05.A BIO Energy, Life, & ATP (PART A)
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Chemical work
Cellular work that involves:
- Growth/Cell Division
- Protein Synthesis
- DNA Replication
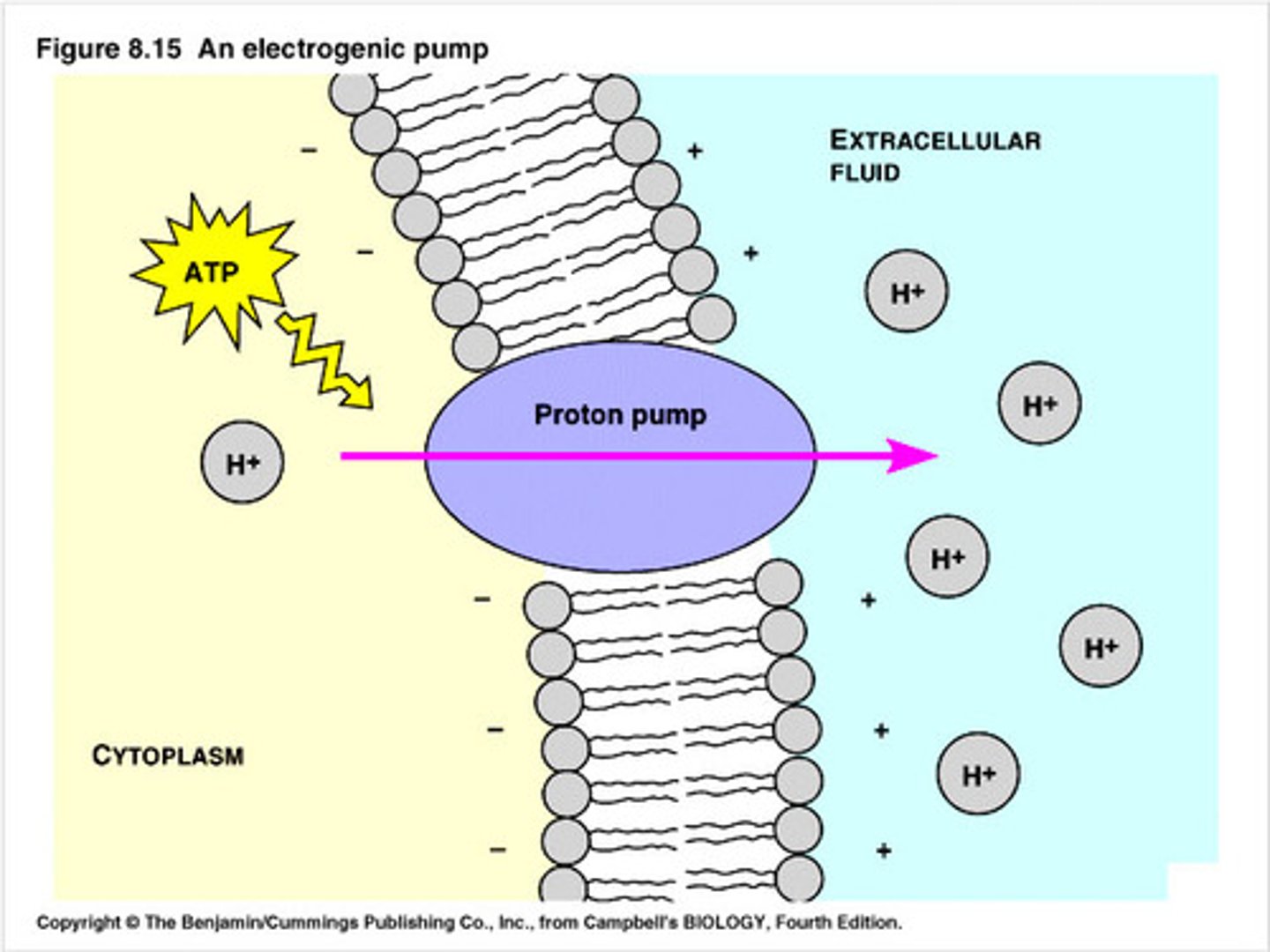
Transport work
Work that involves:
- Movement of Molecules
- Maintain Concentration Gradients
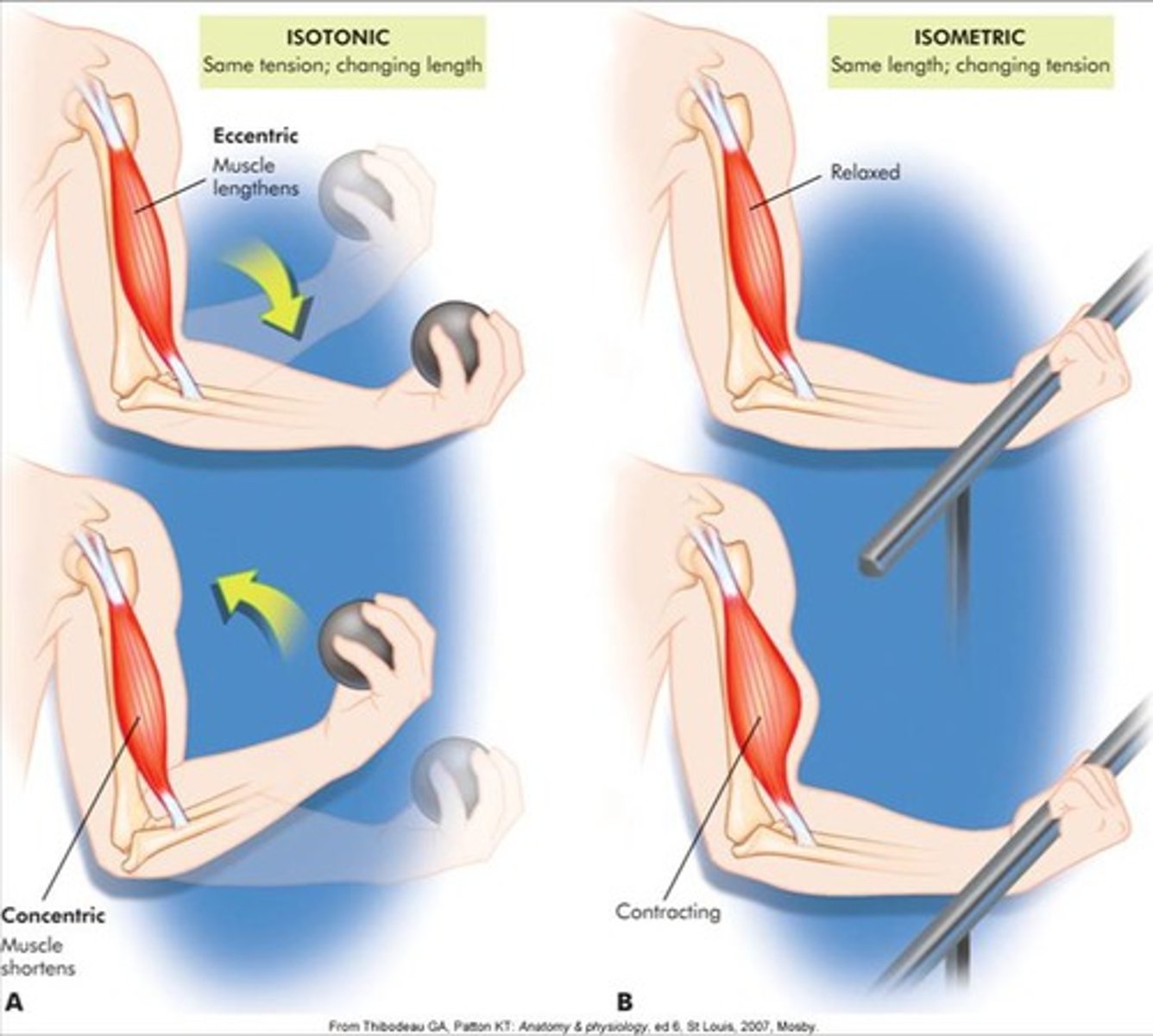
Mechanical work
Work that involves:
- Positioning & Movement of Organelles
- Maintaining Cell Shape
- Beating of Cilia & Flagella
-Muscle Contraction
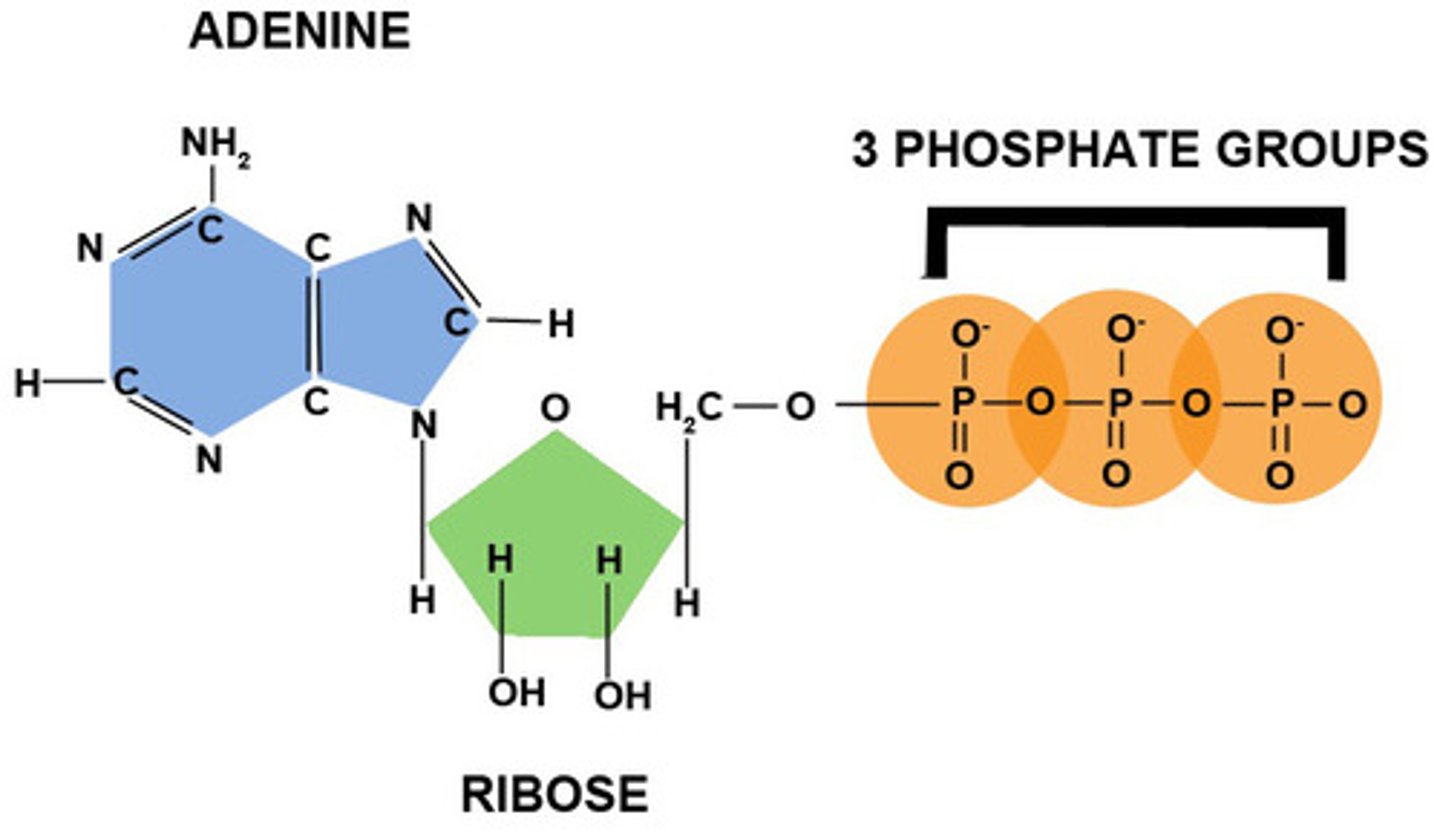
ATP (Structure)
This molecules is made up of:
*Sugar = Ribose
*Phosphate = 3 phosphate groups
*Nitrogen base = Adenine
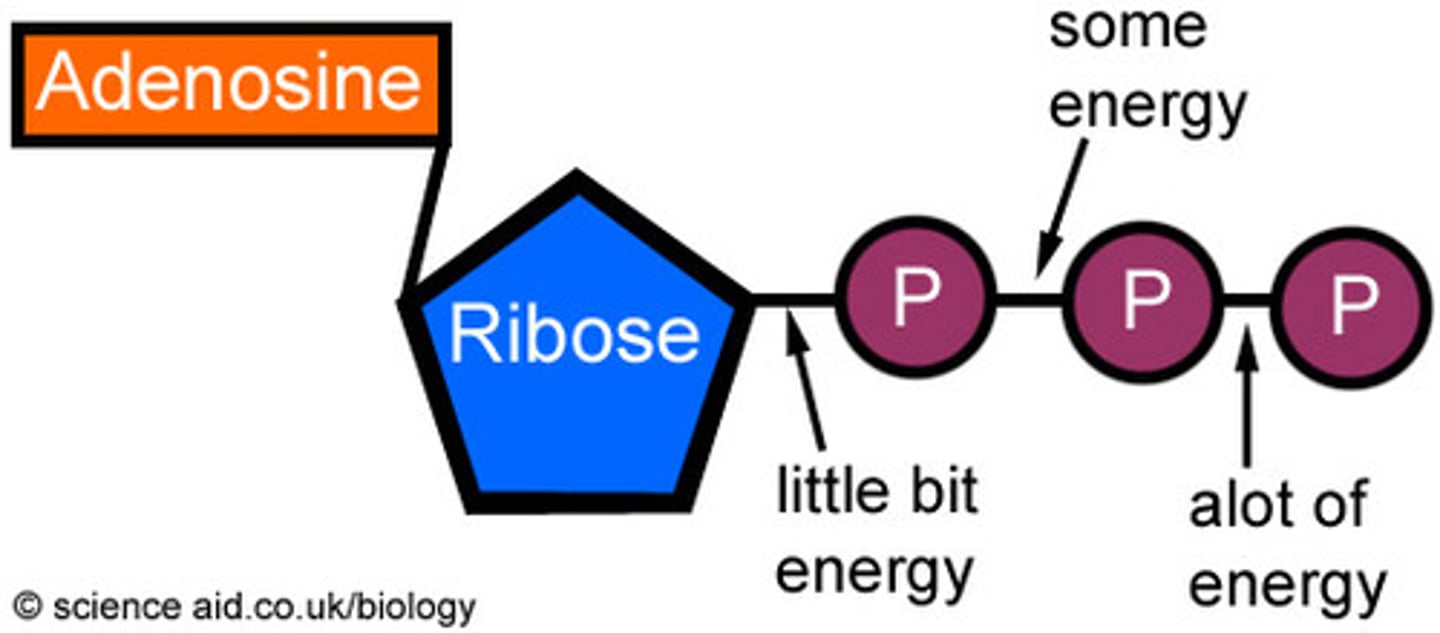
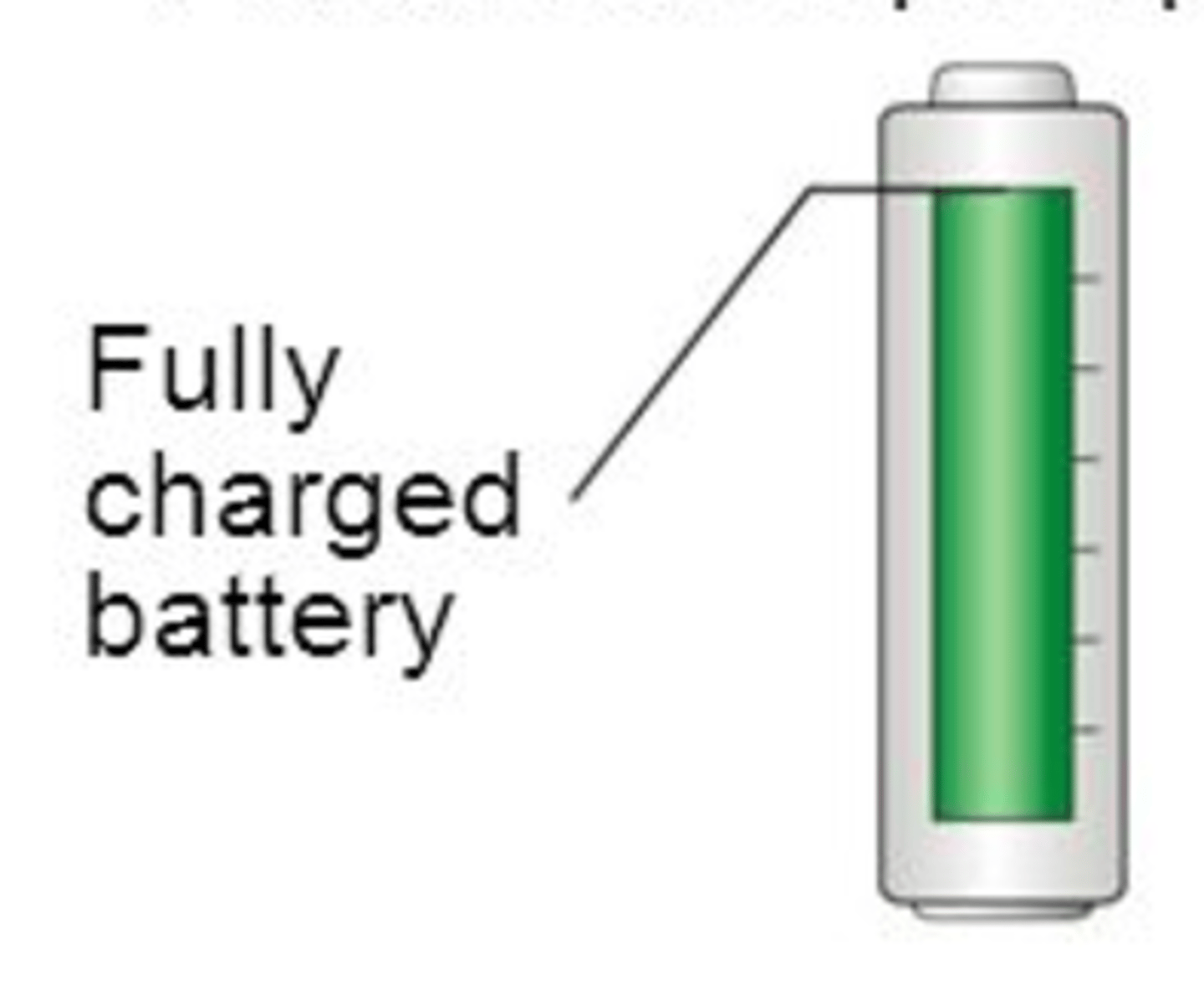
ATP (Function)
A molecule that stores energy that can be used to do cellular work
ADP (Structure)
This molecule is made of:
*Sugar = Ribose
*Phosphate = 2 phosphate groups
*Nitrogen base = Adenine
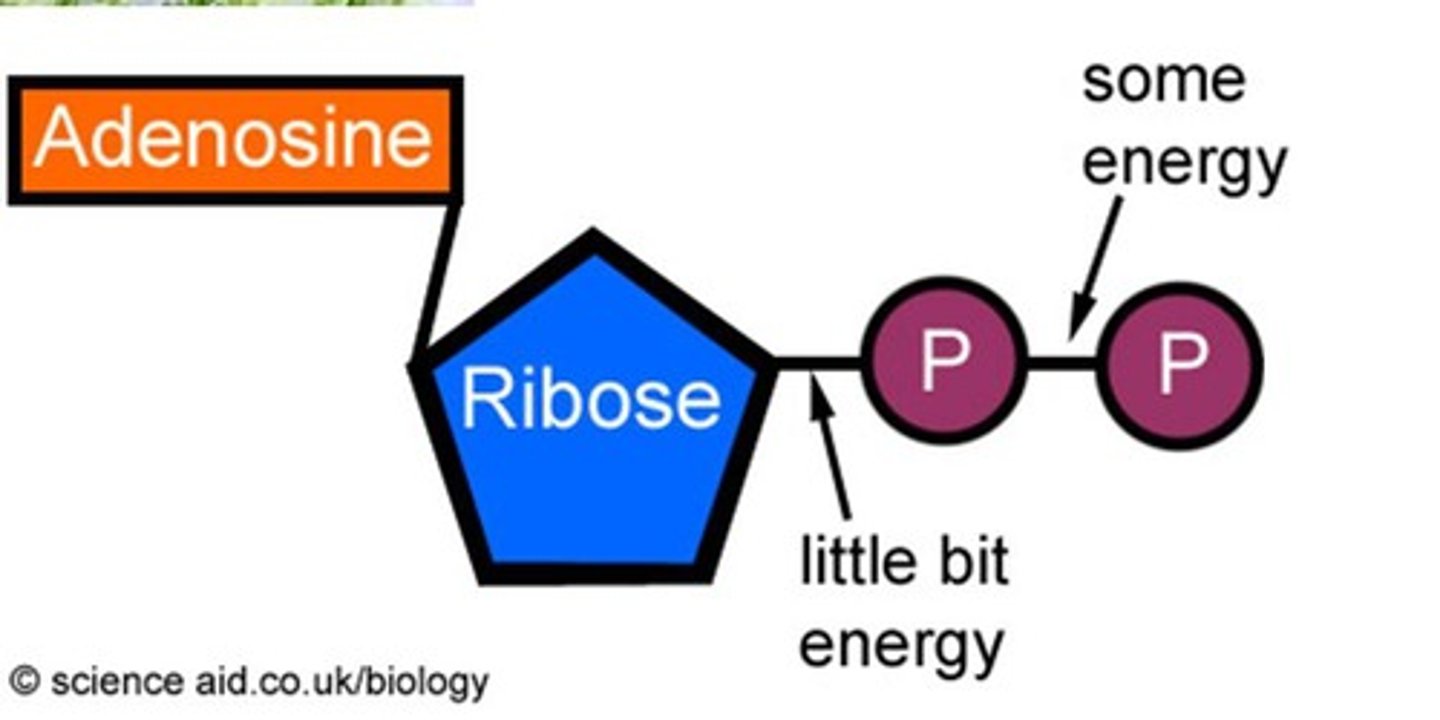
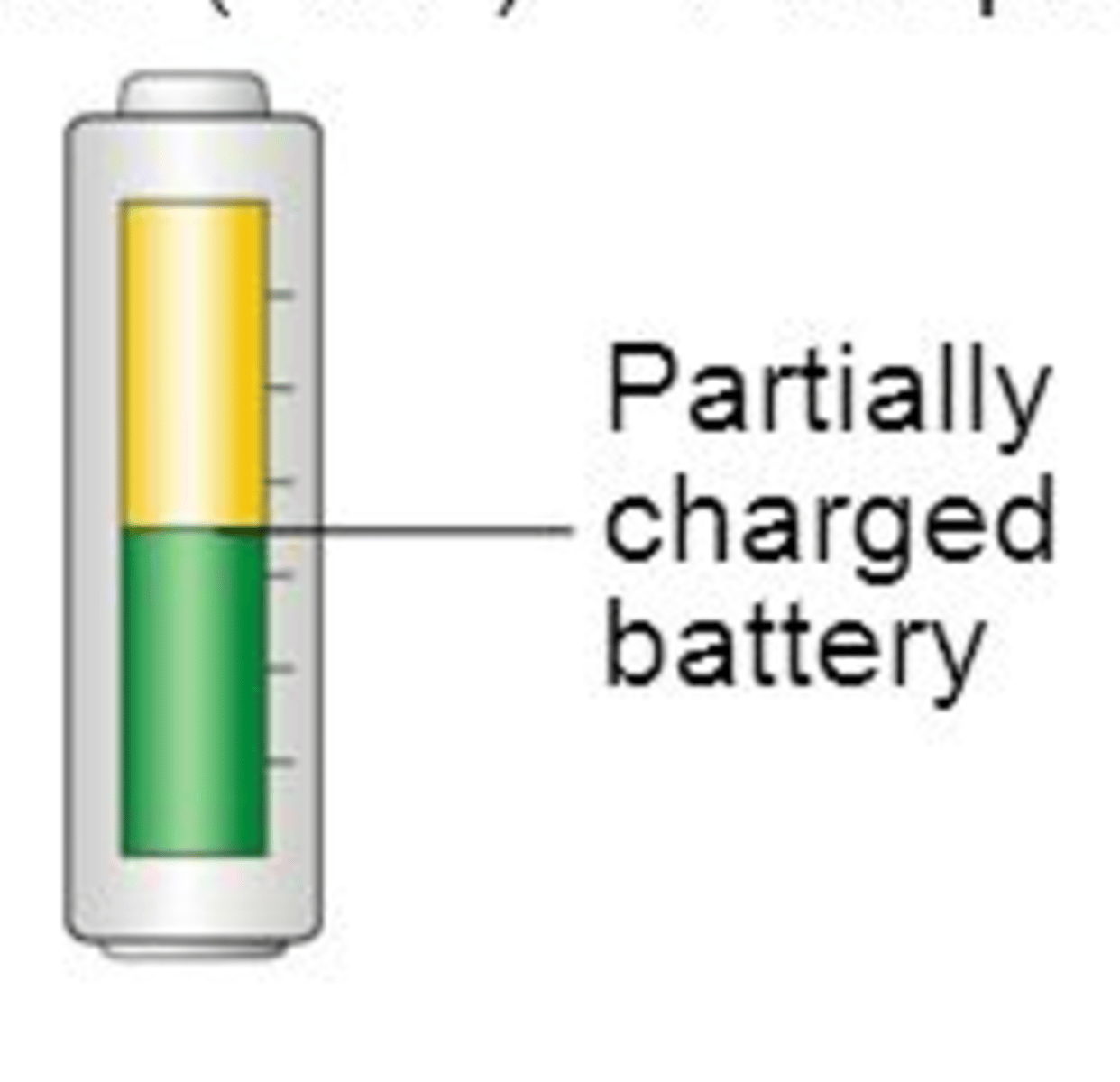
ADP (Function)
A molecule that has "lost" one phosphate and in the process loses/releases energy to do cellular work
ATP-ADP Cycle
The breakdown of ATP into ADP and phosphate releases energy while the formation of ATP from ADP and phosphate stores energy
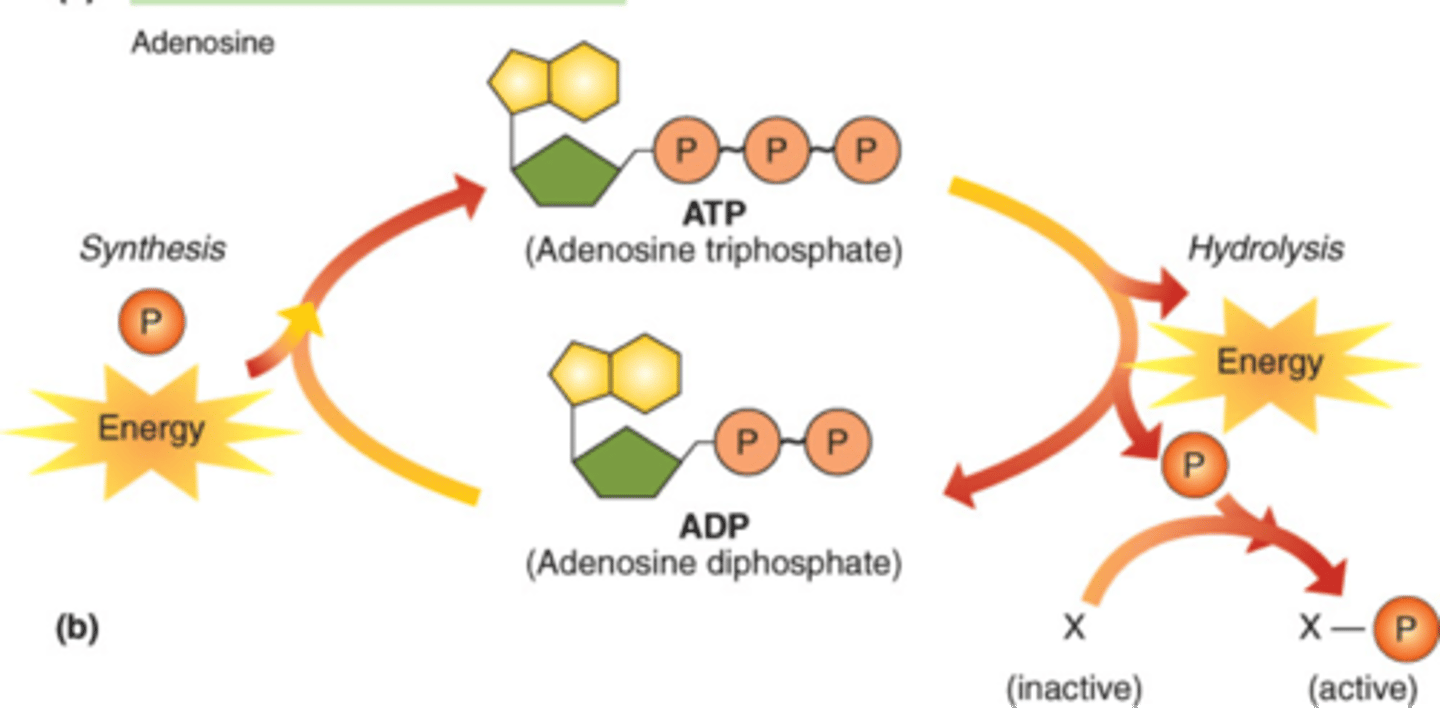
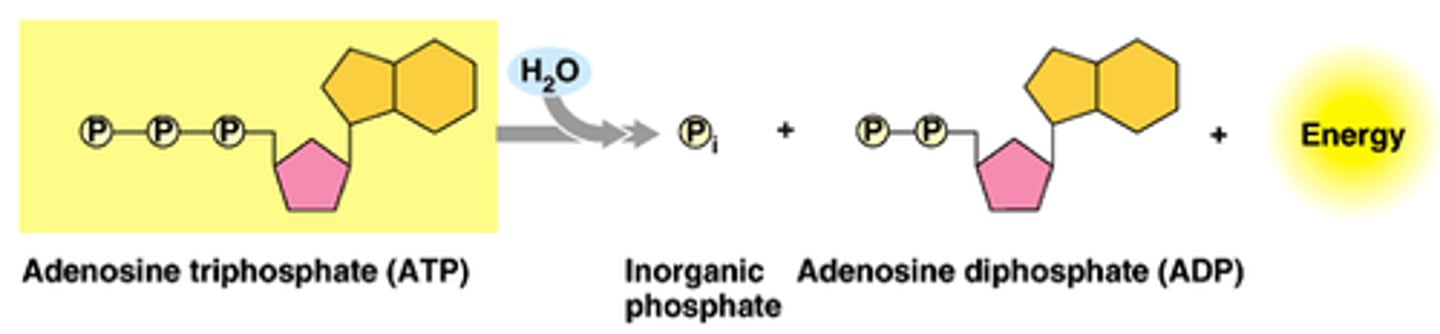
Hydrolysis of ATP
The addition of a water molecule to break the bonds between phosphates; results in the release of energy

Dehydration synthesis of ADP and PO4
The removal of a water molecule to create a bond between the ADP and phosphate

Energy is released
When ATP is converted to ADP and phosphate
Energy is stored
When ADP and phosphate combine to form ATP

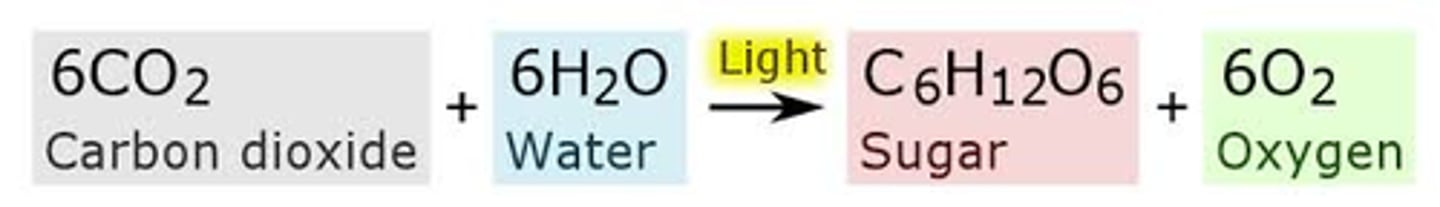
Photosynthesis
A process that autotrophs use to trap light energy and stores the energy in macromolecules like glucose
Cellular Respiration
A process that all organisms undergo that releases energy from macromolecules like glucose to produce ATP that can be used by cells to do cellular work

Chemical bonds & Energy
Store energy; the greater the number of bonds the more energy stored
Lipids (fats, oils, waxes)
A type of macromolecule that provides long-term energy for cells

Carbohydrates (sugars and starches)
A type of macromolecule that provides short-term energy to cells

Protein (amino acids, polypeptides, enzymes)
A type of macromolecule that is rarely used by cells for energy unless the organism is starving; typically makes up tissues, organs and muscles

ATP -" a universal biochemical molecule"
Common "currency" used by all cells to do cellular work