Unit 9 Key Terms + Key Figures
1/76
Earn XP
Description and Tags
All of the terms specifically listed from the note packet. Key terms are bolded and key figures are underlined. It is highlighted by subsection: 9.1 is red, 9.2 is orange, 9.3 is yellow, 9.4 is green, 9.5 is blue, 9.6 is sky blue, 9.7 is purple, and 9.8 is pink. Each definition should be 1-3 sentences only. 10 terms per subunit and photos for the people
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
Green Revolution
A period of agricultural transformation in the mid-20th century that introduced high-yielding varieties of seeds, increased use of fertilizers and pesticides —> significant increases in food production worldwide. However not all nations could afford fertilizers, fewer jobs as mechanized equipment use increased, and environmental harms such as slash-and-burn methods and pesticide overuse.
Internet
A global system of interconnected computer networks that enables the sharing of information and communication. It revolutionized how people connect, access information, and conduct business.
Globalization
The process by which businesses, cultures, and societies become integrated and interconnected on a global scale —> economic 📈 and cultural 🤝
Supply Chain
The network between a company and its suppliers to produce and distribute a specific product; including the flow of materials and information from suppliers to manufacturers. Shipping containers such as cargo planes and giant tankers facilitate these global chains.
Space Exploration
The study and travel beyond Earth's atmosphere that increased after World War II —> advancements in satellite technology and human spaceflight. Now it’s changed to global knowledge/research of space and private company space efforts.
Norman Borlaug
An American agronomist(crop scientist) and humanitarian known as the "father of the Green Revolution" who developed high-yielding crop varieties and advanced agricultural practices to combat hunger worldwide.
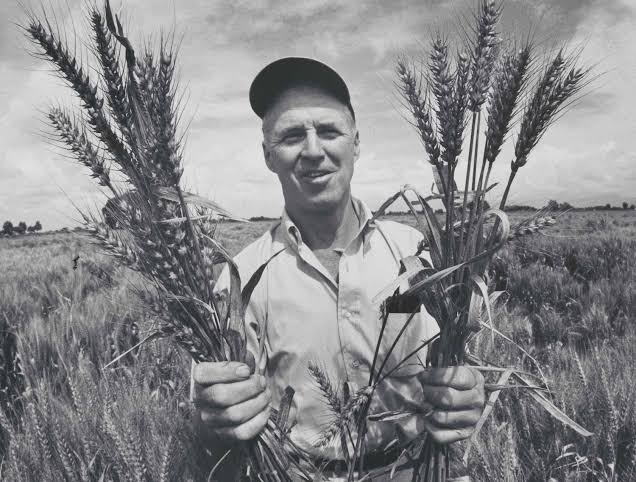

Tim Berners-Lee
A computer scientist best known for inventing the World Wide Web, HTML, and the URL system, enabling the sharing of information via the internet and revolutionizing communication and access to data.
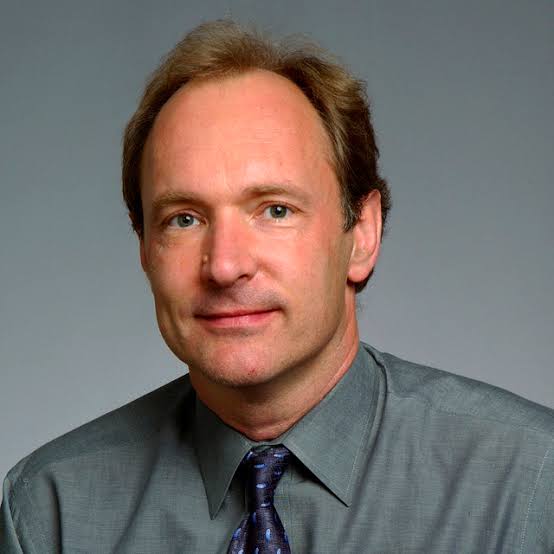

Steve Jobs
An American entrepreneur and co-founder of Apple Inc. —> revolutionizing personal computing and consumer electronics with products like the iPhone and Macintosh. He made devices more commercial and personal forming a market of everyday people.
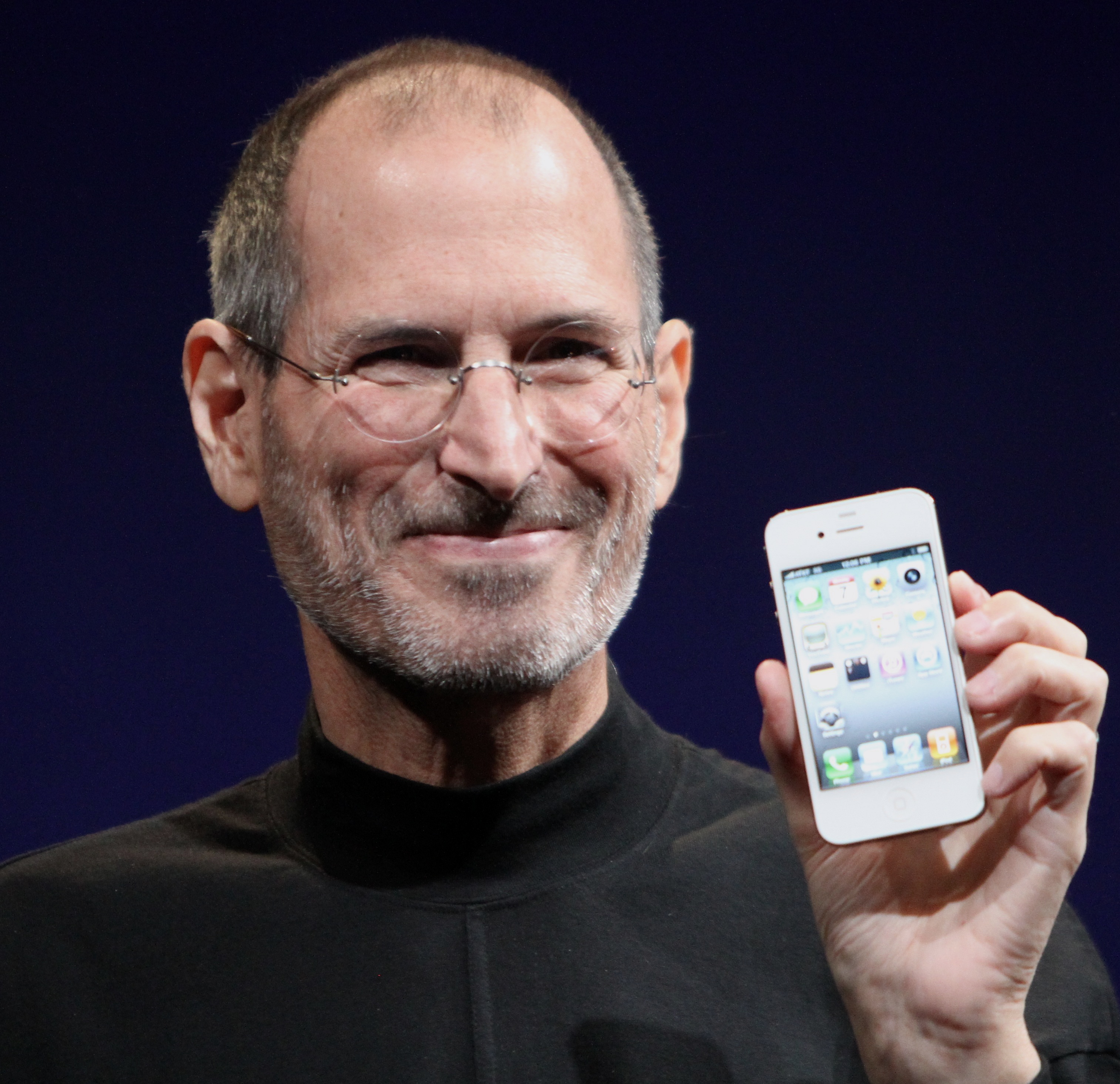

Elon Musk
The world’s richest man and CEO known for founding SpaceX, Tesla, Inc., etc —> significantly impacting space travel, electric vehicles, and renewable energy. Also is a current controversial figure due to his public actions, government involvement, and saying fossil fuels shouldn't be villainize but to make a transition into clean energy.

Jeff Bezos
An American entrepreneur and founder of Amazon, transforming e-commerce and cloud computing, and becoming one of the world’s wealthiest individuals. He also owns the Washington Post and the aerospace company Blue Origin trying to create commercial space travel.

Antibiotics
Medicines used to treat bacterial infections by inhibiting their growth or killing them. They are critical in modern medicine to prevent and treat serious diseases. The first antibiotic, penicillin, was discovered by Alexander Fleming in 1928.
Vaccines
Medicine that stimulate the immune system to provide protection against specific diseases, helping to prevent infections. They have been crucial in controlling and eliminating infectious diseases worldwide. Various diseases have been prevented through vaccination, such as measles, polio, and cholera.
HIV/AIDS (no cure)
A severe disease caused by the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV), which attacks and weakens the immune system, ultimately leading to Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) if untreated. Through vital antiretroviral drugs it manages the condition of your body but the topic is still hard to discuss but changing policy helps provide access to medicine.
COVID-19 Pandemic
A pandemic spreading quickly around the world majorly through 2019-2021. It led to widespread health, economic, and social challenges such as lockdown. Vaccines were developed quickly with global cooperation and research efforts.
CRISPR
A revolutionary gene-editing technology that allows for precise modifications of DNA in organisms. It has applications in medicine, agriculture, and biological research.
Alexander Fleming
A British bacteriologist who discovered penicillin, the first true antibiotic, in 1928, revolutionizing medicine by fighting bacterial infections and saving countless lives. He did warn that infections can develop new strains and become resistant to antibiotics.

Jonas Salk
An American virologist(scientist who studies viruses) who developed the first successful polio vaccine in the 1950s, contributing significantly to the fight against the disease. His work led to the near eradication of polio in many parts of the world. He hoped for everyone to have access to the vaccine

Katalin Karikó
A Hungarian-born biochemist whose research on mRNA technology laid the groundwork for the development of COVID-19 vaccines, specifically the Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna vaccines.
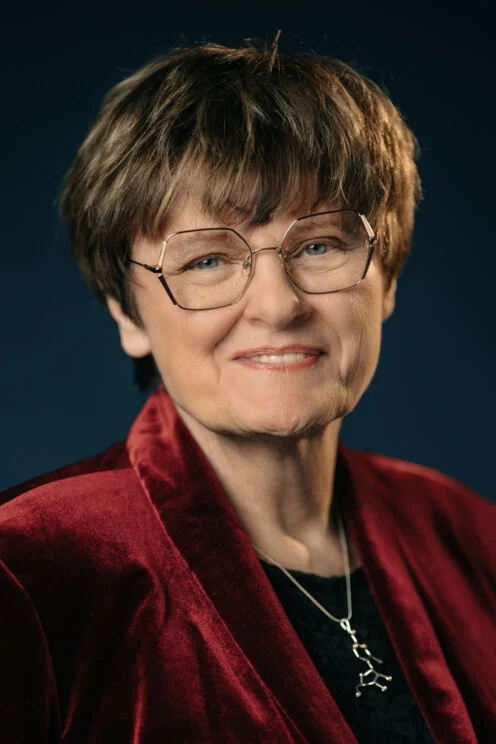

Anthony Fauci
An American physician and immunologist who has played a significant role in guiding the United States' response to infectious diseases, particularly during the HIV/AIDS crisis and the COVID-19 pandemic. He would help inform the people on updating medical developments encouraging people to get vaccinated.
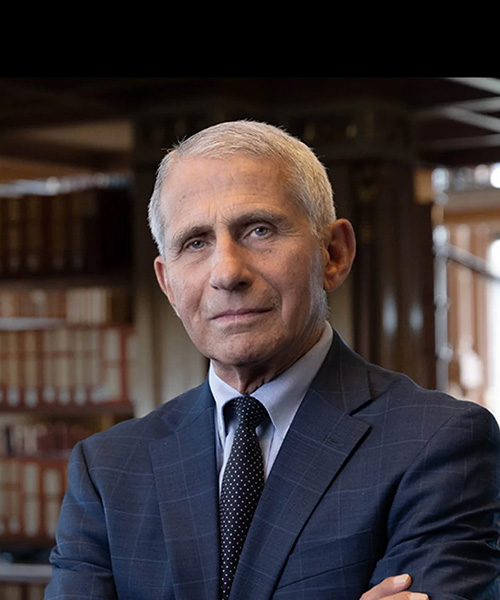

Jennifer Doudna
An American biochemist known for her pioneering work on CRISPR gene editing technology, which has revolutionized genetic research and biotechnology.

Climate Change
Long-term changes in Earth's climate, mainly caused by human activities like fossil fuel combustion and deforestation 📈 global warming, desertification, and deforestation. 📉 supply of fresh water and air quality
Renewable Energy
Energy derived from resources that are continuously replenished (ex. solar, wind and hydroelectric energy) to reduce dependence on fossil fuels but can also be costly.
Deforestation
The removal of trees/forests for agricultural or urban development, contributing to climate change and loss of biodiversity.
Carbon Emissions
The release of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, primarily from burning fossil fuels, contributing to global warming.
Paris Agreement
The Paris Agreement is an international treaty that aims to reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change. Adopted in 2015, it involves commitments from various nations( ex China and the USA) to limit global warming, with the goal of keeping the increase in global average temperature below 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels.
Al Gore
An American politician and environmentalist, Al Gore was VP under Pres. Clinton and promoted climate change awareness, notably through his documentary 'An Inconvenient Truth”
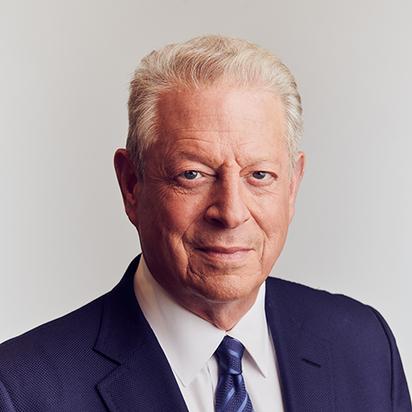

Greta Thunberg
A Swedish environmental activist known for her efforts to raise global awareness about climate change and inspire action. Has participated in civil disobedience and international climate summits(UN 2018); receiving awards for her activism.

Wangari Maathai
A Kenyan environmentalist and activist who founded the Green Belt Movement to combat environmental degradation from colonialism so that rural Kenyan women could plant trees and collect rainwater. She was the first African woman to receive the Nobel Peace Prize.

James Hansen
An American climatology known for his work on advocacy for climate action. He testified before Congress in 1988(which was nuanced topic this time) about the dangers of global warming people stating “99% certainty, that global warming was affecting our planet and should be taken seriously.”

Neoliberalism/economic liberation
A economic philosophy that promotes free-market capitalism. In the 1990s, after the Cold War, various countries had economic liberalization as a result of relaxed restrictions on trade.The privatized state industries and eased trade barriers, leading to expanded global trade and market-oriented reforms.
Free Trade Agreements(FTA)
Treaties between countries that reduce or eliminate tariffs and trade barriers, promoting international trade.
Outsourcing
The practice by companies(MNCs) of relocating business processes(usually manufacturing) to other areas commonly not of home country for lower costs and increase efficiency. It lead to lose of jobs in home country but exploration of workers in developing nations as they had less script labor laws. (Ex. Maquiladoras, Vietnam, Bangladesh)
International Monetary Fund(IMF)
The IMF is an international organization that provides financial aid and advice to countries in economic crisis, aiming to support stability and global trade. It has faced criticism for loan conditions that can harm long-term development in developing countries.
World Bank
An international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of developing countries for the purpose of economic development and reducing poverty.
Milton Friedman
An influential American economist teaching at the University of Chicago known for his advocacy of free-market capitalism. The ‘Chicago Boys’ studying from him made Chile’s unpopular economic reforms. He received the Nobel Prize in Economic Sciences in 1976.

John Maynard Keynes
British economist worked for UK Treasury argued that governments should intervene in the economy during downturns to stabilize it, by increasing spending to boost demand and create jobs. He believed free markets can't always ensure full employment(Keynesian Economics), justifying policies aimed at stability and growth.

Christine Lagarde
A French lawyer and politician who has been the Managing Director of the IMF and was France's Minister of Economic Affairs. She is recognized for her role in global economic policy and promoting international collaboration.

Joseph Stiglitz
An American economist and Nobel Prize winner known for studying information gaps in economics. He was the Chief Economist at the World Bank and criticizes traditional economic ideas. He advocates for reducing inequality in economic policies (progressive capitalism).

Adam Smith
A Scottish economist(capitalist) in the Enlightenment. He authored "The Wealth of Nations," advocating for free-market principles(anti-mercantilism so pro-Laissez-Faire), division of labor, minimal government intervention, can lead to economic prosperity.

Human Rights Movements
Organizations and campaigns that promote and protect fundamental rights and freedoms, focusing on equality/justice, and policy reform while addressing discrimination and oppression. (Ex. Anti-Apartheid Movement and LGBTQ+ Rights Movement)
Feminism
A global social/political movement advocating for women's rights and gender equality. Challenges systemic inequalities and gender-based discrimination. Feminism ideas began during the Enlightenment and made slow progress thereafter.
Environmental Activism
A movement advocating for environmental protection, climate change policies, and global awareness. (Ex. conservation and wildlife campaigns)
Civil Rights
Movements to end discrimination and ensuring equal rights for all individuals(particularly marginalized groups), through legal reform and social activism. (Ex. Civil Rights Movement for African American racial equality in 1960s 🇺🇸)
Decolonization
Decolonization is the process by which colonies gain independence from colonizing powers, often driven by nationalist movements. While some transitions were peaceful, others involved violent struggles as native populations fought to reclaim sovereignty.
Martin Luther King Jr.
A prominent leader in the 🇺🇸 Civil Rights Movement, known for his use of nonviolent protest(civil disobedience) and impactful speeches. Dr. King was influenced by Gandhi's teachings of nonviolent resistance in India decolonization

Malala Yousafzai
A Pakistani activist for female education and the youngest Nobel Prize laureate. Malala is known for her advocacy of girls' right to education.

Nelson Mandela
A South African anti-apartheid revolutionary, political leader who served as President from 1994 to 1999. Mandela is celebrated for his leadership in fighting racial oppression.

Betty Friedan
An American writer/activist best known for her book The Feminine Mystique (1963) which challenged traditional roles of women in society and sparked the second wave of feminism.

Popular Culture
The cultural activities, products, and trends that are widely accepted and consumed by the general public. It relates to mass appeal, commercialization, keeps evolving, and influenced by other global ideas.
Digital Media
Digital media refers to media/content created, stored, and shared in digital form (ex. the internet, social media, information broadcast through radios)
Cultural Diffusion
The spread of cultural traits/practices and social activities from one group to another, influencing the diverse ideas present in various areas —> process happens through migration, colonization, or mass media
Hybridization
The process of combining different cultural elements to create new forms of culture, often seen in music, cuisine, and art, resulting from cultural interaction.
Soft Power
The ability to influence others(and fostering relationships) through attraction and common culture, and promotion of values that resonate with others, rather than coercion. ❌💣 ✅🤝
Taylor Swift
A pop star based in the U.S with billions of listeners around the world. Even as a single figure she creates/influences trend worldwide(ex. new waves of emotional music + activism for voting rights in U.S.)

BTS
BTS is a K-pop boy group from South Korea with one of the largest global fanbases. They blend Korean culture with global music trends(ex. incorporating English) —> gaining fans worldwide.

Hayao Miyazaki
Renowned Japanese animator known for his imaginative films exploring nature and the human experience. Co-founder of Studio Ghibli; his work has spread globally through a unique art style, iconic characters, and universal themes.

Steven Spielberg
American filmmaker known for directing blockbuster movies becoming integral to pop culture. His work feature innovative techniques that have shaped modern cinema. (Ex. 🦈🌊, 🦖🌳, 👽💖)

Mark Zuckerberg
Co-founder and CEO of META, revolutionized global communication with Facebook, Instagram, etc —→ his inventions shaped online interactions leading to more cultural spread and ideas worldwide.

Protectionism
An economic policy aimed at shielding a country's domestic industries from foreign competition (imports) by imposing tariffs and trade barriers.
Nationalism
A political ideology based in loyalty and patriotism toward one’s nation, prioritizing national interests. It drives unity through shared culture and —→ lead to movements for self-determination or even annexation
Anti-Globalization Movements
Collective efforts against the negative impacts of globalization. Advocating for local economies, labor rights, and environmental protections.
Economic Inequality
The gap in income/wealth between different groups in a society; it can form barriers to social mobility. Economic inequality various throughout different countries (Ex. the disparity in wealth distribution in developed vs developing nations)
Cultural Preservation
The practice of maintaining and protecting cultural heritage, traditions, and identity against the influences of globalization and cultural homogenization
Donald Trump
45th President of 🇺🇸, known for his controversial policies and strong stance on immigration and trade. He imposed protectionist tariffs in hopes of getting manufacturing to US.
Marine Le Pen
🇫🇷 politician and leader of the National Rally party(far-right), known for her positions on extreme nationalism, anti-immigration, and Euroscepticism.

Narendra Modi
Prime Minister of 🇮🇳, known for his economic reforms(Ex. allowing more foreign investment in several industries) and policies promoting religious Hindu nationalism. India benefits from globalization/trade as it increases GDP.

Xi Jinping
President of 🇨🇳 (Chinese Communist Party) Centralized power, economic reforms, and strict censorship. China has become a top global exporter with large manufacturing industry and skilled workforce. through his leadership. As a permanent member of the 🇺🇳 Security Council, China can veto any resolution, influencing global security and diplomatic decisions.

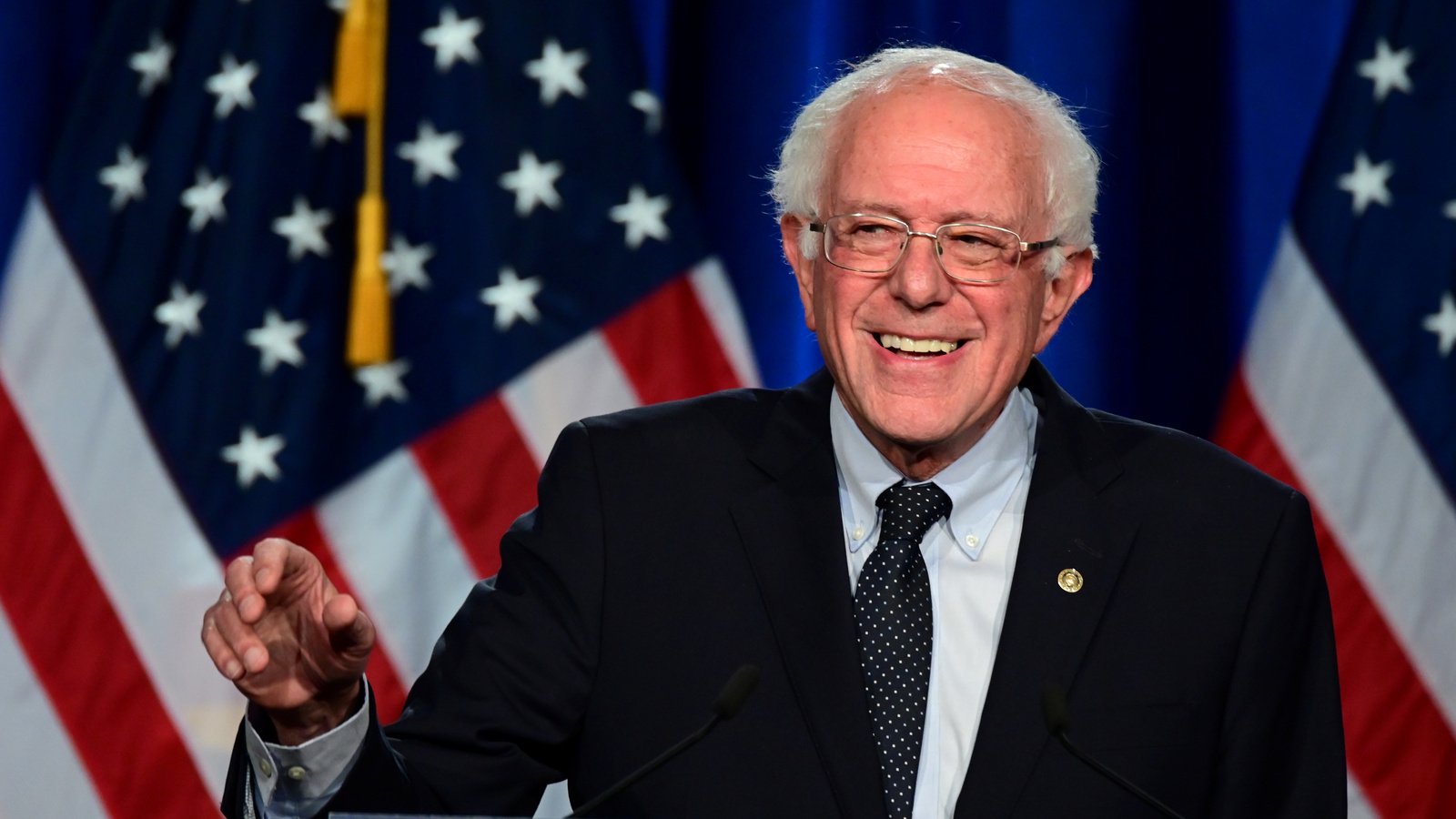
Bernie Sanders
US independent senator known for his progressive policies advocating for social justice, healthcare reform, and income equality. Called a modern-day socialist.

United Nations 🇺🇳
International organization created in 1945 at the end of WWII by the Allies. To maintain world peace and foster cooperation. It operates through committees like the Security Council and the General Assembly, where all member states are represented. The UN also promotes human rights, provides humanitarian aid, education, etc. Has received backlash for giving the powerful nations too much sway with voting.
World Trade Organization (WTO)
An international organization that regulates trade; established to promote fair trade practices among member countries. It provides a framework for negotiating agreements and resolving disputes. Has received backlash because people claim it is swayed by the largest companies and industries.
European Union (EU) 🇪🇺
A political and economic union of 27 European countries promoting integration, cooperation, and stability, facilitating free trade, movement, and governance among member states. Example of EU Benefits is a company in 🇩🇪 can easily sell its products to customers in 🇫🇷 without facing trade barriers.
African Union (AU)
A continental union consisting of 55 African countries aimed at promoting unity, peace, and development across the continent. It addresses issues such as economic development, political stability, and human rights.
G20 Summit
An international forum for governments and central bank governors from 19 countries and the European Union, focused on global economic governance, international financial stability, and sustainable development.
António Guterres
Ursula von der Leyen
Ngozi Okonjo-Iweala
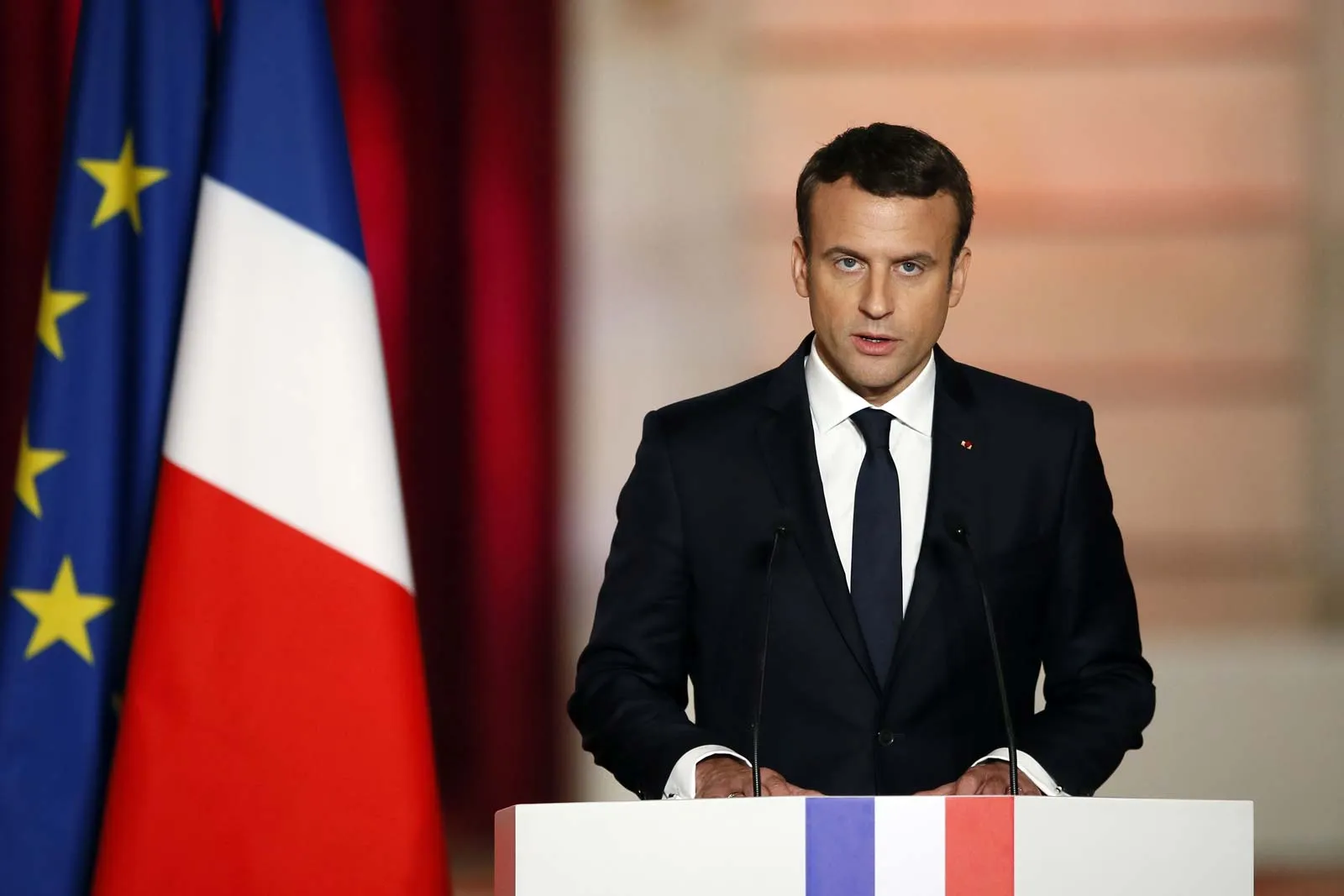
Emmanuel Macron
