(chapter 10) intro to management denis hamilton final review flashcards
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
performance management
the delivery of superior results through the ongoing measurement, assessment, evaluation, and
improvement of the organization.
why performance management is important
helps leaders to:
Manage their organizations more effectively and efficiently
Improve faster than their rivals
Create a distinctive competency that provides a competitive advantage leading to superior results.
performance management principles
Role of Leadership
Customer Focus
High-Performance Environment
Fact-Based Management
Relentless Improvement
Innovation and Renewal
role of leadership
Develop and communicate a clear direction for the organization and support that vision by investing in the capabilities necessary to fulfill it.
customer focus
create superior value for customers based on an understanding and commitment to economically delivering customer requirements better than competitors.
high performance environment
use a process-based view of the organization that effectively integrates multiple activities and functions working collaboratively to create outstanding results.
fact based management
use a collection of balanced measurements and objective, comprehensive business assessments that are routinely reviewed and evaluated to understand how well the organization performs against standards of excellence. use this data to identify performance gaps and improvement opportunities.
relentless improvement
Embrace a commitment to continually do better through use of proven methodologies and tools coordinated by experts trained in managing and delivering successful improvement initiatives
innovation and renewal
continually seek creative ideas for transforming and renewing the organization by not only adopting today’s best practices, but also by authoring tomorrow’s best practices.
Approach to Embed Performance Management into the Culture of the Organization
Role of Leadership
Use of Experts and Training
Use of Proven Methodologies and Tools
role of leadership (approach to embed)
the leadership of the organization needs to communicate and reinforce the commitment to excellence achieved through a continual focus on the Performance Management Principles
use of experts and training
Superior results often require repeated and ongoing successful improvement initiatives. To that end, successful improvement initiatives are more likely to be accomplished when using individuals who have the training and experience in repeatedly delivering successful improvement initiatives. These individuals will be experts in project selection and management. They will also know how to apply proven improvement methodologies and tools
use of proven methodologies and tools
The experts described above need to rely on a set of tools to be successful with their improvement efforts. These tools don’t need to be re-invented with each project; they already exist as a set of tools that have been demonstrated to repeatedly lead to high-impact, successful project results. Application of tools and methods such as Six Sigma and Lean Methodology have routinely delivered significant results when used by properly trained and experienced experts.
process
a series of steps or actions taken to convert a set of inputs into a set of outputs
Performance Management Key Elements
business process management
business measurement, assessment, and evaluation
business improvement methods and tools
business process management (BPM)
definition: an underlying framework for understanding the interrelated activities performed in an organization.
managers use this to better understand and manage the activities in their organizations.
“Process Maps” are visual depictions of the multiple steps involved in the conversion of inputs to outputs.
• SIPOC
• Swimlane
• Lean Value
business measurement, assessment, and evaluation
helps organizations to understand how effectively and efficiently specific processes are performing as well as to understand how well the organization is performing overall to aid in the identification and prioritization of opportunities for improvement
requirements of a customer
the necessary characteristics of the product and service (at a given price) that will result in the customer perceiving that the output creates value for them and motivates them to behave in ways that are beneficial to the converter
effective process
one that delivers outputs that results in obtaining the desired behaviors from the intended users (customers) of the outputs of that process
efficient process
an Effective Process that also generates an adequate return on the capital employed to operate the process.
process maps
visual depictions of the multiple steps involved in the conversion of inputs to outputs
SIPOC
supplier, inputs, process, outputs, and customers — simple depiction of a process
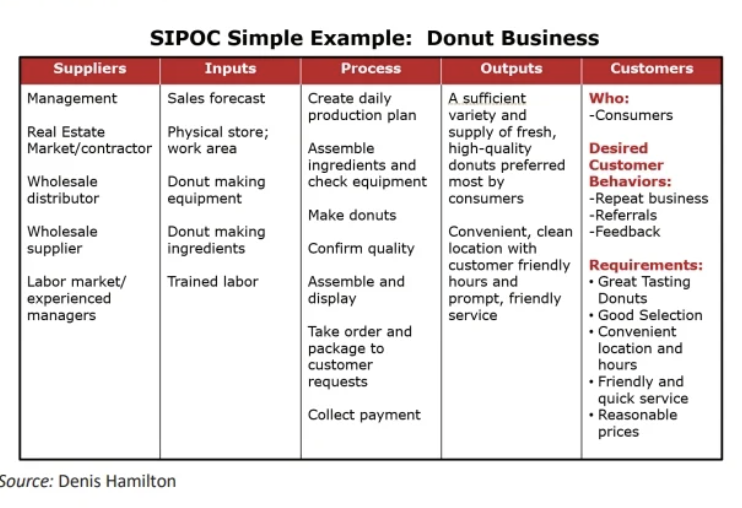
Business Measurement, Assessment, and Evaluation
helps organizations to understand how effectively and efficiently specific processes are performing as well as to understand how well the organization is performing overall to aid in the identification and prioritization of opportunities for improvement
measures of effectiveness
evaluate whether customer requirements are being met.
measures of efficiency
evaluate whether the value of outputs relative to the cost of inputs is creating value for the organization
well dressed measure
the concept of having measurement charts that include all the information necessary to allow for rapid, complete, and accu-rate interpretation of the data presented. they include:
Title: clearly labeled at top of chart indicating what is being measured
Goal: clear indication of the target performance
Min: clear indication of the minimum acceptable performance
Results: clear indication of current and past performance
Competitor: clear indication of competitor’s performance
Benchmark: clear indication of world-class standard of performance
Axes: clearly labeled to indicate what is measured and in what time frame
Performance Status: color-coded indicator of whether the performance is meeting standards (green), needs immediate improvement (yellow), or is seriously deficient (red)
Owner: Name of person responsible for producing chart
Updated: Date chart was most recently updated with data
Projects/Impact/Project Mgr: Description of what actions are being taken to address yellow or red performing processes, the current status of those actions, what those actions are intended to deliver, when they are expected to be completed, and who is responsible for leading those actions.
business assessment (the baldridge framework categories)
leadership
strategy
customers
measurement, analysis, and knowledge management
workforce
oper
Business Evaluation
is the process of collecting and analyzing external and internal business data, assessing overall business performance, and identifying and prioritizing opportunities for improvement
business improvement methods and tools: three major things that successful organizations do differently
Role of Leadership
Leadership plays a proactive role in overseeing the prioritization, selection, and routine monitoring of improvement projects. This involvement by leadership reinforces the importance of these projects and helps ensure that necessary time and resources are being allocated to them.
Use of Experts and Training
Highly trained and experienced improvement experts are used to manage key improvement projects. Managing an improvement project, like managing most activities, requires knowledge, skill and experience.
Use of Proven Methodologies and Tools
These “experts” use proven improvement methodologies and tools as a key part of their approach. When used properly in improvement projects, these methods and tools save a lot of time in organizing a project and executing the steps necessary to complete it successfully.
METHODS & TOOLS (Examples)
DMAIC/Six Sigma
In using a Six Sigma concept for Performance Management purposes, the upper
and lower limits that are set for measuring outputs of a process are determined by defining the range of output quality (effectiveness) that fully meets customer requirements. As long as the output of the process falls within this acceptable range it is considered to fully meet the standard, or fully meet customer requirements. Any output that does not fall within the acceptable range is considered a defect. In order for a process to be considered a Six Sigma process no more than 3.4 outputs per million can be defective (thus fail to fully meet customer requirements).
Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control
Six Sigma goes beyond simply measur-ing the output data from processes - it also includes a methodology for improving processes to get closer to achieving six sigma performance. This methodology is called DMAIc. The acronym is Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control.
Lean Methodology
an improvement tool with a primary focus on eliminating waste in processes
7 causes of waste
1. Overproduction (producing more products or components than are currently required to meet demand),
2. correction (having to rework a defective output of a process),
3. Inventory (the need to store output until it is required),
4. Motion (the need for excessive movement of materials and/or people as part of performing a process),
5. conveyance (similar to motion in terms of requiring a component of the process to be transported some distance for further processing),
6. Overprocessing (performing steps in a process that do not create value for the customer or the converter),
7. Waiting (not having parts or people available when required to perform the next step in the process). The Lean Methodology minimizes these seven causes of waste. By using tools like the Lean Value Map described in Topic 10.2 in this chapter, organizations are able to identify areas of waste in the process and use Lean tools to reduce or remove those wastes