Where is bile stored and concentrated?
After a meal, where does bile go?
Liver; Gallbladder; Between meals
Gallbladder
Duodenum
Bile salts are derivatives of _____________. They convert large _______ globules to a small ___________ emulsion.
Most of the bile salts REABSORBED into the blood after participating in fat _____________ and ______________
Cholesterol
Fat
Liquid
After participating in fat digestion and absorption
Site where most digestion and absorption take place
What does motility here include? Which one is the primary method?
Small intestine
Segmentation
Migrating motility complex
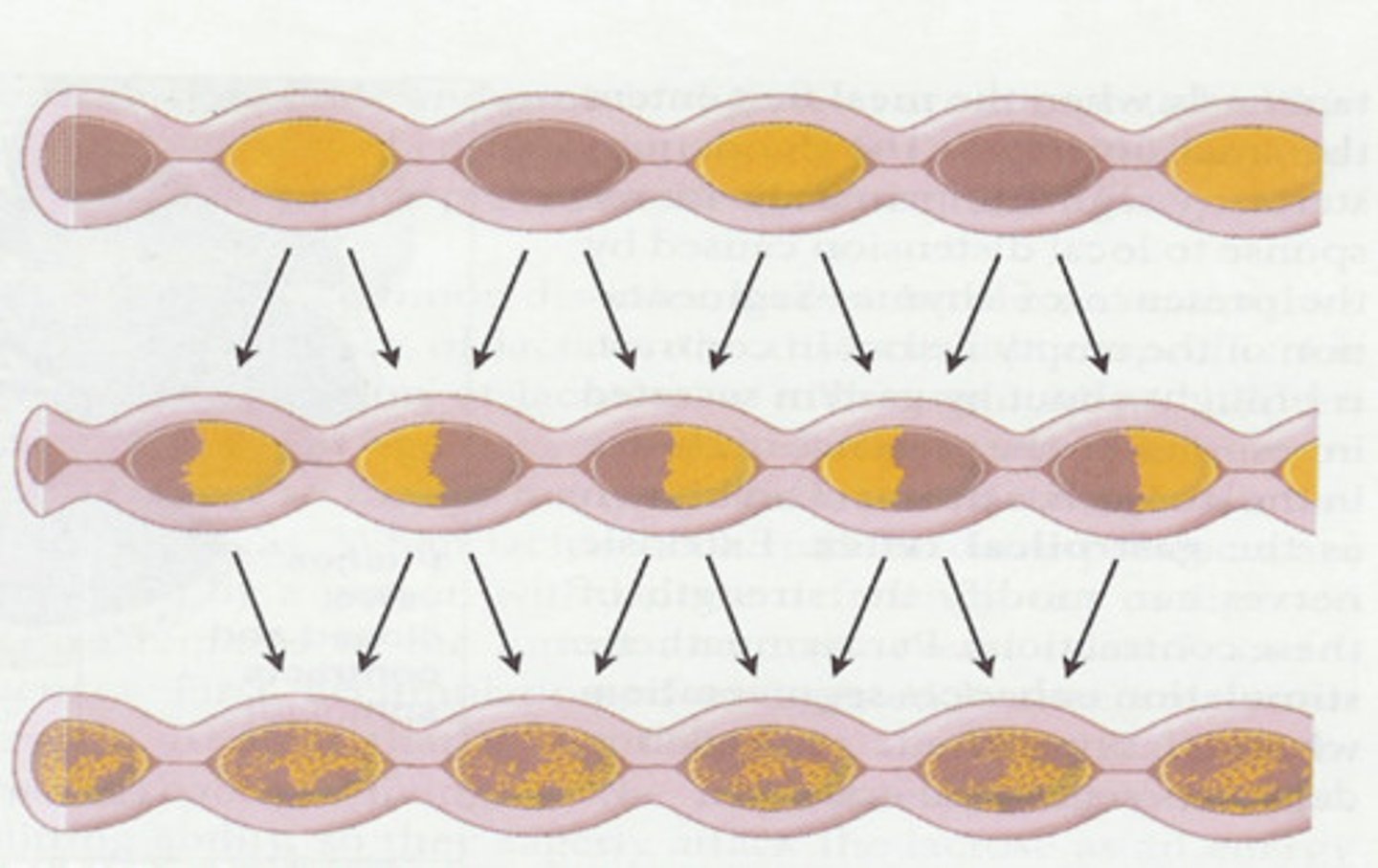
Segmentation
Segmentation:
Segmentation consists of ____________ contractions along the length of the ________ intestine.
Within seconds, ___________ segments __________ and ____________________ segments ______________.
This action mixes chyme with ______________ juices throughout the small intestine's lumen.
Chyme is exposed to all absorptive surfaces of the small intestine's ______________.
Segmentation also __________ the small intestine BETWEEN meals.
Within seconds, contracted segments relax and previously relaxed areas contract
Small
Digestive
Mucosa
Cleans
The small intestine absorbs just about everything presented to it. Most of the absorption occurs where?
The small intestine also has adaptations that can increase its _______________. What is its adaptation on the inner surface? What else does it have?
How often in the small intestine's lining replaced?
Duodenum and jejunum
Surface area
Inner: Permanent circular folds
Microscopic finger-like projections called villi
About every three days
The large intestine is primarily a __________ and _____________ organ.
It consists of a __________, ____________, ____________ then _____________.
Drying and storing
Colon, cecum, appendix the rectum
The contents that the large intestine receives from the small intestine include ________________ food residues, unabsorbed __________ components and remaining ________.
What does the colon do with these contents? What is the stuff that is left to be eliminated through the rectum/ anal cavity called?
Indigestible; Bilary; Fluid
Extracts more water and salt from them
Feces
Large intestine has massive contractions. Why must they be so big?
__________ contents are into DISTAL part of large intestine
Masses
Must be so big because moving solid. Mainly liquids moving through small intestine
Colonic
DEFACATION Reflex:
Starts when ___________ stimulates the _________ receptors of the ________ wall.
This causes what to relax and what two things to contract vigorously?
Something else has to be relaxed for defamation to occur. It is a skeletal muscle under VOLUNTARY control.
Distension; Stretch; Rectal
Relax: Internal Anal Sphincter
Contract: Rectum and Sigmoid Colon
External Anal Sphincter