Kognity chapter 1.1 vocabulary
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Change
An act or process through which something becomes different.
ethics
The moral principles that govern the behaviour of a person or group.
sustainability
Meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
stake holders
Any individual or group that affects, or is affected by, an organisation.
Businesses are systems
A system is a set of interconnected parts that work together to make a more complex whole to achieve a purpose. Systems have inputs, processes, outputs and feedback.
Entrepreneur
A person who organises human, physical and financial resources to start a business.
The
inputs
of a business
all the resources needed to create a product. These resources belong to one of three categories:
physical
financial
human
Physical resources
The raw materials and semi-finished goods that a business needs to begin production.
capital goods
such as equipment and machines that will be used to produce other goods//These might include computers or robots used to build goods.
Financial resources
The funds needed to set up and invest in a business and keep it running; can be short-term, medium-term and long-term.
Long term financing
Large-scale funds needed to finance expensive equipment and facilities that a business needs to operate.
short term financing
Small-scale funds needed to pay for inputs that will soon be processed and sold by the business; used to cover short-term working capital needs.
Human Resources
the people needed to run a business
Entreprise
Enterprise is the process of taking risks to combine the other resources to create a good or service.
function: Human resources management
makes sure the business employs the correct number of skilled employees to produce and deliver its products. This process also involves ensuring that employees are treated ethically and in line with laws.
function of: Finance and accounts
Financing and accounting processes ensure that the business has enough money to carry out its business activity over time.
function of marketing
Marketing involves the process of selling the right product, at the right price, at the right time, to the right customers.
function of operations
All businesses have a core business process (making a product, constructing houses, selling clothes, growing crops, etc.). Operations refers to how this core activity is carried out. Operations must plan how and in what quantity goods and services are to be produced.
two main categories of business outputs
1. Goods
are tangible, meaning they have physical characteristics and can be measured.
2. Services
are intangible, meaning they cannot be touched or described by physical characteristics.
negative feedback
When the output feeds back into the inputs in a way that moves the system in the opposite direction.
positive feedback
Occurs when the output feeds back into the inputs in a way that moves systems and processes in the same direction.
What is the name of the business input that refers to the money needed to start up and operate a business?
All businesses need capital to finance investment and operations.
Sociocultural sustainability (people):
businesses provide for human needs and are deeply connected with the communities they serve. They have a responsibility to support the wellbeing of all stakeholders.
Environmental sustainability (planet):
businesses should do more than minimise the negative impact of their activities on the planet. Instead, businesses should work to improve the ecosystems on which we all depend.
Economic sustainability (profit):
businesses/entrepreneurs are risk-takers and seek to make a profit and to continue their businesses. Sustaining business activity is especially important when businesses are providing for human needs, supporting the wellbeing of varied stakeholders in the community, and providing tax revenue to support public services.
what is the doughnut model
A model that outlines the social foundation (human needs) and ecological ceiling (planetary boundaries) that economic activity needs to respect to find the 'safe and just space for humanity'.
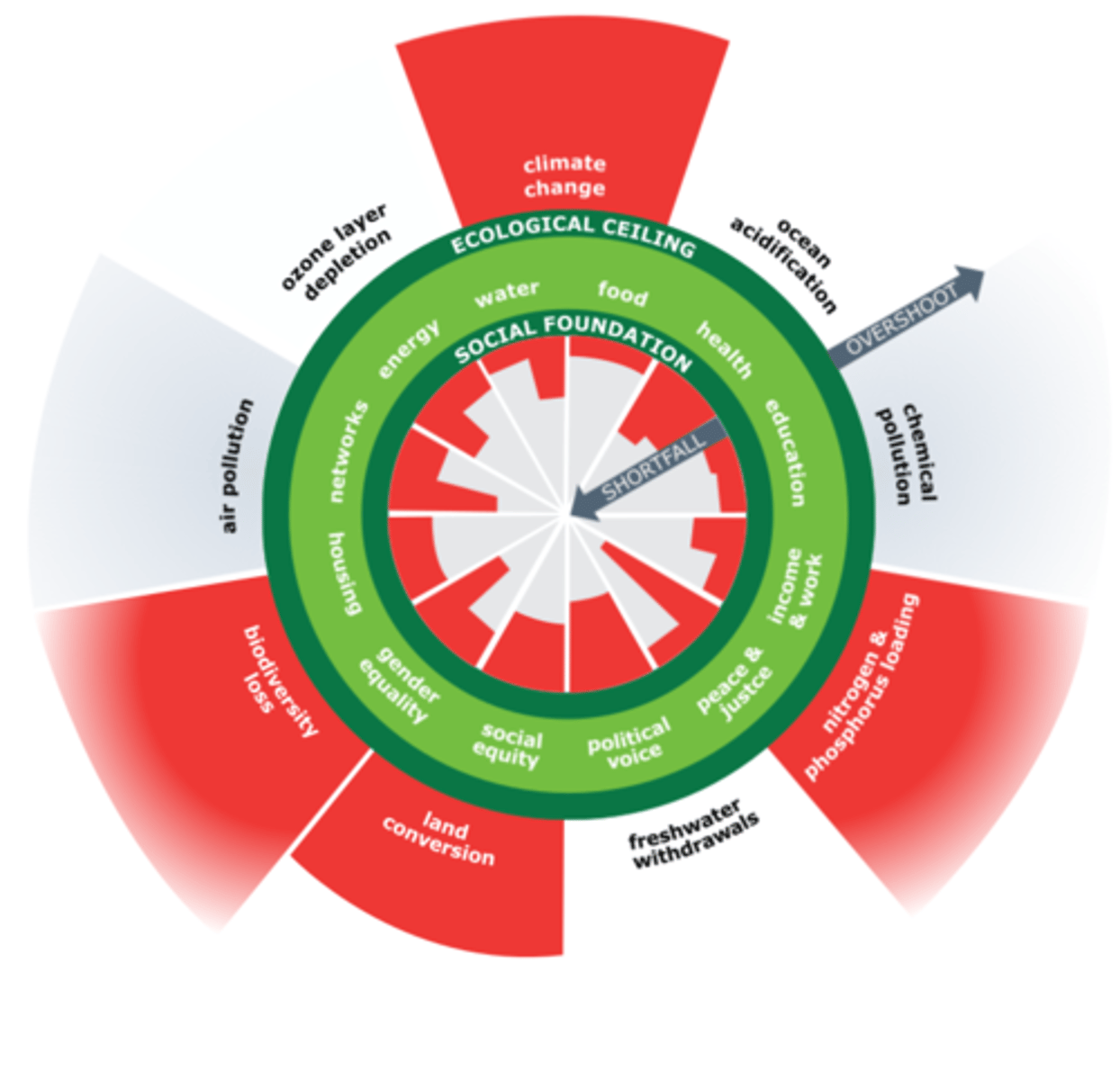
planetary boundaries
The limits of planetary systems (how much the environment can handle from a business); the outer ring of the Doughnut Economics model.
what does the inner ring of doughnut model represent?
Human needs, also called the social foundation, are represented by the inner ring of the Doughnut Economics Model
the economy
A system for producing and provisioning or distributing goods and services among a group of people.
embedded economy model
A model that shows the economy embedded in nature, with inputs of energy from the Sun and outputs of waste; provisioning occurs through markets, households, the state and the commons.
different systems and groups of people that distribute goods and services
households, state, commons, market
The primary sector
A section of an economy that extracts materials (minerals, oil, etc.) or harvests products from the Earth.
secondary sector
The area of economic activity that produces finished goods through manufacturing.
tertiary sector
The area of economic activity that provides services.
quaternary sector
The area of economic activity involved with knowledge and the movement of information.
supply chain does what
uses a combination of the 4 sectors to produce finished goods
integrated businesses
A business whose activities span two or more sectors.
SWOT
A business management tool that analyses the internal strengths and weaknesses as well as the external opportunities and threats for a business.
what is STEEPLE
A business management tool that analyses the external conditions that may be opportunities or threats for a business.
Intraprenuer
A person who develops new ideas, processes or products for a business in which they already work.
internal factors of swot
Internal factors: strengths and weaknesses
opportunity
Any favourable external condition or trend that might be beneficial for a business.
SWOT
In the SWOT analysis, an opportunity refers to an external condition or situation that is favourable for the business.
what does steeple stand for?
Sociocultural
Technological
Economic
Environmental
Political
Legal
Ethical
Sociocultural factors
Sociocultural factors are all the social and cultural characteristics of a region or country.
GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP) - the total monetary value of all final goods and services produced in an economy in a given period of time; represents the size of the economy
GDP per capita
GDP per capita - divides total GDP by the population of a country
Expansion
- when the total value of all goods and services produced within the borders of a country (GDP) is increasing
Recession -
when the total value of all goods and services produced within the borders of a country is decreasing, usually for six or more months
Inflation -
an increase in the general price level, usually expressed as percentage change
Deflation
- a decrease in the general price level, usually expressed as percentage change
Exchange rate -
the price of one country's currency in terms of another country's currency
Subsidy
- government payment to businesses
The strengths and weaknesses part of the SWOT only refer to -------- ---------?
internal factors.
The opportunities and threats part of the SWOT only refer to ------- -------?
external factors. External opportunities and threats refer to factors that are outside the organisation that it cannot control. Usually, external factors will be the same for a business and its competitors in the same industry and location.
technological factors (steeple)
The state of current technology will affect what products a business offers its customers. Technology will also affect how a business operates. Businesses are constantly offering new products based on new technologies.
Economic factors
use the business cycle chart to help.
Countries and regions have different economic conditions that will affect the demand for goods and services. For example, as incomes increase, demand for goods and services will increase. This is an opportunity for businesses. However, rising incomes also cause consumers to demand different kinds of products. These changing economic conditions will be an opportunity for some businesses and a threat to others
Environmental factors
Environment in the STEEPLE analysis refers to the natural environment. Many businesses rely on natural resources as inputs and changes in the natural environment can have a large impact on businesses.
Political factors
Politics has a huge impact on business decisions. Political parties have different ideas about how much government regulation there should be of businesses. They may also change laws at short notice, affecting business operations.
Legal factors
Businesses must follow all laws and regulations. These laws may be made at a national, regional, or local level. Multinational companies must obey the law in their home country as well as other countries in which they operate.
Ethical factors
Business activity should serve human needs and respect the health of the planet. Many businesses, however, have conflicts between the goals of business growth and profit and their social and/or environmental responsibilities.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a tool used to describe a business.
What is the golden circle?
the basic elements of a business plan (why, how, what)
(-What are the characteristics of the product you are offering)
lobbying
Some businesses try to influence the laws to their favour. This is called lobbying
Ethics
Ethics
Ethics refers to moral principles that govern the behaviour of a person or groups. Businesses are often engaged in the question of 'what is the right thing to do?'. Ethical responsibilities in business come from the relationships and networks that are formed when business organisations are started.