Foley Catheter Insertion
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Sterile Technique
Method to prevent contamination during procedures.
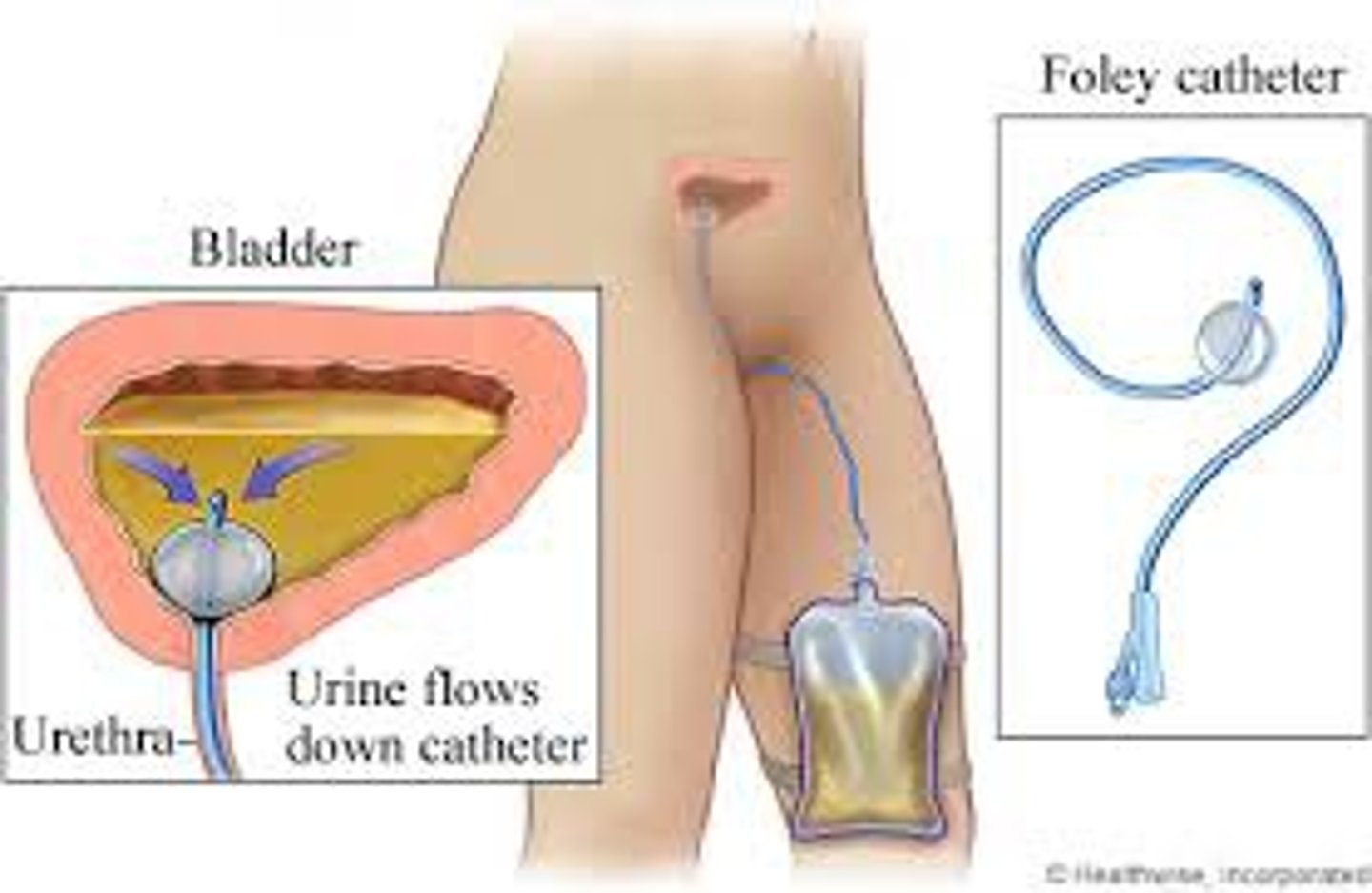
Foley Catheter
A tube inserted into the bladder for urine drainage.
Contraindications of Foley
latex allergy, iodine allergy, adhesive allergy
Perineal Care
Cleaning the genital area before catheter insertion.
Dorsal Recumbent Position
Female patient lying on back with knees bent.
Supine with legs open
Male patient lying on back with hips open wide.
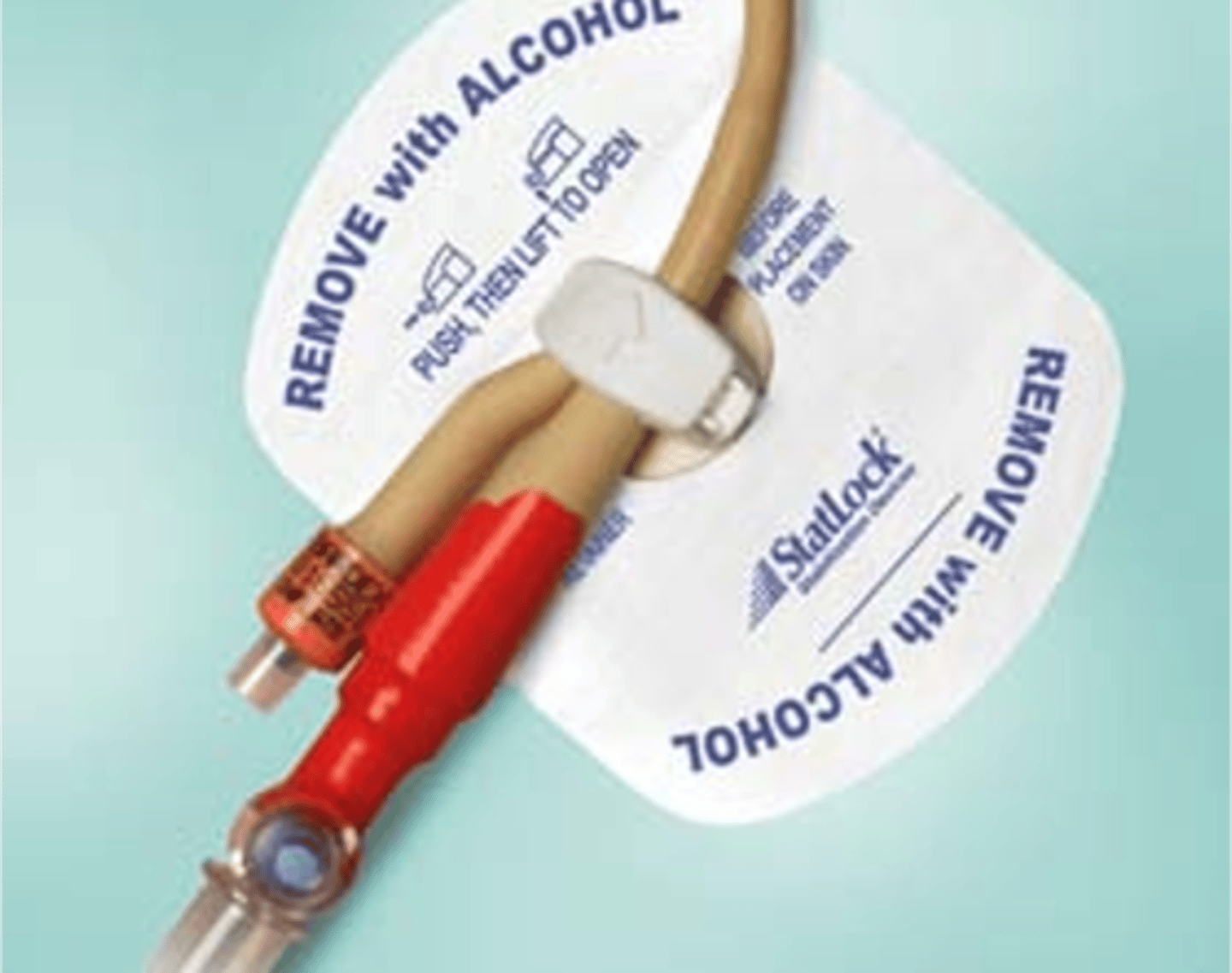
Catheter Stabilizer Device
Device to secure catheter after insertion attached to the thigh
Urinary Meatus
Opening for catheter insertion in the urethra.
Foreskin Retract
Pull back foreskin for uncircumcised patients.
Sterile Gloves
Gloves used to maintain a sterile field.
Fenestrated Drape
Drape with an opening for catheter insertion.

Syringe Attachment
Connecting syringe to catheter balloon port.
Catheter Lubrication
Applying lubricant to catheter for smooth insertion.
Labia Minora Separation
Holding labia apart for female catheterization.
Penis Positioning
Holding penis at right angle for male catheterization with foreskin retracted.
Urinary Cleansing
Cleaning meatus from front to back for females.
Circular Cleansing
Cleaning meatus in circular motions for males.
Patient Instruction
Asking patient to bear down during insertion to open urethra further.
Catheter Insertion Depth
Insert until urine flows, then advance 1-2 inches for females, for males insert all the way to the Y port.
Catheter Holding
Secure catheter at least 1 inch from meatus with opposite hand.
Balloon Inflation
Inflating balloon after catheter insertion for retention. (10 mL)
Patient Discomfort Inquiry
Ask patient about discomfort during balloon inflation, discomfort can indicate balloon is in the urethra and can cause urethral rupture.
Catheter Balloon Inflation
Inflate catheter balloon slowly with dominant hand.
Catheter Release Technique
Release catheter from non-dominant hand, pull gently until resistance is felt.
Foreskin Replacement
Replace foreskin on male manikin after procedure.
Catheter Securement
Secure catheter in device, arrow points to head.
Catheter Bag Attachment
Attach bag below bladder level, avoid loops. Loops can cause backflow of urine and infection.
Assistive Personal can...
Assist the nurse with patient positioning, focus lighting for the procedure, maintain privacy, empty urine from collection bag, and help with perineal care.
Report postprocedure patient discomfort or fever to the nurse.
Report abnormal color, odor, amount of urine in drainage bag, and if the catheter is leaking or causes pain.
Must review patient's EHR for previous catheterization and response
Identifies purpose of inserting catheter (such as for measurement of PVR, preparation for surgery, or specimen collection) and potential difficulty with catheter insertion.
Review EHR for any pathological or anatomical conditions that may impair passage of catheter
(e.g., enlarged prostate gland in men, urethral strictures).
Ask patient and check EHR for history of allergies. Check allergy bracelet.
Catheter made of different material is needed if patient has latex allergy.
Assess for pain and bladder fullness.
Palpation of full bladder causes pain and/or urge to void, indicating full or overfull bladder.
Expected Outcomes following completion of the procedure
Patient's bladder is not palpable.
Patient verbalizes absence of abdominal discomfort or bladder pressure/fullness.
Patient has urine output of at least 30 mL/h as measured in urinary drainage bag.
Position portable light to illuminate genitals or have assistant available to hold light.
Adequate visualization of urinary meatus assists with accuracy of catheter insertion.
Evaluation of proper catheterization
Palpate bladder for distention or use bladder scan as per agency protocol.
Indwelling catheter: Determine that there is no urine leaking from catheter or tubing connections.
Ask patient to describe level of comfort and if sensation of bladder fullness was relieved.
Observe character and amount of urine in drainage system.
Catheter goes into vagina
• Leave catheter in vagina.
• Clean urinary meatus again. Using another catheter kit, reinsert sterile catheter into meatus (check agency policy). NOTE: If gloves become contaminated, start procedure again.
• Remove catheter in vagina after successful insertion of second catheter.
Sterility is broken during catheterization by nurse or patient.
• Replace gloves if contaminated and start over.
• If patient touches sterile field but equipment and supplies remain sterile, avoid touching that part of sterile field.
• If equipment and/or supplies become contaminated, replace with sterile items or start over with new sterile kit.
Patient complains of bladder discomfort, and catheter is patent as evidenced by adequate urine flow.
• Check catheter to ensure that there is no traction on it.
• Notify health care provider. Patient may be experiencing bladder spasms or symptoms of urinary tract infection (UTI).
• Monitor catheter output for color, clarity, odor, and amount.
Documentation
Document reason for catheterization, type and size of catheter inserted, amount of fluid used to inflate balloon, specimen collection (if applicable), characteristics and amount of urine, patient's response to procedure, and evaluation of patient learning. Document I&O.