Enzyme Catalysis and Inhibition
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Group Transfer
-Nucleophilic attack by the enzyme
-Enhanced electrophilicity of E-S covalent intermediate
-Elimination of the enzyme
Result: transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another
catalyst
-speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction
-regenerated
-changes the path of the reaction
Enzymes are...
proteins that function as catalysts
active site
The part of an enzyme or antibody where the chemical reaction occurs.
Natural substrates for enzymes
The reactant that an enzyme acts on
enzyme-substrate complex
A temporary complex formed when an enzyme binds to its substrate molecule(s).
enzyme catalysis
the increase in the rate of a chemical reaction by the active site of a protein
alternate reaction pathway with a lower energy barrier
enzyme can repeat reaction many times
enzyme is regenerated
5 enzymatic strategies
1. General Acid Base Catalysis
2. Approximation
3. Stabilizing charge of the TS
4. Distortion
5. Group Transfer
general acid-base catalysis
Catalysis in which a molecule other than water plays the role of a proton donor or acceptor.
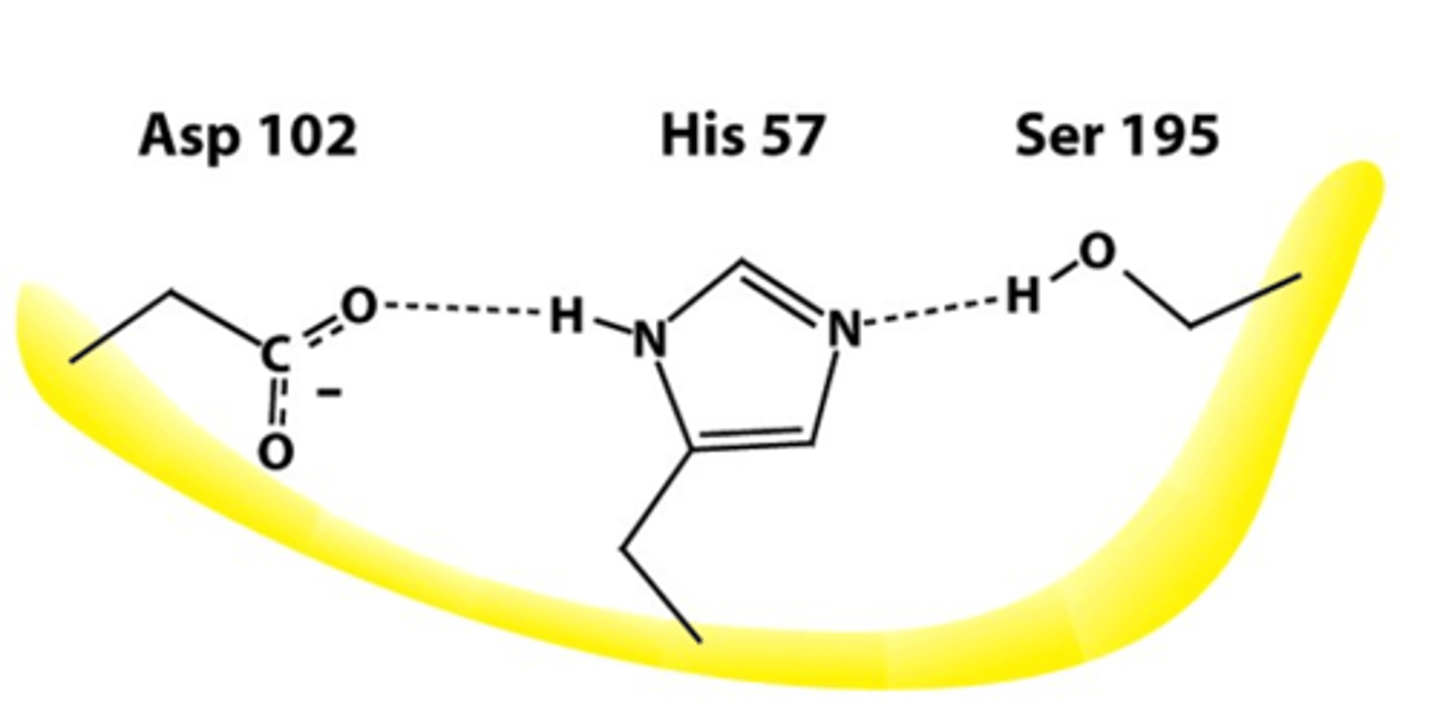
Catalytic Triad
Ser, His, Asp
Approximation Catalysis
the reaction rate of the enhanced by bringing two substrates into close proximity (near each other)
overcomes the negative entropy
Distortion in Enzyme Catalysis
• Substrates do not fit the binding site
• Substrate distorts during binding
• Distorted conformation ≈ transition state conformation
Induced Fit Model of enzyme action
Change in the shape of an enzyme's active site that enhances the fit between the active site and its substrate(s)
components of enzyme-catalyzed reaction
substrate, enzyme, enzyme-substrate complex, product + enzyme molecule
Enzyme-product complex
The intermediate structure in which product molecules are bound to an enzyme molecule.
Valley on Rxn Profile Diagram
Enzyme-Substrate Transition State
The transition state in the reaction (bond-making & breaking in progress
bound to an enzyme
Peak on Rxn Profile Diagram
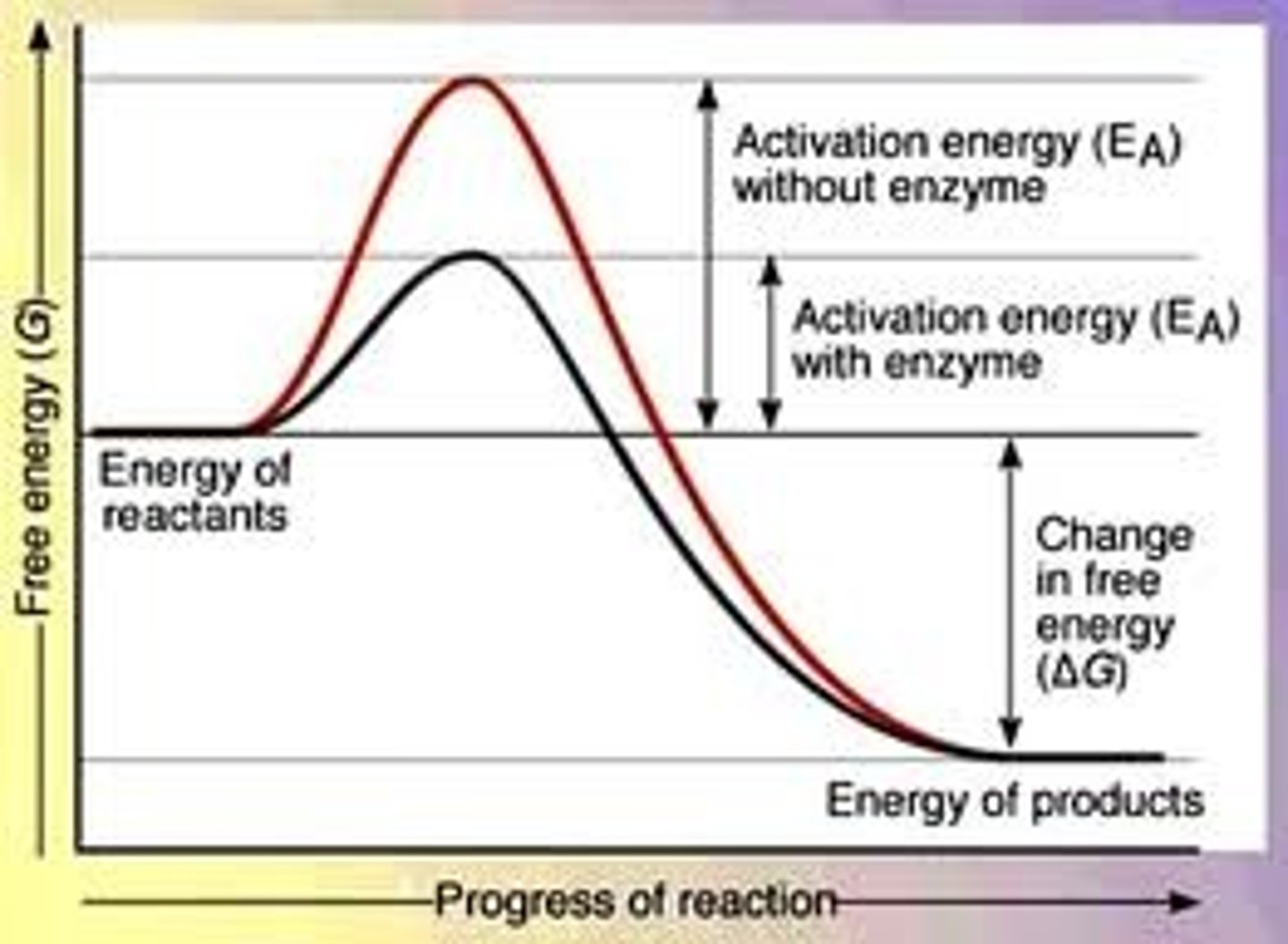
To catalyze a reaction, the Activation barrier (TS) must
TS must be stabilized lowering the Ea
enzyme inhibitors
substrate imposters that bind the active site
transition state
a high-energy intermediate state of the reactants where the bonds are being broken and bonds are being formed
transition state analogs
synthesized compounds that mimic the form of the transition state of an enzyme reaction
inhibitors of the enzyme because they bind more tightly to the enzyme than substrate
transition state analogs must match_________ & _________ of the ES Complex TS
geometry and stereoeletronics
specificity of enzymes
The ability of an enzyme to choose the exact substrate from a group of similar chemical molecules.
competitive inhibition
substance that resembles the normal substrate (transition state) and competes with the substrate for the active site
suicide substrates
molecules used to bind to an enzyme irreversibly and inactivate it
Denaturation
-A process in which a protein unravels, losing its specific structure and hence function; can be caused by changes in pH or salt concentration or by high temperature.
-Non-specific
Still learning (15)
You've started learning these terms. Keep it up!