Economics section 3
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Forms of money
Money - any commodity that can be used as a medium of exchange for the purchase of a good or service.
Bank deposits - money reserves placed in commercial bank accounts
Central Bank reserves - money held by the central bank and used by the commercial bank to make payments between themselves.
4 Functions of money
Medium exchange - way to conduct trade
Measure of value - measures the market value of different goods + services
Store of value - can be stored and used in the future
Standard of deferred payment - used as a standard for future payments of debt
6 characteristics of money
durable - fairly long lasting
acceptability - widely recognised and accepted as a medium of payment
divisibility - must be divisible
Uniformity - all forms of a particular banknote should look the same
Scarcity - money must be limited in its supply to hold its value
Portability - money must be conveniently portable
bartering
swapping items in exchange for other items
functions of the central bank
sole issuer of banknotes and coins
The governments bank - performs the same service for the government as a commercial bank to its customers
The bankers bank
The lender of last resort - all commercial banks are required to keep a percentage of their money at the central bank incase of a financial emergency.
central bank definition
monetary authority that oversees and manages an economies money supply and banking system
functions of a commercial bank
accepting deposits- from individuals, businesses, government
making advances - providing loans to their customers
credit creation - increase the money supply in an economy by making money available to borrowers
(Secondary-)
(collecting and clearing cheques on behalf of clients, offering additional financial services, providing safety deposits, providing money transfer facilities, offering credit card facillities)
Current vs Capital expenditure
current - money spent on goods and services that will be consumed within a year. food, clothing, entertainment
Capital - money spent on fixed assets that will last more than 12months. e.g car,computer
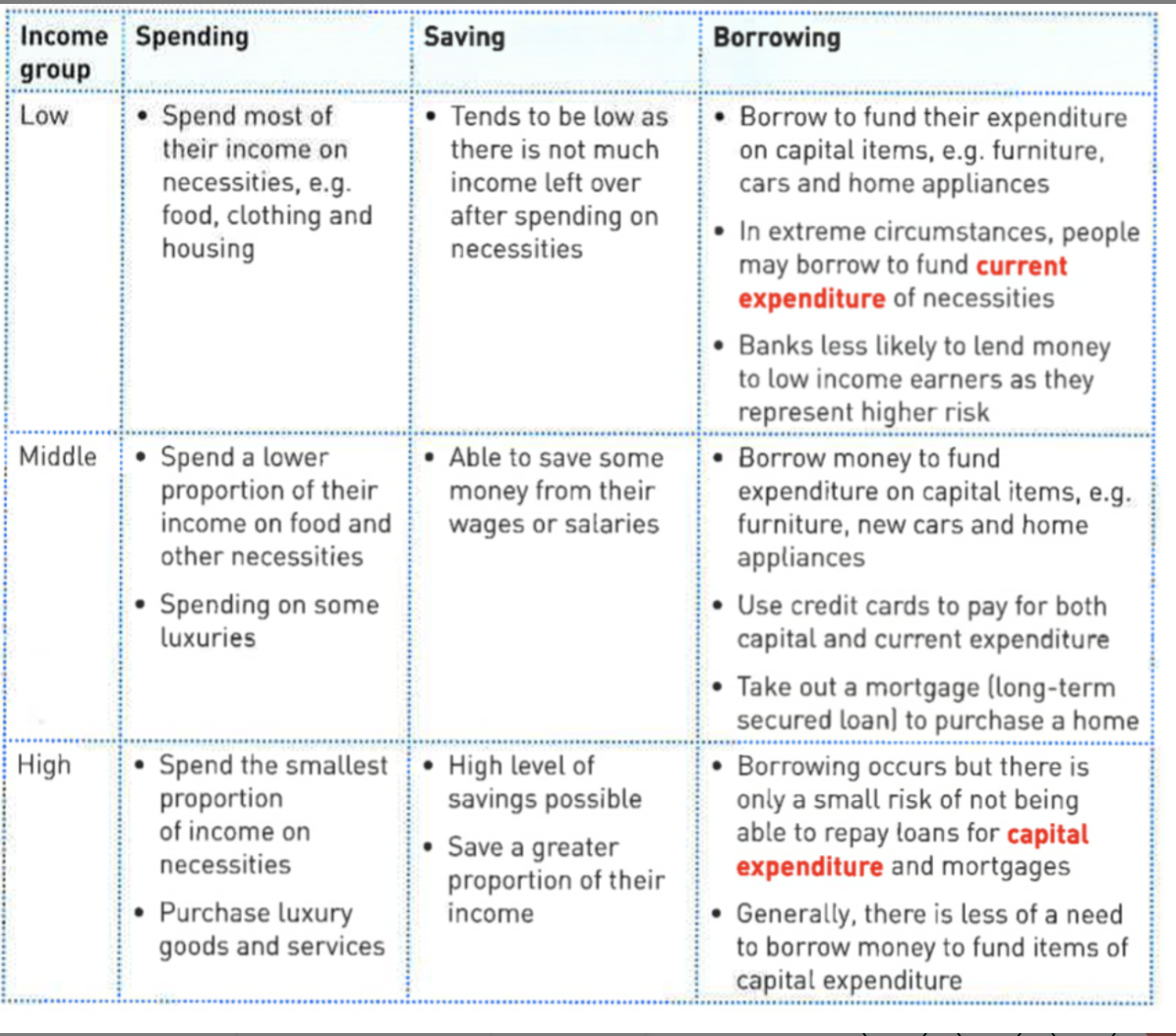
Low, middle, high income groups
Low- spending is mostly on necessities, saving is small, borrowing is unlikely as they are risky for banks, can borrow for current items.
Middle- most money is spent on necessities but can afford some luxuries, some saving, can borrow money for capital items, can pay with credit cards.
High - smallest amount of income is spent on necessities most in spent on luxuries, most amount of savings, can borrow but it is unlikely that they need to
Wealth + positive wealth affect + Negative equity + conspicuous consumption
wealth - amount of assets a person owns - liability
positive wealth affect - value of assets such as property and investment increase
negative equity - value of a secure loan or mortgage exceeds the market value of property
conspicuous consumption - when people purchase goods / services to increase their status + image
effects of Interest rates
borrowing becomes more expensive → demand for loans fall
savings become more attractive due to higher return → people save more + spend less
If a individual has an existing loan or mortgage the increase in interest repayments is likely to cause a fall in disposable income, spending falls
Influences on household spending
Income
Interest rates
Inflation
age
size of households
Influences on household borrowing
Availability of funds
confidence levels
interest rate
credit cards
store cards
wealth
Wages vs Salary vs Piece rate vs commission vs profit related pay vs share options (WAGE FACTORS)
Wages - time based, payed hourly,monthly weekly,etc.
Salary - payed monthly at a fixed rate no matter how much work was done
Piece rate - fixed amount payed per item produced or sold
commission - a percentage of the value of products or services sold.
profit related pay - additional payment to workers based on the amount of profit made by the firm
Share options - workers receive shares of the firm( gives incentive to work hard)
Non wage factors
level of challenge
level of danger
level of training required
level of experience required
career prospects
recognition in the job
personal satisfaction gained from the job
derived demand
labour is not demanded for itself but the goods/services it is used to produce
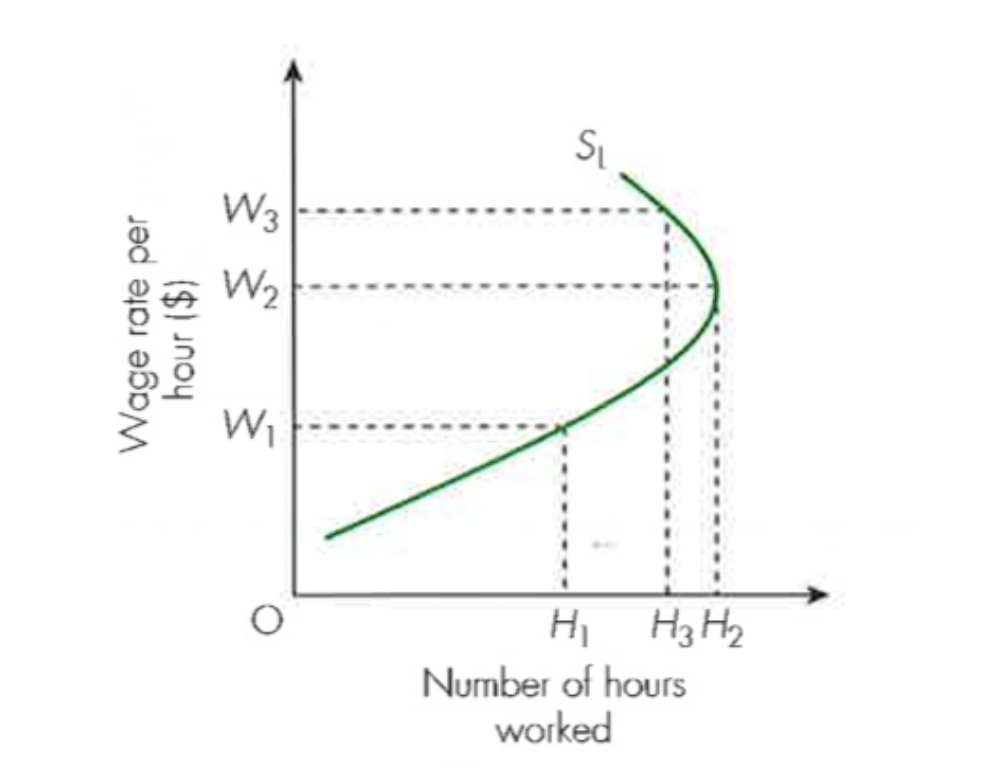
Back-ward bending supply of labour curve
when wage rates rise high and allows workers to work less
factors influencing labour force participation rate
availability + level of welfare benefits
changing social attitudes
occupational mobility
geographic mobility
labour force/total working age population
collective bargaining + corporate social responsibility
collective bargaining - trade union reps negotiating on behalf of the workers
corporate social responsibility - the ethical approach taken by firms
Types of trade union
Craft- organise workers of a particular skill(egineers)
Industrial- all workers in a industry (oil)
white collar- represent professional + non manual workers
general- accept anyone
Role of trade unions in a economy
better pay raise and working conditions
ensuring equipment at work is safe to use
giving support to members when they are made redundant
Providing financial + legal assistance to workers who have been unfairly dismissed or disciplined
Pursuing the government to pass legislation for workers
factors influencing strength of trade unions
number of members, degree of unity
reasons for higher membership - widening wealth gap, increase in manufacturing jobs
Negatives of trade union memberships
strikes → loss of productivity
better pay and conditions → firms production costs increase
profits reduced → government revenue falls
How to measure size of firms
number of employees, Market share, Market capitalization (total amount of shares x current price of shares), sales revenue (unit price of product x quantity sold)
Internal vs external economies of scale
internal- cost saving that arise from within the business(purchasing, techincal financial)
external - economies that arise due to the location of the firm and are external to the business
(proximity to related firms-easy access to supplies
availability of skilled labour-makes recruitment easier
reputation of geographical area-free publicity
access to transport networks-roads,ports)
Diseconomies of scale
average costs of production increase as firm size increases.
( operate in areas they don't have expertise in, workers may loose motivation → reduced productivity, may be necessary to employ new empolyees and build new buildings, unsuccessful merger, slow decision making)
production vs productivity
production - total output of goods and services in the production process
productivity - measure of efficiency output per unit of a factor input
factors of production + productivity = production
Importance of higher productivity for an economy
economies of scale - reduce per unit cost leading to reduction in prices for customers
Higher profits
Higher wages - attract best workers
improved competitiveness- firms can compete at a global scale
economic growth - raise standards of living + employment
Influences in productivity
investment - expenditure on capital
innovation - the commercialization of new ideas and products
Skills + experience - enhancing human capital(training)
entrepreneurial spirit - take risks in the production process in pursuit of profit
competition - rivalery between businesses creates incentive to be more productive
advantages of small firms
can provide more personal services,
able to adapt to changes in the market quickly,
if demand for product is small a firm producing it cannot be large
disadvantages of small firms
cannot enjoy economies of scale- spend more on raw materials
don’t have name recognition
can’t attract talented workers as easily
harder to expand - have to rely on loans
Different types of costs
total costs - sum of all fixed + variable costs
average fixed - fixed costs per unit
average variable - variable cost per unit
average total - total costs of making one product.
objectives of firms
survival- need to be profitable
social welfare- business activity with concerns for the quality of life in society
growth- increasing size of business to enjoy greater customer loyalty + economies of scale
profit + profit maximization -
Market structure
the key characteristics of a particular market
number + size of firms
degree + intensity of price and non price competition
Nature of barriers to entry
competitive market characteristics
Price - Firms are price takers
Quality - firms sell homogeneous products
Choice - focus on selling differentiated products
Profit - both buyers + sellers have access to information about the product + prices being charged by competitors
High competition → benefit to customers
characteristics of a monopoly
single supplier
Price maker - controls enough of the market supply to be able to charge higher prices
Imperfect knowledge - has the ability to protect prestigious position and trade secrets.
High barriers to entry - obstacles preventing other firms from entering the market
Advantages of monopolies
enjoy economies of scale
ability to invest in innovation - reaserch + development expenditure helps to develop new ideas.
Eliminate wasteful competition
disadvantages of monopolies
restrict output of a product
charge a higher price
Demand is price inelastic as monopolists are price makers
High barriers to entry limits competition
less incentive to innovate than competative markets