Drug-Receptor Interactions: Affinity
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Ligand
A molecule that binds to a specific receptor site on another molecule
Affinity
Tendency for a drug to bind to a receptor
Efficacy
Tendency for a drug, once bound, to activate a receptor
Agonists have significant efficacy, antagonists have zero efficacy
KD
Constant that defines the affinity of a drug for a receptor
Drug-receptor interaction
Most of the interactions are reversible
Involve the interaction of 2 molecules
Forward rate of reaction equations
k+1[A]*[R]
Reverse rate of reaction equation
k-1 [AR]
Reaction when at equilibrium equation
k+1[Aeq]*[Req] = k-1 [AeqReq]
KD= k-1 / k+1 = [Aeq]*[Req]/ [AeqReq]
Occupancy
Proportion of receptors occupied that varies with drug concentration
Measured that equilibrium
Governed by affinity
Varies between 0 (no drug present) and 1 (receptors occupied)
Occupancy equation
Occupancy = number of receptors occupied/ total number of receptors
Some experimental approaches to measure drug affinity
Radioligand Binding Assays (RBA)
Fluorescence Polarization Assays
Surface Plasmon Resonance
Isothermal Titration Calorimetry
Computational Modelling
RBA: source of receptors & incubation conditions
Sources: tissues/ cells selected to contain recognition sites of interest (isolated membranes, slices, synaptosomes, cultured cells, purified receptors)
Incubation: to preserve integrity of both ligand and receptors. Temperature is usually low room temperature to 0
RBA: the radioligand
must be biologically active
Must be extremely pure chemically
No degradation
Labelling must achieve high specific activity to allow very low concentrations
RBA: how to solve the problem of degradation
Store at low temps
Avoid light
Incorporation of antioxidant
Free-radical scavenger in drug solution
RBA: examples of radio-labels used
3H, 125I
RBA: separating bound from free ligand
usually done by filtration or centrifugation.
For soluble binding: techniques like dialysis, column chromatography, precipitation.
Major consideration: rate of dissociation of ligand-receptor complex.
Does lower affinity requires a faster or slower separation
Faster and more efficient separation
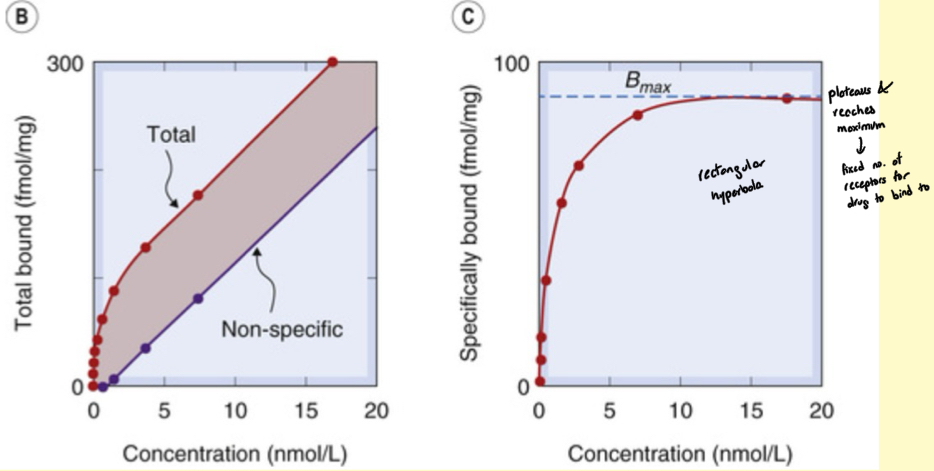
RBA: Non specific binding
Ligands bind non-specifically to substances like plastic, filter paper, glass, etc.
Can be reduced by anti-absorbants
Measuring proportion of specific and non-specific binding is key element to assay
What is non-specific binding determined by
Addition of excess non-radioactive drug
Specific binding equation
Specific binding = total bound - nonspecific binding
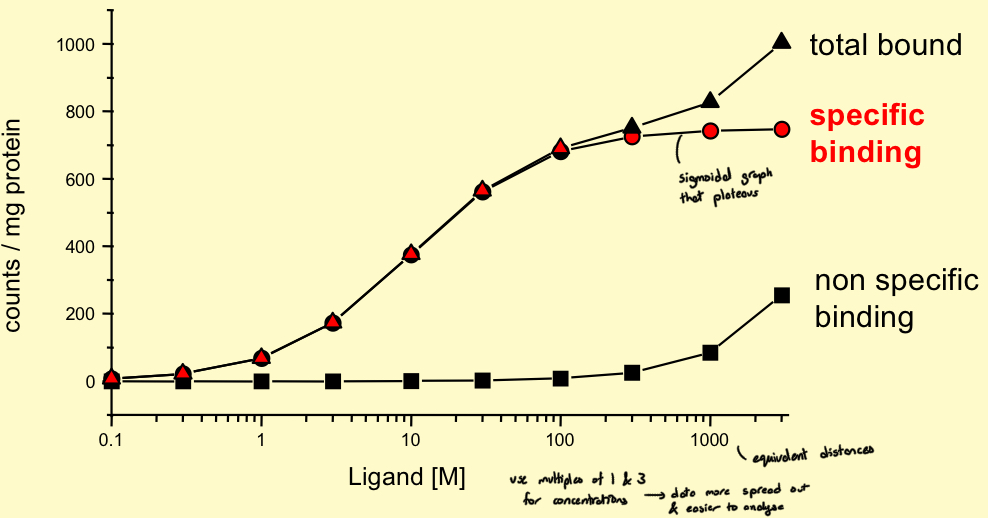
Binding data is plotted on what type of scale
Semi-logarithmic
(Specific binding has a sigmoidal shape that plateaus)
What does the Langmuir/ Scatchard equation describe
Relationship between receptor occupancy, affinity and drug concentration
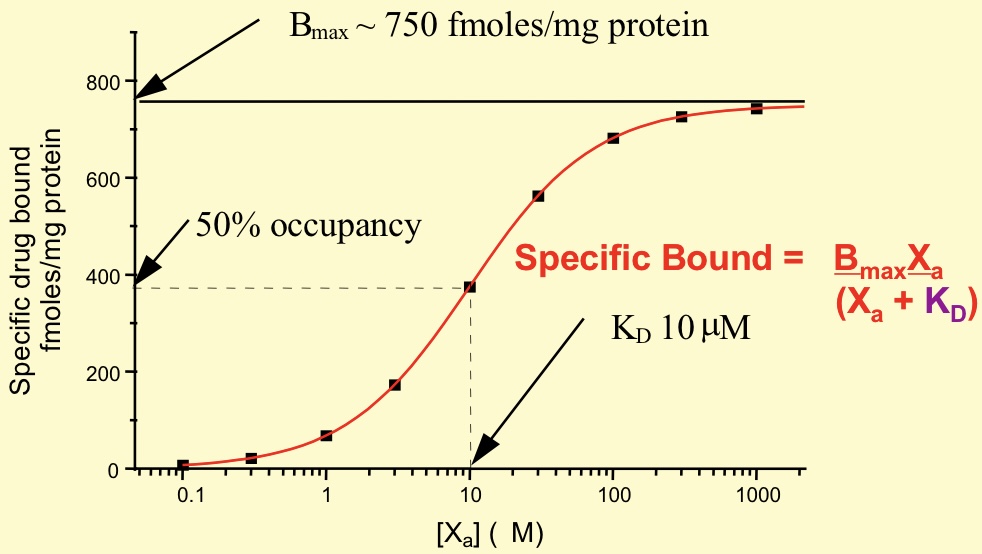
Specific binding equation in relation to Langmuir/ Scatchard equation
Specific Bound = (Bmax - Xa)/ (Xa + KD)
measures occupancy
What is Bmax
Binding capacity, expressed per mg protein
direct measure of concentration of receptors present
How do you determine KD from Langmuir/ Scatchard graph
The concentration of ligand require to ‘occupy’ 50% of receptors at equilibrium
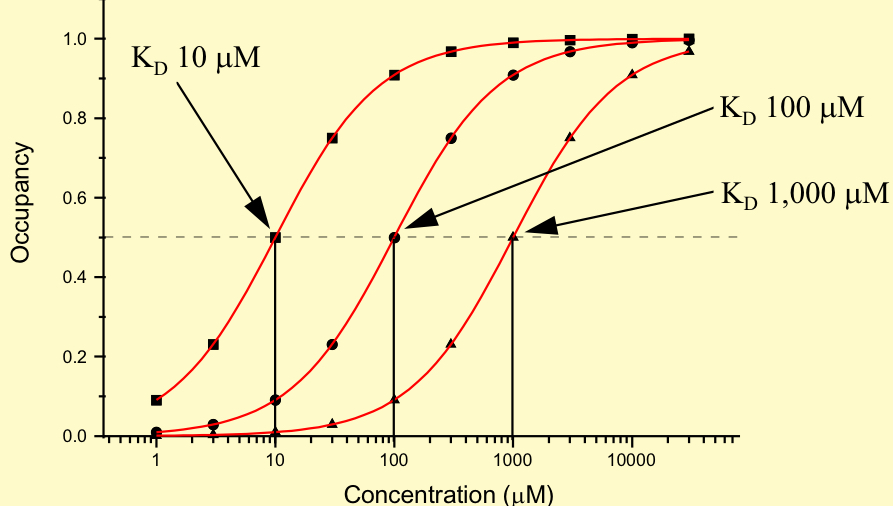
Does low KD show high or low affinity
High affinity
Low KD —> high affinity
High KD —> low affinity
When does Ki ≈ KD
When the inhibitor competes with the ligand for the same binding site on the receptor