13. Imaging techniques in pulmonology
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
What is a chest x ray + fluoroscopy used for
create 2D image
fluoro- functional information about lung function
What are the standard projections of a CXR
PA
AP
Lateral
What are the indications of imaging
asymptomatic → low dose CT screening, staging
symtpomatic- suspicion of lung disease, cancer, chest trauma, PTX, HF
unconscious, polytrauma
follow up
intervention techniques
What are the contraindications of imaging
pregnancy
extreme obesity
What are the shadows seen on a CXR
Intrapulmonary
alveolar, interstitial, blood vessels shade, bronchial shadow
Extrapulmonary
pleural, extrathoracic
Findings
nodules, pulmnoary infiltrates, line/ linear shadows, coverage
What are the different nodules seen on a CXR
solitary
multiplex
describe the appearance of bengin nodules on a CXR
round
segmented
sharrp edges
central calcification- popcorn
well defined boundary
Describe the appearance of malignant nodules on a CXR
irregular
spiculated
blurred contour
eccentric calcification
What are the causes of calcerous deviations
hamarthoma
TB
malignancy
What are the regular settlings seen on a CXR
TB- apical location due to increased ventilation
Metastasis- base due to increased perfusion
What are the pulmonary infiltrates seen on a CXR
Bronchopneumonia
spotted structure- patchy, inhomogenous
multifocal
Lobar pneumonia
respects borders of lobes
airbronchogram
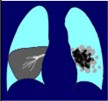
What are the causes of atelectasis shadow
lung cc
compression of LN
mucous plugs
foreign body
pleural effusion
abdominal diseases
What are the causes of infiltrate shadow
pneumonia
lung cc
TB
pulmonary infarction
What are the causes of scattering shadow
spread/ dissemination
coniosis
granulomatous disease
TB
metastasis
sarcoidosis
What are the causes of linear shadow
pulmonary embolism
lymphangiosis carcinomatosa
What are the causes of nodular shadow
primary lung cancer
metastasis
tuberculoma
benignoma
arteriovenous malformations
echinococcus
What are the causes of hilar expansion shadow
central lung cc
mediastinal tumours
sarcoidosis
lymphomas
oesophagus dilation
pulmonary circulation’s stagnation
What are the causes of vessel shadow
pulmonary hypertension
dilation of vessels
What are the causes of pleural effusion shadow
Meniscus sign
What are the causes of Barbelll shadow
focal TB + lymphangitis + enlarged hilar LN
What are the causes of Kerley line shadow
Pulmonary oedema
What are the causes of apical bullous emphysema shadow
Thin walled sacs
What are the causes of bronchial shadow
thickened bronchial wall
Tram track lines
signet ring
Bronchiectasis
What are the causes of calcificated residual nodules shadow
curvilinear opacities
extend from subpleural mass towards hilum
distortion of vessels and bronchi that lead to an adjacent area of rounded atelectasis
TB, asbestos, pleuritis, tumour
What are the causes of fissures shadow
Horizontal, oblique
Intrapleural recess
outlined if thickened
if in pleural soace- air, effusion, other appearing
What are the causes of basket shadow
Pulmonary abscess
What are the causes of aspergilloma shadow
mycetoma, fungus ball
What are the causes of cavity shadow
TB, tumour
Calcareous tisssue- hamarthoma, tumour, tb
What are the Negative shadows on CXR
watermark sign
airbronchogram
What is a watermark sign on a CXR
behind obstruction or valvular bronchoconstriction
lung parenchyma= brighter or with increase transparency
What is an air bronchogram on CXR
when no air in alveoli
surrounding lungs infiltrated
bronchial lumen outlined
What can cause volume increase on CXR
intrapulmonary
inflammation, haemorrhage, pleural fluid, hematoma, pneumothorax
Needs more space than usual- size of lung is unchanged
What causes volume decrease on CXR
Atelectasis
Fibrosis
pneumectomy
What are the differences in effusion and atelectasis
Effusion
mediastium pushed away
diaphragm pushed down
Ateletcasis
mediastinum pulled
diaphragm raise
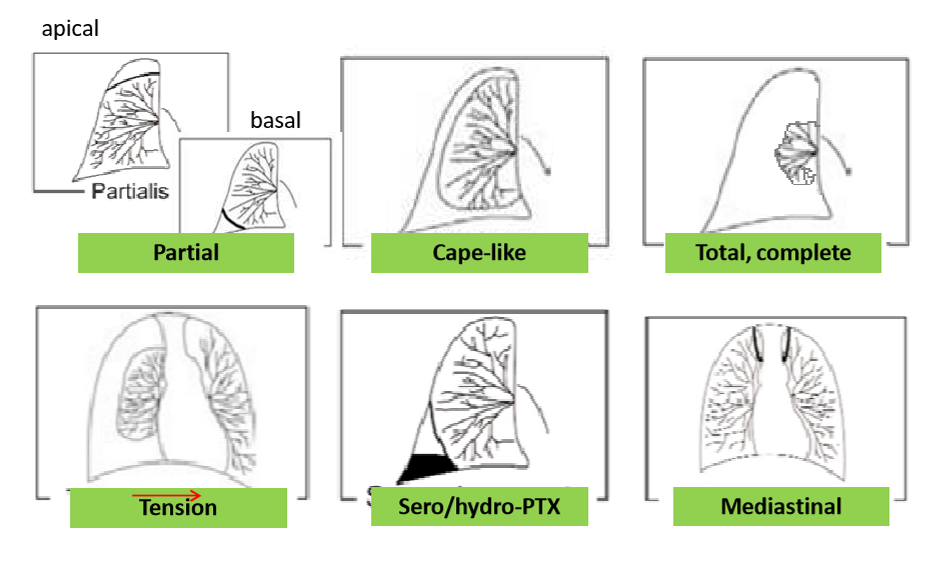
What are the different appearances of pneumothorax
partial- apical, basal
cape like
complete
tension
sero/ hydro PTX
mediastinal
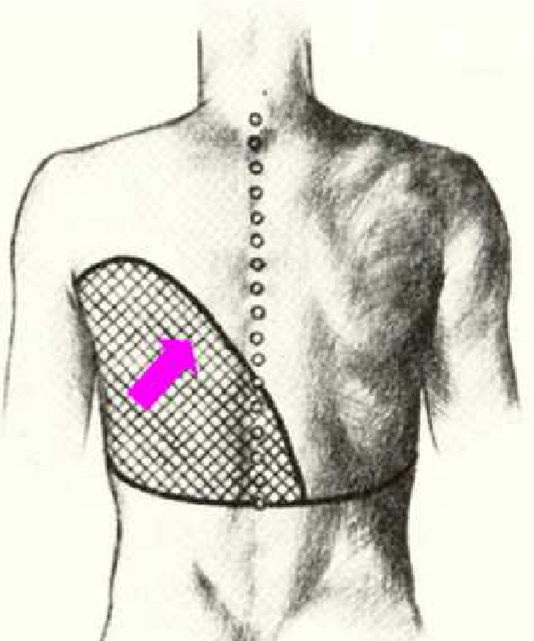
What is the Ellis Damoiseau line
curved upper border of a pleural effusion
concave upward
homogeneous opacity
What are the advantages of chest fluoroscopy
shows movement of diaphragm
pulsation of heart, hilus
judgement of paradoxical movement
Holzknecht Jacobson sign
eliminate superposition, localisation of target lesion
What are the disadvantages of chest fluoroscopy
higher radiation exposure
bad resolution
documentation is difficult
What is the Holzknecht Jacobson sign
pendulum movement of mediastinum during inspiration and expiration
hilus moves towards the obstructed lung during inspiration, expiration teh other direction
What can be seen on contrast enhanced fluoroscopy
enlargement of heart
chest tightness
contrast media passe through
locate/ rule out fistula- aspiration
confirm hiatus hernia
What are the indications for a CT
suspisious CXR, inaccurate difference
tumour staging, RECIST
intesrstitial lung disease
lung transplant patients
traumatology
negative CXR, abnormal spirometry, chronic cough
CT guided biopsy
What are the uses of CT angiography
vessel representation
normal/ abnormal vessels
AVM, VCS syndrome
thromboembolic process
representation of parenchymal organs
3D reconstruction of plane
What is a virtual bronchoscopy
used before interventio of trachea, for planning
What are the uses of HRCT
morphology reflects morphological function
only in exams by inhalation and exhalation- air trap, obstruction
ILD, bronchiectasis, COPD
pulmonary fibrosis, CF, pneumonia, COVID
What is the indicatio of low dose CT
screening for lung cancer
What can US be used to detect
pleural fluid
heart + big vessel abnormalities
close pathologies of thorax and pleura
pneumothorax
What are the advantages of US
non invasive, non ionising
cheap, no prep needed
simple, fast
What are the disadvantages of US
air makes exam hair
disturbing shadows can occur
fat can cause deflection and increased attenuation
accuracy is dependent on examiner
What are the indications for an MRI
for chest wall + mediastinal structures
pancoast tumour, hematoma
DWI- pathological lymph nodes
detection of perfusion disorders
What are the indications for PET CT
detection of primary/ metastatic cancer
staging of cancer
follow up after cancer therapy
before invasive procedures