Ch. 1 - Kinematics and Dynamics
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
6% of MCAT Physics content
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
1.2 Vectors and Scalars
What is the difference between a vector and a scalar?
Vector have magnitude and direction
ex. displacement, velocity, acceleration, force
bolded = vector quantity
Scalar have only magnitude
distance, speed, energy, pressure, mass
italic = scalar quantity
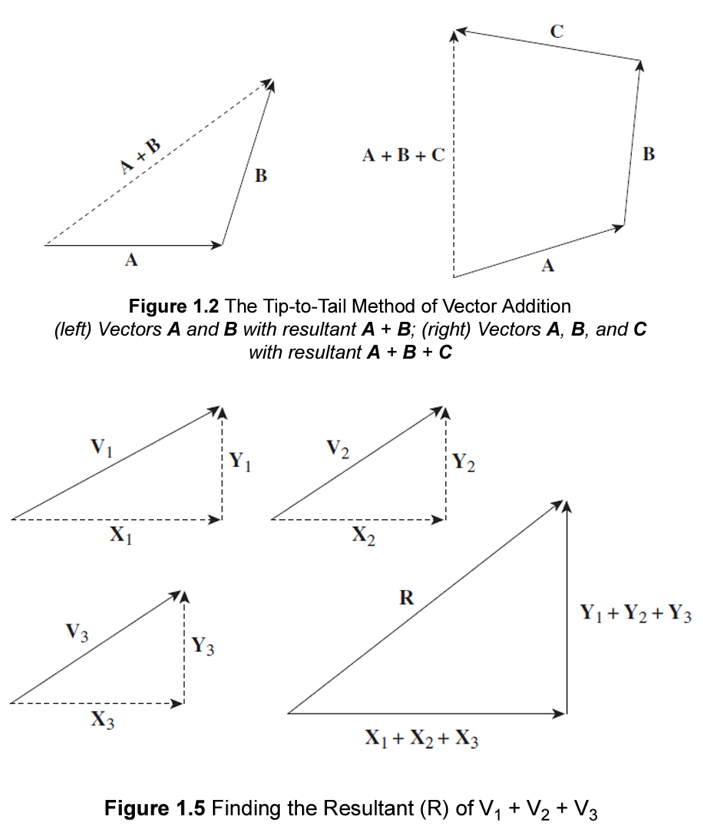
Vector Addition technique
tip-to-tail method (resultant)
breaking vector into perpendicular components (horizontal and vertical)
x-component = Vcosθ
y-component = Vsinθ
Vector magnitude = Pythagorean theorem
angle of resultant θ = tan-1 (Y/X)

Vector Subtraction technique
Adding vectors but in opposite direction to the first vector:
A - B = A + (-B)
with either tip-to-tail or component method
What happens when you multiply a vector by a scalar?
It changes the magnitude and may reverse the direction.
B = nA
What happens when you multiply a vector by a vector?
Generate a scalar (magnitude) quantity by using dot product (A · B):
A · B = |A| |B| cos θ
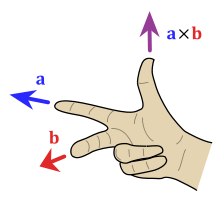
Generate a vector (magnitude and direction) quantity by using cross product (A X B) and right-hand rule:
A × B = |A| |B| sin θ
1.3 Displacement and Velocity
What is the difference between displacement (x or d) and distance (d)?
displacement is a vector representing the straight-line distance between start and end positions, path independent
distance is a scalar that is path dependent
What is the difference between velocity (v) and speed (s)?
velocity is a vector representation of the change in displacement over time
SI units = m/s
direction is the same as the displacement vector
speed is a scalar representation of the rate of distance over time
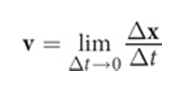
What is the difference between instantaneous velocity and instantaneous speed?
Instantaneous velocity is a vector; average velocity as the change in time (Δt) approaches zero
Instantaneous speed is the magnitude of that vector
not always as speed accounts for total distance traveled whereas velocity does not
1.4 Forces and Acceleration
What is a force (F)?
vector quantity that is the pushing or pulling on objects with the potential to cause acceleration
SI unit = Newton (N) = (kg*m)/s2
What is gravity?
an attractive force felt by all forms of matter
all objects exert gravitational forces on each other
Magnitude of gravitational force between two objects:
Fg = (Gm1m2)/r2
G = gravitational constant (6.67 × 10-11 Nm2/kg2)
inversely related to square of distance: r is halved then Fg is quadruple
directly related: m1 is doubled then Fg will double

What is the difference between static friction and kinetic friction?
Friction is a force that opposes movement of objects
coefficient of friction (μ) is unitless
normal force = perpendicular to the plane of contact of object and surface it rests on
Static friction (fs) exists between stationary object and surface
magnitude of static friction: 0 ≤ fs ≤ μsN
range of possible static friction values
do not assume that objects that are stationary are experiencing a maximal friction
increase contact area = increase frictional force
Kinetic friction (fk) exists between sliding object and the surface
ex. sliding on ice
magnitude of kinetic friction: fk = μkN
constant kinetic friction value
independent of surface area of contact and velocity of sliding object
What determines the coefficient of friction?
The materials in contact.
coefficient of static friction is higher than that of kinetic friction
maximum value of static friction > constant value of kinetic friction
It always requires more force to get an object to start sliding than it takes to keep an object sliding.
What is the difference between mass (m) and weight (Fg)?
Mass is a scalar quantity of inertia - the amount of matter in the object
SI unit = kg
Weight is the gravitational force acting on a mass.
force = vector quantity
SI unit = newtons (N)
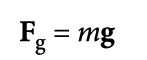
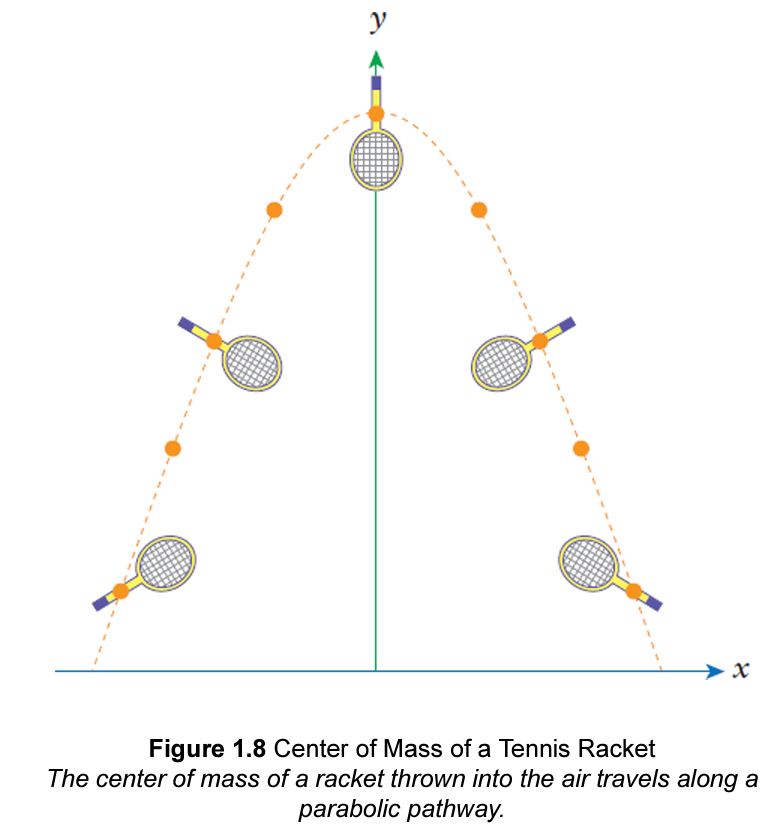
Define center of mass
weight of an object applied at a single point
for a system of particles distributed in all three dimensions: center of mass defined by three coordinates (xyz)
center of mass of a uniform object is at the geometric center of the object.
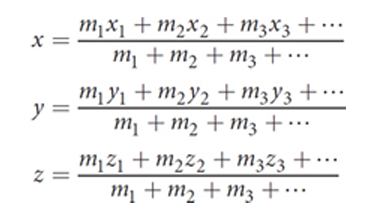
Define acceleration (a)
A vector representing the rate of change in velocity over time.
SI unit = m/s2
Average acceleration: Δv over Δt
Instantaneous acceleration: average acceleration as Δt approaches zero
velocity vs. time graph: tangent at any time indicates instantaneous acceleration at that time
positive slope = +a in same direction as v
negative slope = -a in opposite direction of v (deceleration)
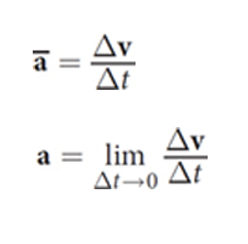
1.5 Newton’s Laws

What does Newton's First Law state (law of inertia)?
An object remains at rest or in constant velocity if no net force acts on it
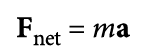
What does Newton's Second Law state?
Acceleration is the result of the net force divided by the object’s mass.
No acceleration will occur when the vector sum of the forces results cancels
net force and acceleration vectors in same direction
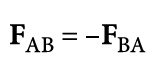
What does Newton's Third Law state (law of action and reaction)?
Any two objects interacting exert equal and opposite forces on each other.
Physical contact is not necessary; the mutual gravitational pull between the Earth and the Moon
1.6 Motion with Constant Acceleration
Describe linear motion.
Motion where velocity and acceleration are parallel or antiparallel, including free fall.
What forces act during projectile motion?
Gravity is the only force if air resistance is negligible.
How is motion on an inclined plane analyzed?
By breaking it into parallel and perpendicular components relative to the surface.
What defines uniform circular motion?
The centripetal force points radially inward, while instantaneous velocity is tangential.
What is translational equilibrium?
When the net force is zero
Object has constant velocity and may or may not be in rotational equilibrium.
What is rotational equilibrium?
When the net torque is zero
Object has constant angular velocity (usually zero on the MCAT)
What are free-body diagrams?
Visual representations of all forces acting on an object, useful for solving equilibrium and dynamics problems.