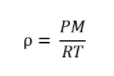PRACTICE DAT EXAM #8 - General Chemistry
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
What is the temperature at which 64 g of O2 will occupy a volume of 8.2 L at 760 Torr?
[(1)(8.2)]/[(2)(0.082)]
IDEAL GAS LAW: PV=nRT
![<p>[(1)(8.2)]/[(2)(0.082)]</p><p>IDEAL GAS LAW: PV=nRT</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/af8050d8-deb8-4cc7-972f-543c342bc6b4.png)
An element X forms an oxide X2O3 with a mass ratio of 0.50 g X / 1 g O. What is the atomic mass of X?
12.0 amu; use dimensional analysis to solve this stoichiometric problem
Which of the following 0.25 M solutions would exhibit the lowest electrical conductivity?
a. HCl
b. K2SO4
c. NaCl
d. HF
e. Ba(NO3)2
d. HF
In general, strong acids and bases will fully ionize when in contact with water, creating solutions with large electrical conductivity. Of all molecules present, HF is the only one that qualifies as a weak electrolyte, and therefore it will not completely ionize in solution leading to the lowest electrical conductivity of all answer choices present.
Key Takeaway:
Strong acids and bases are able to fully dissociate creating solutions with large electrical conductivity.
For the reaction 2NO(g) + O2(g) → 2NO2(g), the concentration of NO was monitored from 0 to 100 seconds. Given the following data, what is the average rate of disappearance of NO from 0 to 100 seconds?
t (s) | (NO), M
0 | 1.0 x 10-3
100 | 5.0 x 10-4
5.0 × 10-6 M/s

Which of the following reactions will be spontaneous at all temperatures?
A. 2H2(g) + O2(g) → 2H2O(g) ΔH = –483.6 kJ
B. 2NCl3(g) → N2(g) + 3Cl2(g) ΔH = –460.1 kJ
C. N2(g) + O2(g) → 2NO(g) ΔH = + 180.5 KJ
D. 2Na(s) + Cl2(g) → 2NaCl(s) ΔH = –821.8 kJ
E. C(s) + 2S(s) → CS2(g) ΔH = + 92.0 KJ
B. 2NCl3(g) → N2(g) + 3Cl2(g) ΔH = –460.1 kJ
creation of more gas moles means there is an increase in disorder, an increase in disorder/more disorder is indicative of a positive (+) change in entropy (S)
negative change in enthalpy and a positive change in entropy means the reaction will be spontaneous at ALL temperatures!
Based on the reaction below, which of the following statements is correct?
HClO3 + H2O ⇌ H3O+ + ClO3-
A. H2O acts as a base and ClO3- is its conj. acid
B. H2O acts as a base and H3O+ is its conj. base
C. HClO3 acts as a base and H3O+ is its conj. base
D. H2O acts as a base and H3O+ is its conj. acid
E. HClO3 acts as a base and ClO3- is its conj. acid
D. H2O acts as a base and H3O+ is its conj. acid
In the reaction above:
HClO3 acts as an acid because it is a proton (H+) donor. Therefore, ClO3- is the conjugate base.
H2O acts as a base because it is a proton (H+) acceptor. Therefore, H3O+ is the conjugate acid.
Key Takeaway:
According to the Bronsted-Lowry definition of acids and bases, an acid is a proton (H+) donor and a base is a proton (H+) acceptor.
Which of the following gases will have the greatest density at STP?
a. Cl2
b. N2O
c. Ar
d. SO3
e. CO2
d. SO3
The density, ρ of a gas:
P is the pressure of the gas, M is its molar mass, R is the ideal gas constant(0.082), and T is the absolute temperature. Because all of the gases are at the same temperature and pressure, the density is only dependent on the molar mass. Density increases with molar mass.
SO3 has the highest mass and the highest density.