8th grade History STAAR Review
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
Jamestown
-1607-First successful colony in the New World
-Struggled due to poor resources and lack of skilled workers
-Present day state of Virginia

Reasons for Exploration
-Social
-Political-gain new land
-Religious-spread Christianity
-Economic-looking for the Northwest Passage, gold, spices

Mayflower Compact
1620-self-government of the Pilgrims

Virginia House of Burgesses
First representative assembly in North America

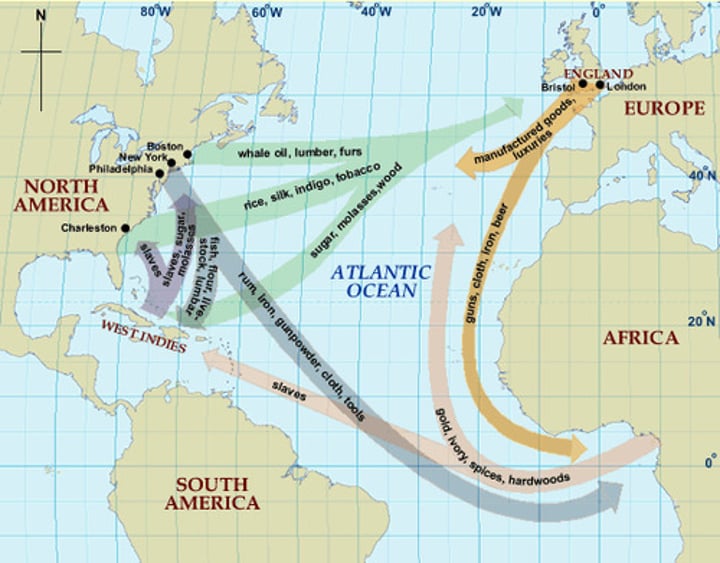
Triangular Trade
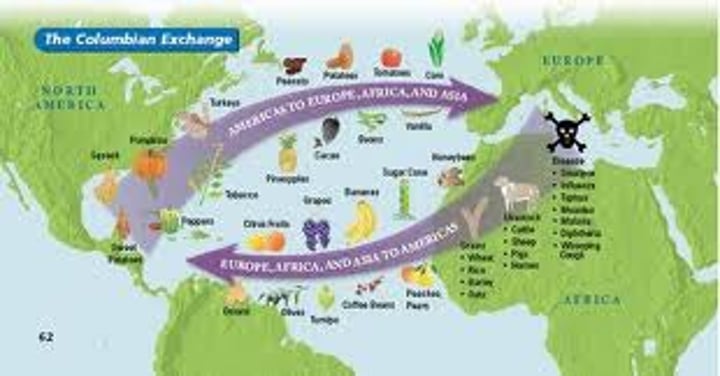
Colombian Exchange
Mercantilsim
-Colonies support the mother countries economy
-Can't trade with anyone except the mother country
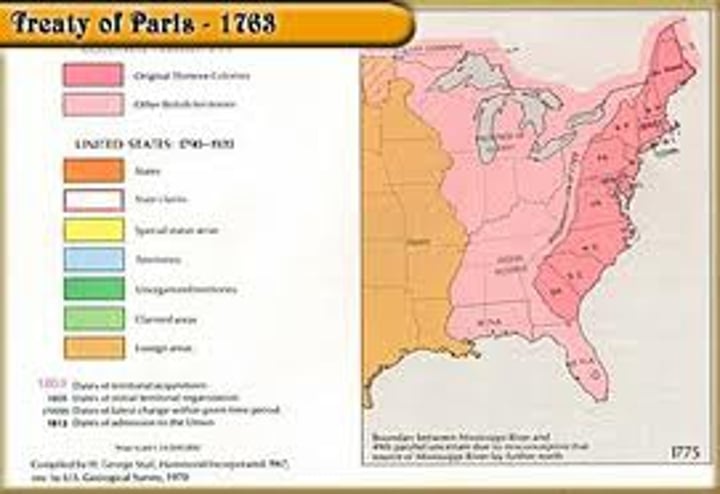
Treaty of Paris-1763
-Ended the French and Indian War
-Britain gained land from the French
-Britain began taxing the colonists to pay for the war
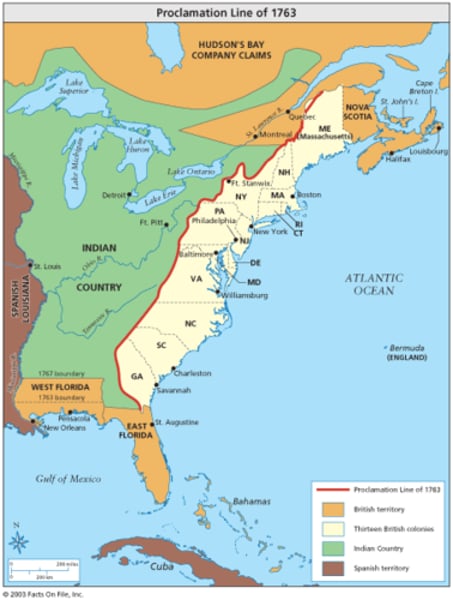
Proclamation of 1763
-Colonists weren't allowed to settle west of the Appalachian mountains
-King George couldn't afford to pay for protection if the colonists moved west
Townshend Acts
Tax on imported goods: tea, glass, lead, paint

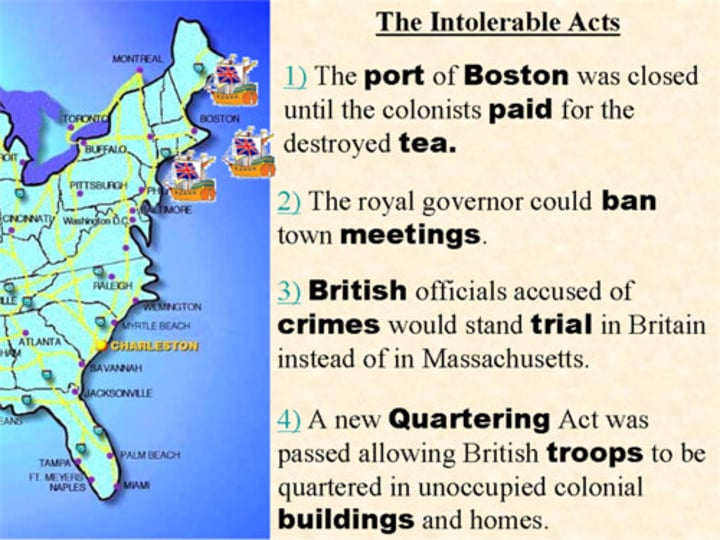
Intolerable Acts
-Closed Boston Harbor
-No town meetings
-Quartering soldiers
-British officials accused of crimes were tried in England
Declaration of Independence
-1776-Colonies declared independence from Britain
-Based on the ideas of John Locke and Charles de Montesquieu
-Written by Thomas Jefferson
-A list of grievances (complaints) against King George

Yorktown
-Last battle of the American Revolution
-Lord Cornwallis surrendered after the French blockaded him at sea and he was surrounded by Lafayette and Washington on land
John Locke
-Said government is developed by the people
-Inalienable rights: Life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness

English Bill of Rights
-Guaranteed citizens certain rights
-Influenced the American Bill of Rights
George Washington
-Commander-in-Chief of the Continental Army
-First U.S. President
-Set precedents (Mr. President. posing for a portrait, setting up a cabinet, serving only two terms, farewell address)
-Warned against forming political parties
-Encouraged American to stay neutral-out of other countries business

Samuel Adams
Leader of the Sons of Liberty-a group dedicated to gaining independence from Britain

Benjamin Franklin
-Diplomat and founding father
-Helped write the Declaration of Independence
-Got France's support in the American Revolution

Alexander Hamilton
-First Secretary of the Treasury
-Leader of the Federalist Party
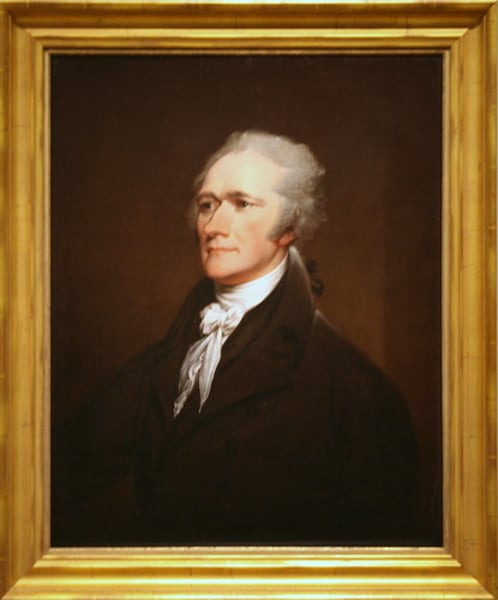

James Madison
-"Father of the Constitution"
-Author of the Federalist Papers
-4th President
-President during the War of 1812
Thomas Paine
-Wrote Common Sense
-Supported independence from Great Britain

Articles of Confederation
-First government in the U.S.
-Could not tax, no army to put down a rebellion, had only one branch (Congress)

Constitutional Convention
1787-Wrote a new constitution
Shays Rebellion
-Daniel Shays led a rebellion over taxes
-The rebellion led leaders to realize the Articles of Confederation were too weak

Federalists
-Supported a strong central government and the Constitution
-Loose interpretation of the Constitution

Anti-Federalists
-Supported a strong state government and wanted the Bill of Rights added to the Constitution
-Strict interpretation

War of 1812
-Second fight for independence with Britain
-England tried to prevent the U.S. from trading with other countries
-England kidnapped (impressed) our sailors and forced them into the British Navy
-U.S. maintained independence and led to the "Era of Good Feelings"
-Started the American Industrial Revolution
Era of Good Feelings
-Period after the War of 1812
-U.S. proved it could protect itself
-Americans felt more Patriotic
Popular Soverignty
Government was created by the people who have the power

Republicansim
Government in which the people are represented by representatives that they elect

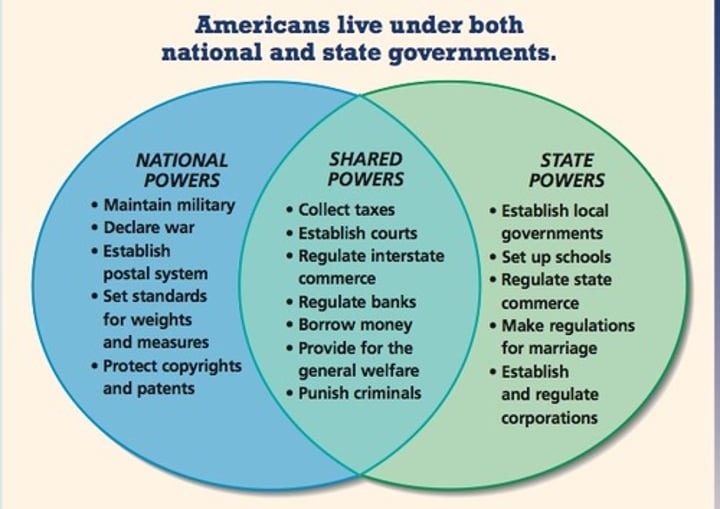
Federalism
Power is divided between the state and national government
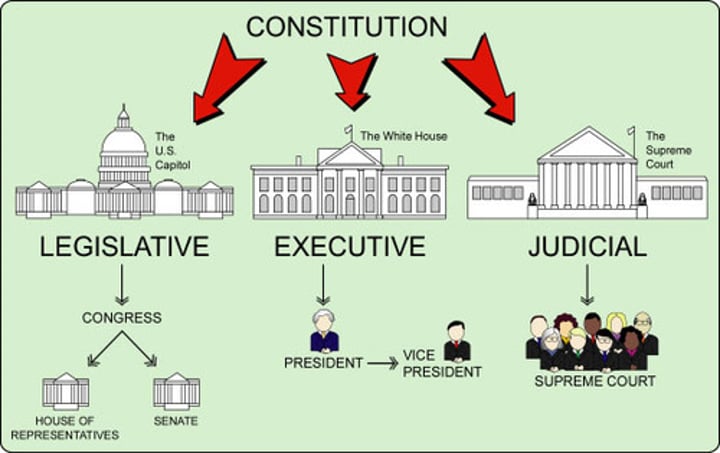
Separation of Powers
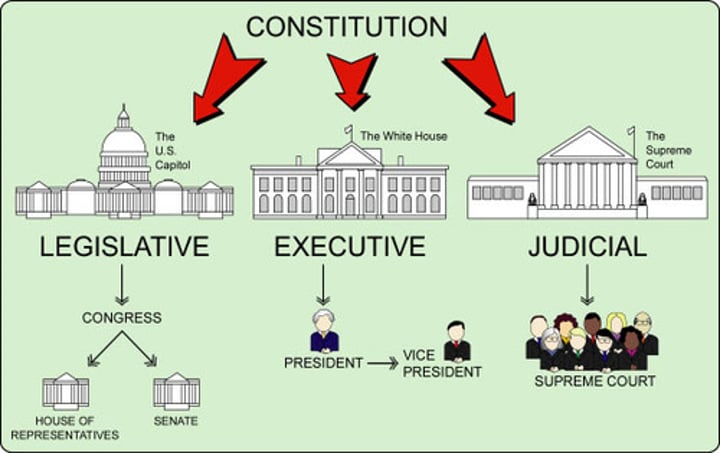
The government is divided into three branches: Legislative, Executive, and Judicial
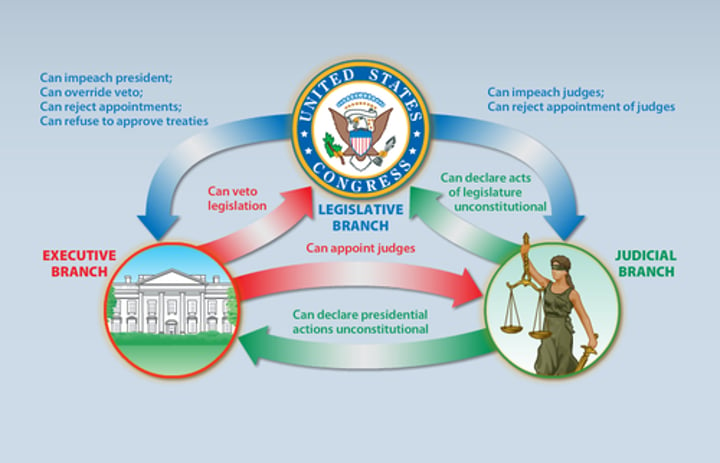
Check and Balances
Each branch checks on the others to make sure they are working like they are supposed to
Limited Government
Limits on the government protect the public

Individual Rights
Bill of Rights protects individual rights from the power of the government

1st Amendment
Freedom of speech, religion, press, petition, and assembly

2nd Amendment
Right to bear arms (keep guns)

3rd Amendment
No quartering (housing) of troops during times of peace

4th Amendment
Protection from unreasonable search or seizure

5th Amendment
No one can be tried for a serious crime unless indicted (accused) by a grand jury
No one can be forced to testify against herself or himself. No one can be punished without due process of law
People must be paid for property taken for public use
Cannot be tried for the same crime twice

6th Amendment
Right to have a jury for criminal trials
Right to a speedy, public trial
Right to a lawyer
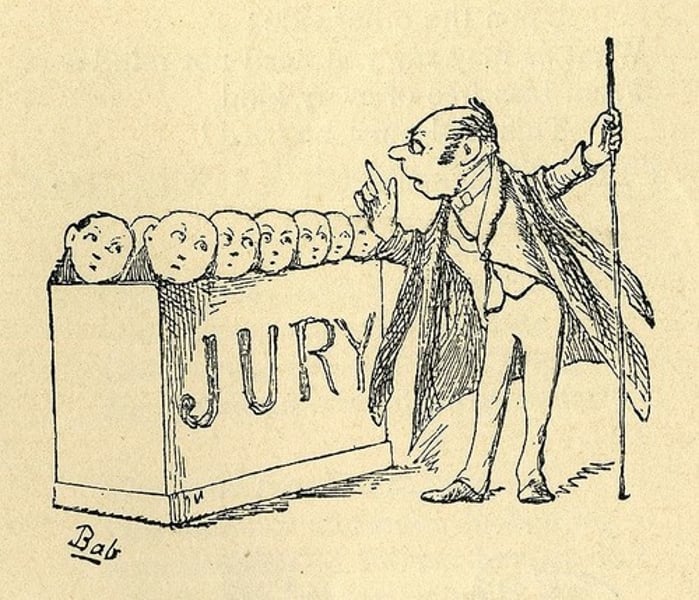
7th Amendment
Right to a jury in a civil trial

8th Amendment
No cruel or unusual punishment
No excessive bail

9th Amendment
This amendment means that the rights that are not listed in the Constitution cannot be taken away

10th Amendment
Powers not listed in the Constitution are reserved for the states

John Adams
-2nd President
-XYZ Affair-France demanded a bribe to talk to Americans
-Alien and Sedition Acts-The Alien and Sedition Acts of 1798 were a collection of four laws that were passed by Congress in the aftermath of the French Revolution and during the Quasi War with France-Increased time for immigrants to become an American citizen and did not allow the press to speak badly about the government
Thomas Jefferson
-3rd President
-Purchased the Louisiana Territory from France in 1803
-Approved the Embargo Act of 1807, restricting trade with any country

James Monroe
-5th President
-Issues the Monroe Doctrine
Monroe Doctrine
-Stated North America was closed to colonization from any other country
-No one could come into the Western Hemisphere
Mexican War
-American and Mexico argued over the border of Texas and Mexico and who Texas belonged to
-Mexico said they owned Texas and the border was the Nueces River
-U.S. said they owned Texas and the border was the Rio Grande River
-U.S. won
-Ended with the Treaty of Guadalupe Hildalgo
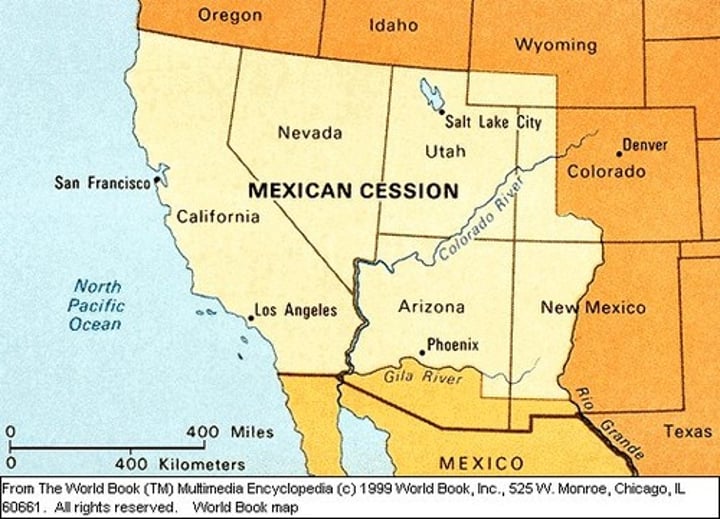
Mexican Cession
-Land gained after the Mexican War
-Helped complete Manifest Destiny
James K. Polk
-President during the Mexican War
-Supporter of Manifest Destiny
-Helped gain the Oregon Territory-54-40 or Fight
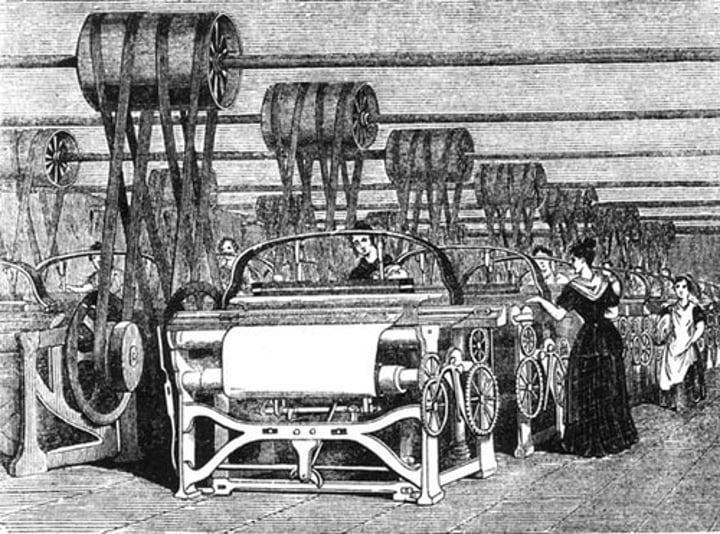
Industrial Revolution
-America began to manufacture their own goods
-Led to urbanization (moving to cities)
-Led to the discovery of many inventions
-Took place in the North
Free Enterprise System
-Government does not control business, but regulates it
-Businesses can produce any thing they want
-Motivated by profit (making money)
Transcendentalism
Spiritual world is more important than the physical world

Hudson River School
-Opened by Thomas Cole
-Famous for painting natural landscapes

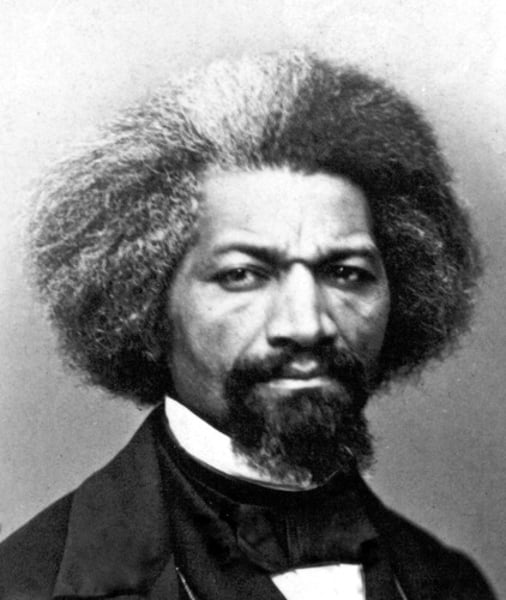
Frederick Douglas
Former slave who fought for abolition and wrote the North Star

Emancipation Proclamation
-Issues by Abraham Lincoln during the Civil War, freeing all slaves in the rebelling states
-Used as a war strategy
Battle of Gettysburg
Humiliating loss for Lee; he never tried to invade the North again

Reconstruction
-Process of putting the nation back together after the Civil War
-Lincoln did not want to punish the south, but to treat them with kindness

Freedmen's Bureau
Helped to feed, clothe, and educate former slaves

Reconstruction Admendments
13-Free
14-Citizens
15-Vote
John C. Calhoun
Vice-President of U.S. who led supported the Nullification Crisis
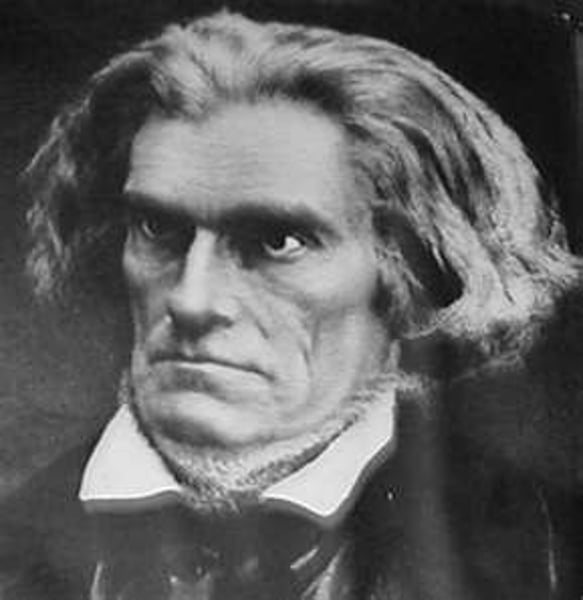

Nullification Crisis
South Carolina wanted the government to nullify (cancel) the tariff and threatened to secede from the Union if they did not
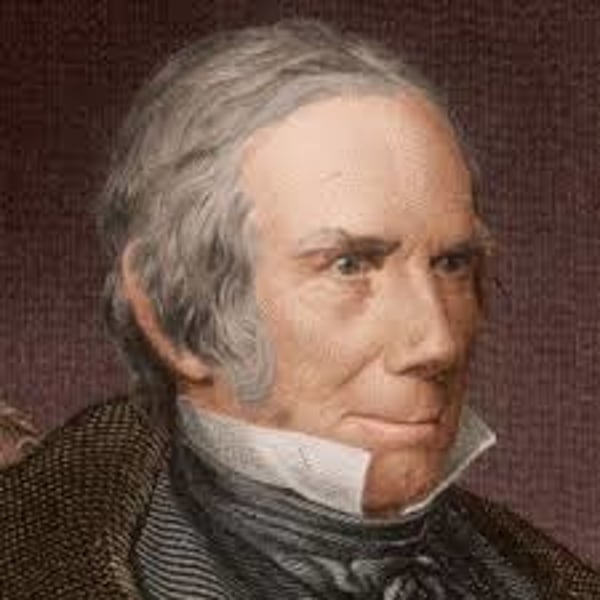
Henry Clay
Known as the Great Compromiser; created the Missouri Compromise, the Compromise of 1850, and helped end the Nullification Crisis

Marbury v. Madison
-Said the Supreme Court has the right to review all laws made by Congress
-Strengthened the federal government

Worcester v. Georgia
Cherokee Nation sued Georgia to keep their land and won, but were removed by Andrew Jackson anyway
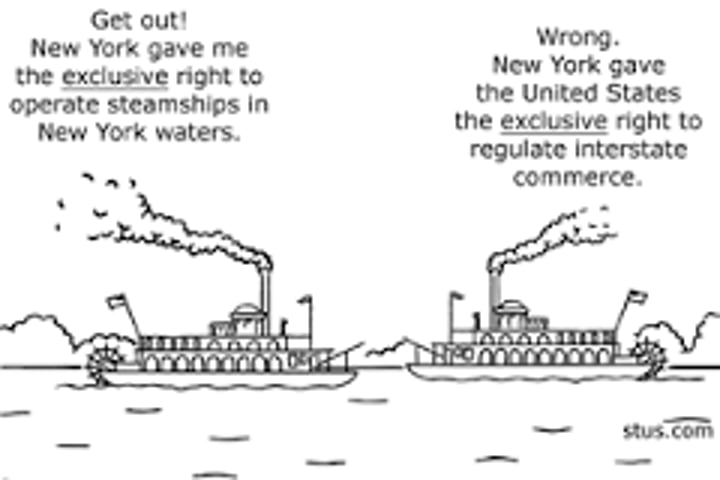
Gibbons v. Ogden
Said that the federal government had the power to regulate trade between the states
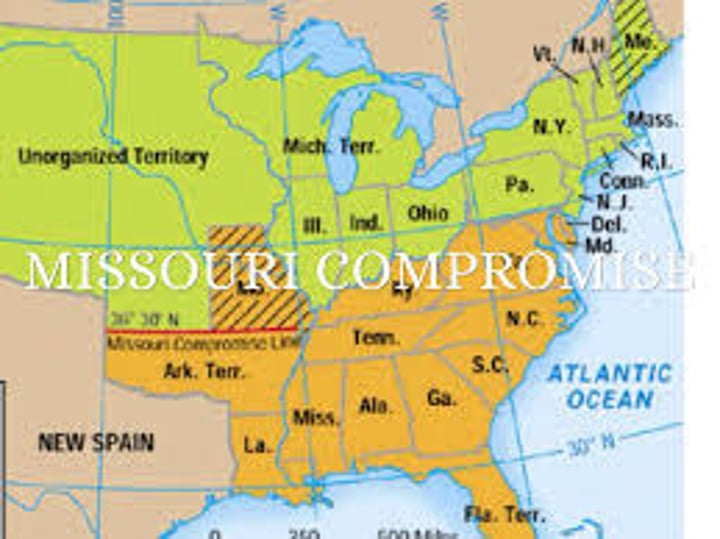
Missouri Compromise
1820-Admitted Missouri as a slave state and Maine as a free state; maintained the balance of power in Congress
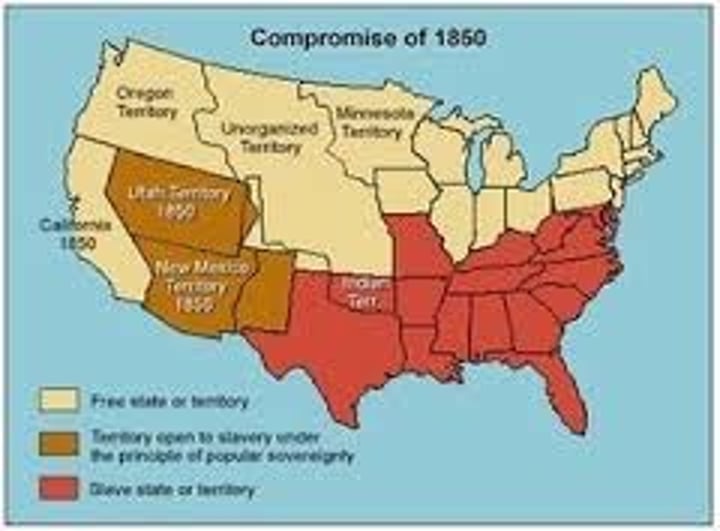
Compromise of 1850
Preserved the balance of free and slave states; California was admitted as a free state; no slave trade in D.C.
Homestead Act
A person could claim 160 acres of land in western territories

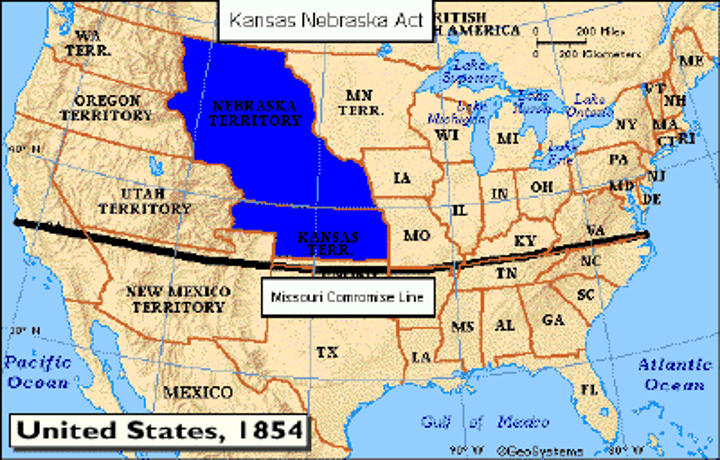
Kansas-Nebraska Act
Split the territory into two and allowed the individual territories to vote on slavery
1st Great Awakening
Religious revival in the 1700's

2nd Great Awakening
Religious revival in the 1800's that led to social reform

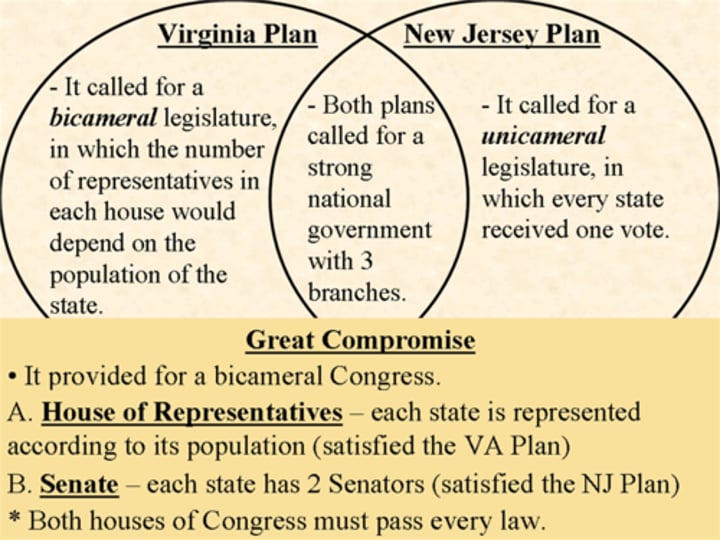
New Jersey Plan
Number of representatives in Congress is based on equal representation
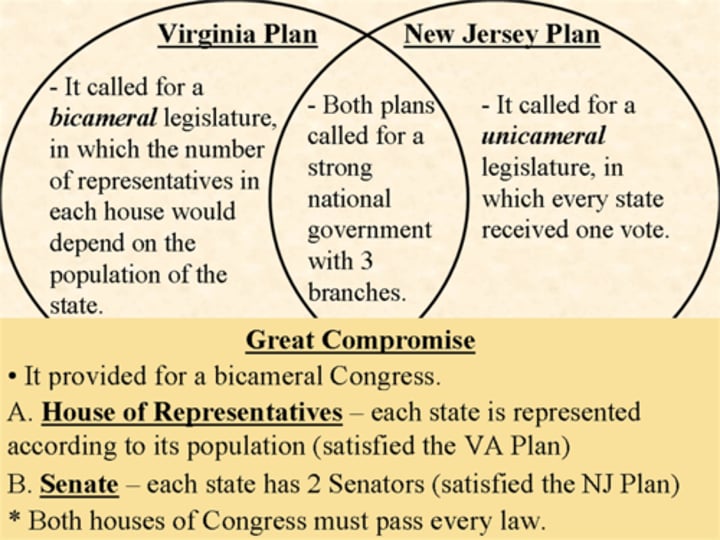
Virginia Plan
Number of representatives in Congress is based on population
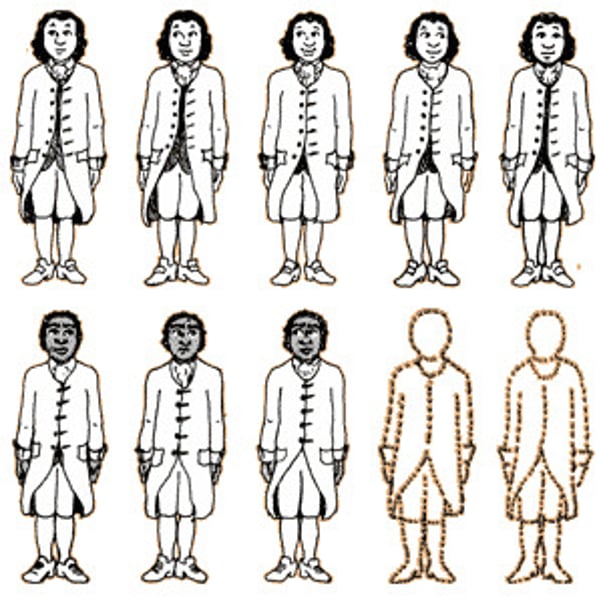
3/5 Compromise
3/5 of the slave population in would count toward the population census

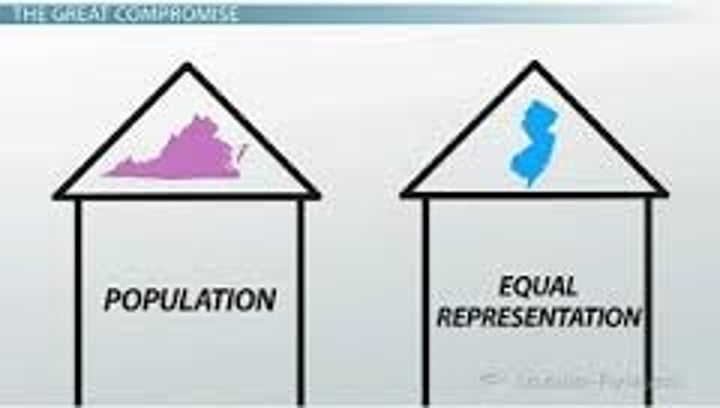
The Great Compromise
-Created a two house legislature--bicameral
-House of Reps-based on population
-Senate-based on equal representation
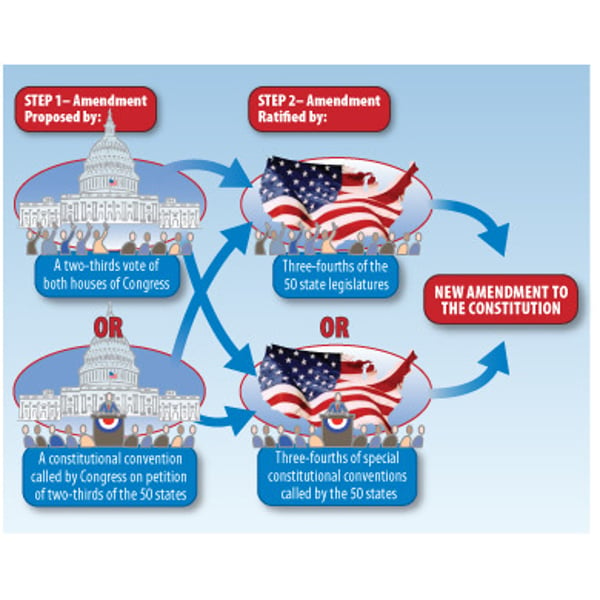
Amending the Consitituion
-The Constitution can be amended
-Amendment is proposed by 2/3 of Congress and ratified by 3/4 of the states
Legislative Branch
Makes the laws
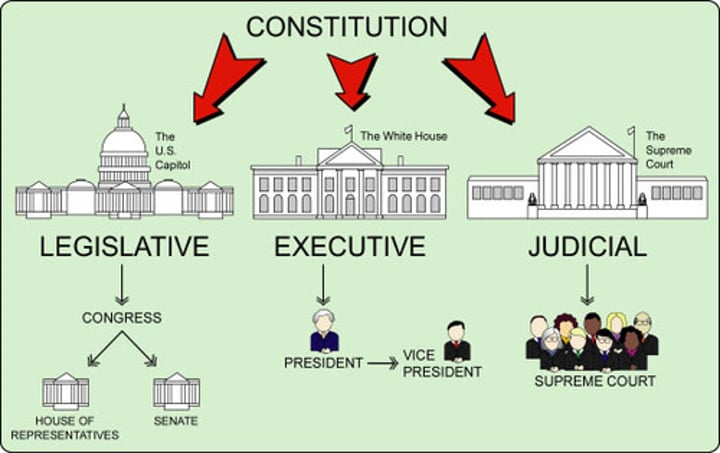
Executive Branch
Enforces the laws
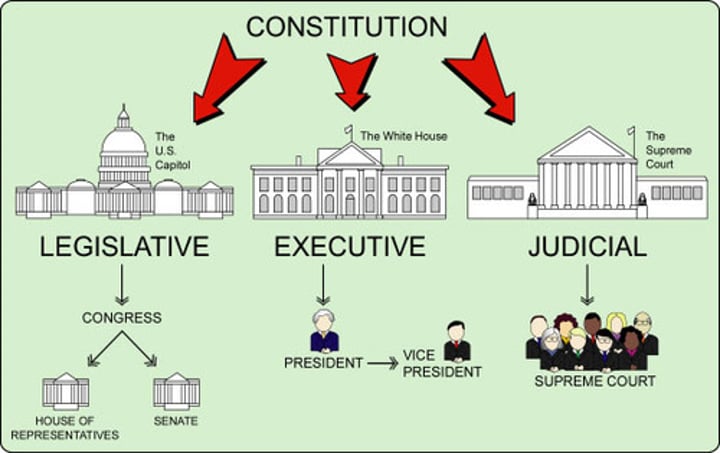
Judicial Branch
Interprets the laws
1776
Declaration of Independence written

1787
Constitution is written
