Spectroscopy Lecture Notes Review
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts and definitions related to spectroscopy, electron energy levels, and experimental procedures.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What is the purpose of a spectroscope in spectroscopy experiments?
To observe and compare continuous emissions and line emissions from various sources.
How is the energy change during an electron transition calculated?
Δ𝐸 = 𝐸final − 𝐸initial
What is the formula relating the emitted or absorbed energy to the energy of a photon?
Δ𝐸electron = 𝐸photon = ℎ𝜈
What is the wavelength range of visible light?
Approximately 400 nm to 800 nm.
what is c?
the speed of light, 3.00 × 108 m/s
What does the Bohr model state about electron energy levels in hydrogen?
Electrons can only exist in certain energy states labeled with a quantum number (n = 1, 2, 3, …).
What is the energy formula for a photon?
𝐸 = ℎ𝜈.
What is a spectrometer and its basic function?
An instrument used to quantify light phenomena, separating and measuring the spectral components.
What causes an electron to emit a photon?
When the electron transitions from a higher energy level to a lower energy level.
What is black-body radiation?
Thermal electromagnetic radiation emitted by objects at room temperature, appearing black.
What is the significance of the Rydberg constant in spectroscopy?
It simplifies the calculation of energy changes during electron transitions.
What safety precautions should be observed when making a spectroscope?
Ensure accurate folding and cutting according to instructions and tape securely to the camera.
What specific light sources were listed for collecting spectroscope data?
Mercury Lamp, Hydrogen lamp, Neon Lamp, Nitrogen Lamp, Sunlight, LED light.
What is a flame test used for?
To identify the emission spectra of specific metals.
what is planck’s constant?
6.626 x 10^-34 Js.
what is the balmer series equation for hydrogen?
1/wavelength = R( 1/22-1/ni2)
what is the total energy for hydrogen equation?
-Rhc (1/n2) = 13.6 eV/n2
What is R?
1.09737 × 107 m-1
what is the equation for the wavelengths of an emitted photon of hydrogen?
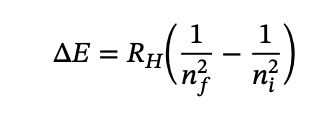
what is emission spectra?
every element. and compound has a unique spectrum of colors from energy emission wavelnegths
what is electromagnetic radiation?
a form of energy consisting of oscillating electric and magnetic fields
what are spectral lines?
distinct, narrow bands of light resulting from the emission/absorbance or light of specific frequencies
what is the speed of light equation?
c=wavelength (v)
what does it mean for an electron to be excited?
It refers to the process where an electron absorbs energy and moves to a higher energy level within an atom. it is unstable.