Unit 8 Pancreatic Pathology- Pancreatitis (Elie)
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
What is pancreatitis?
Inflammation of pancreas
What does pancreatitis occur from?
Damage or malfunction
Pancreatitis can be either _____ or ______
Acute or chronic
Pancreatitis can be classified as:
Mild to severe
What are the lab values for Pancreatitis?
Increases Amylase and Lipase
If obstructed: Increased Alk Phos
What are the main causes of Acute Pancreatitis?
Biliary Tract Disease (Most common cause)
Alcoholism
What are the lab values for Acute Pancreatitis?
Amylase
Lipase
WBC
What are the clinical symptoms of Acute Pancreatitis?
Sudden onset Abdominal Pain to back
Fever; N/V, Distention
Risk of Abscess/Hemorrhage
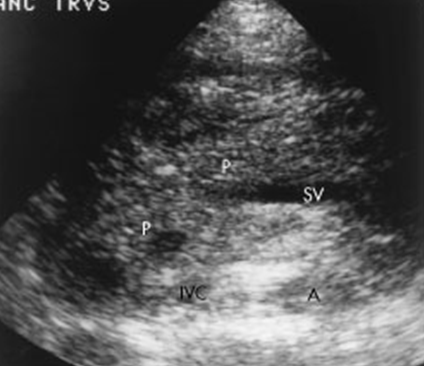
What is this image showing?
Acute Pancreatitis
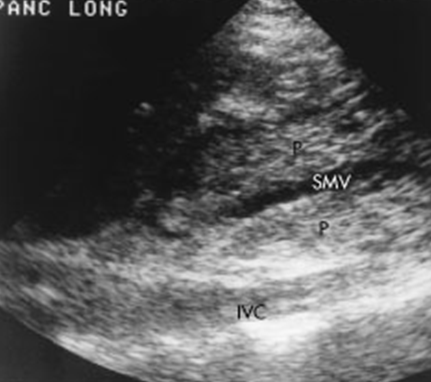
What is this image showing?
Acute Pancreatitis
US Appearance: What are the sonographic findings of Acute Pancreatitis?
29% Normal
52% Increased Size
Hypoechoic – anechoic
Loss of distinction of SV/Borders
US Appearance Acute Pancreatitis: What should the sonographer check for?
Check for peripancreatic fluid
Pancreatic Ductal Dilatation
Check for stones in GB & bile duct
What are the percentages associated with other complications with Acute Pancreatitis?
18-20% Phlegmon
10% Pseudocyst formation
1-9% Abscess
5% Hemorrhage; Intra & Extra pancreatic Fluid Collections
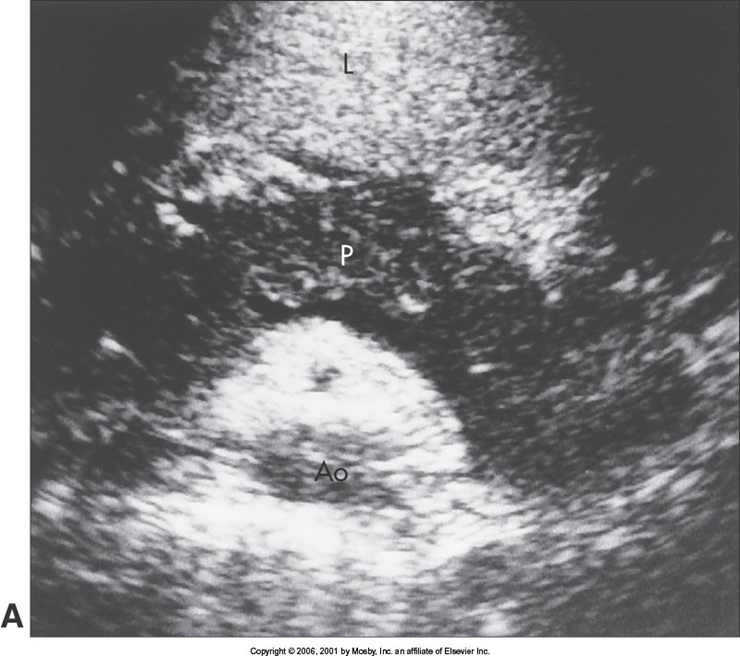
What is this image showing?
Acute Pancreatitis in Children (9 year old with pancreatitis)
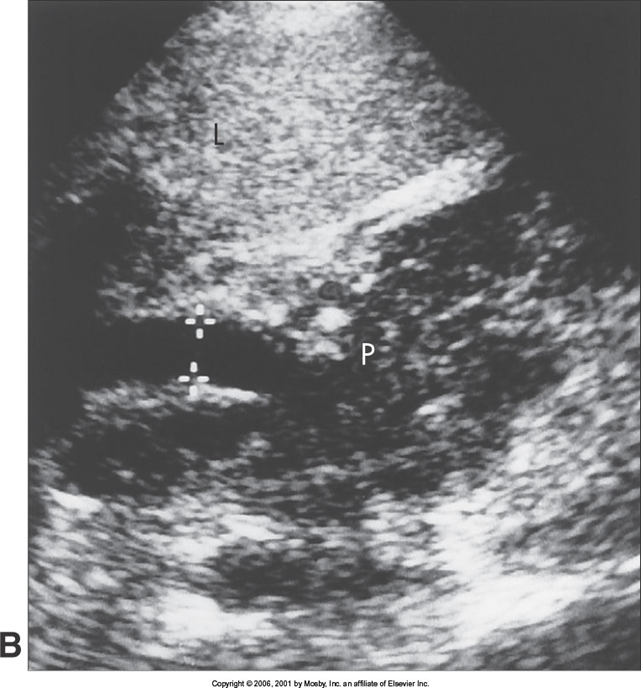
What is this image demonstrating?
Acute Pancreatitis in Children (Dilated CBD)
Where are the most common sites for Extrapancreatic Fluid collections and edema to occur?
Lesser sac
Anterior pararenal spaces
Mesocolon
Perirenal spaces
Peripancreatic soft tissue spaces
When looking at extrapancreatic fluid collections and edema what does it look like?
Anechoic or fine linear lines
What is Chronic Pancreatitis?
Recurrent attacks of acute pancreatitis
What are the causes of Chronic Pancreatitis?
Chronic Alcoholism
Chronic Biliary Disease
Hypercalcemia
Hyperlipidemia
What are the clinical symptoms of Chronic Pancreatitis?
Epigastric Pain
GI problems
Jaundice-CBD obstruction
Sonographically, what are the classic findings of Chronic Pancreatitis?
Calcifications
US Findings for Chronic Pancreatitis:
Hyperechoic
Irregular borders decreased in size
Dilated PD
Ductal Stones
What percentage of pancreatic calcifications are associated with cancer?
25%
What are the complications of Chronic Pancreatitis?
Pseudocysts
PV or SV Thrombosis
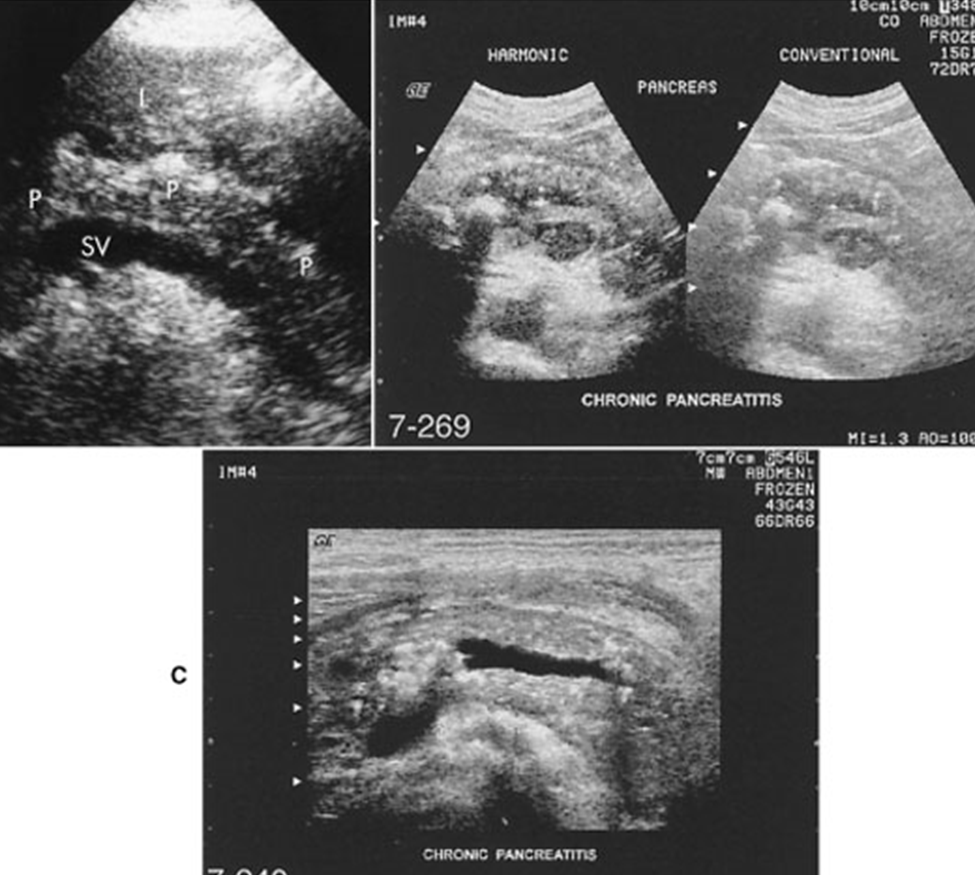
What are these images demonstrating?
Chronic Pancreatitis
What are the complications of pancreatitis?
Fluid collections
Pseudocysts
Bile duct or duodenal obstruction
Ascites
Pancreatic CA
SV Thrombosis
Pseudoaneurysms
Aneurysms secondary to pancreatitis
Splenic artery – most common site
What is the most common complication of pancreatitis?
Pancreatic Pseudocyst
What is a Pancreatic Pseudocyst and where does it arise from?
A collection of fluid
Arises from loculation of inflammatory processes, necrosis or hemorrhage
When does a pancreatic pseudocyst develop?
Develops when pancreatic enzymes escape from gland & break down tissue to form sterile abscess somewhere in abdomen
Usually over 4-6 weeks after onset
What are the causes of Pancreatic Pseudocysts?
Acute pancreatitis
Chronic pancreatitis
Loculation of inflammatory processes, necrosis, hemorrhage
Where are the locations of pancreatic pseudocysts?
Lesser sac
Pararenal space
May become large
What is the regression associated with Pancreatic Pseudocysts?
20% spontaneous regression
Decompression into duct or GI tract
50% Mortality rate with rupture into peritoneal cavity
US appearance of Pancreatic Pseudocysts:
Well-defined mass
Sonolucent interiors
Possible debris and septations
Increased through transmission
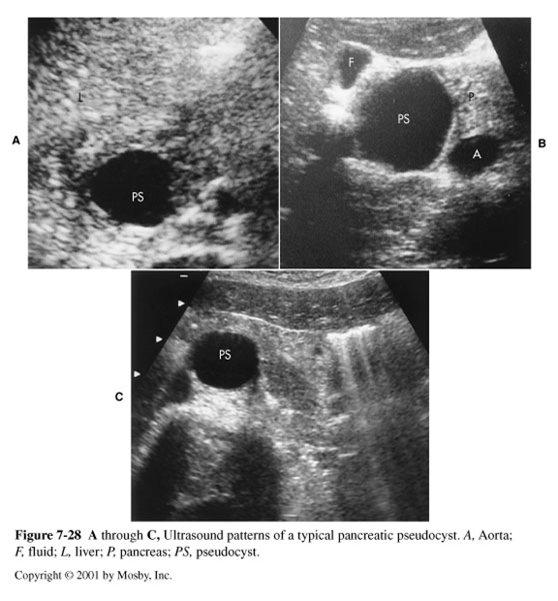
What are these images showing?
Pancreatic Pseudocysts
What are the classifications of Pseudocysts?
Septated
Excessive internal echoes
Pseudocyst without posterior enhancement caused from calcification
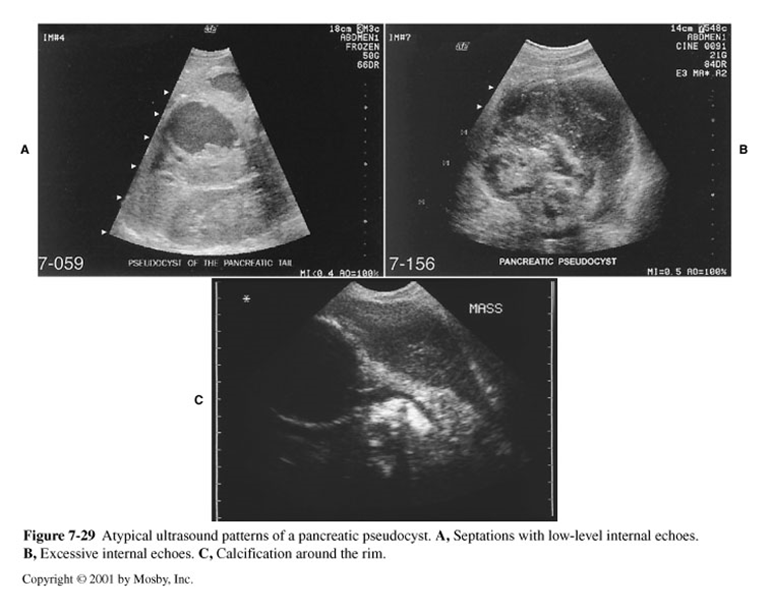
What are these images demonstrating?
Classifications of Pseudocysts
What is the most common complication of Pseudocysts?
Spontaneous rupture
In spontaneous rupture of pseudocysts what percentage ruptures in the peritoneal cavity?
3%
In spontaneous rupture of pseudocysts, what is the mortality rate in the peritoneal cavity?
50%
In spontaneous rupture of the GI tract with a pseudocyst, what is usually shown?
Typical pseudocyst appearance 1st
Then disappearance
What is hemorrhagic pancreatitis?
Rapid progression of Acute pancreatitis
What are the characteristics of hemorrhagic pancreatitis?
Rupture of pancreatic vessels & hemorrhage
Necrosis of pancreatic tissue
Ascites
What are the symptoms of hemorrhagic pancreatitis?
Intense, severe pain
Hypotension
What are the decreased lab values for hemorrhagic pancreatitis?
Decreased hematocrit
Decreased calcium levels
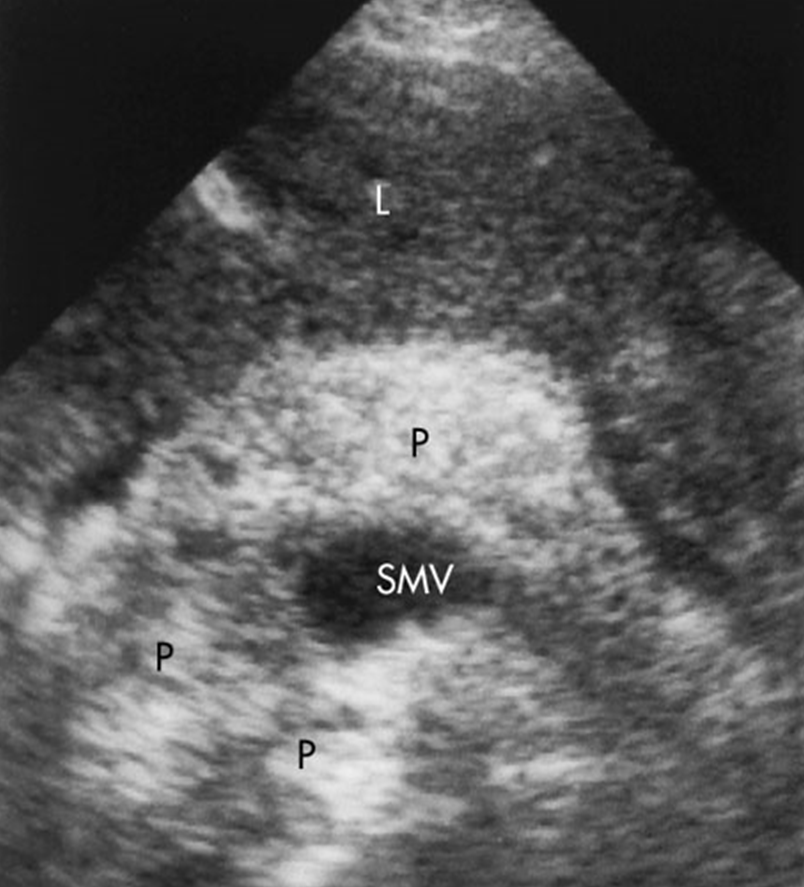
What is this image showing?
Hemorrhagic Pancreatitis
What is Phlegmonous Pancreatitis?
Spread of diffuse inflammatory edema of soft tissues
What does Phlegmonous Pancreatitis look like on ultrasound?
Hypoechoic
ill-defined mass
Good through transmission
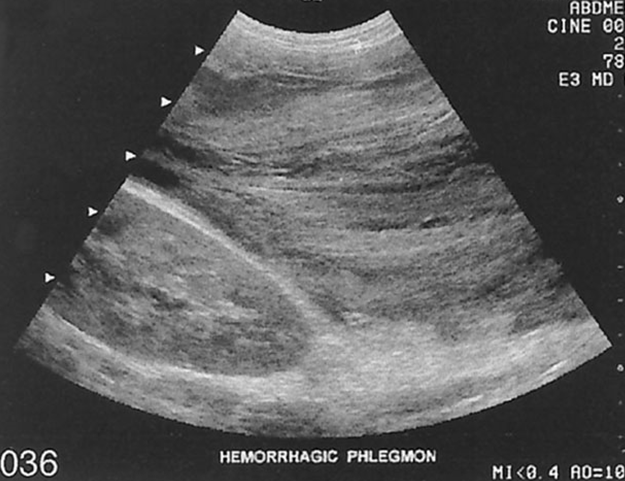
What is this image showing?
Phlegmonous Pancreatitis
A pancreatic abscess is a complication of pancreatitis and has a low incidence of what percent?
1-9 %
What are the clinical symptoms and lab work for a pancreatic abscess?
Fever, chills, Hypotension, Tender abdomen with growing mass
Elevated WBC, Bacteremia
US findings for a pancreatic abscess include:
Hypoechoic mass with smooth or irregular thick walls; unilocular or multilocular
May have air/gas bubbles causing “dirty shadows”
Depends on amount of debris