BIO 189- Chapter 23 : Animal Tissues and Organ Systems
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
What is anatomy?
The study of the STRUCTURE and FORM of bodies
What is physiology?
The study of the FUNCTION of body parts
What can structure indicate?
Function
What are the basic characteristics of defining kingdom: animalia?
Eukaryotic, multicellular, heterotrophic, no cell walls or chloroplasts, motile
What do all animals share in early development stages?
Zygote to blastula
What is blastula?
A hollow ball of cells formed that can make up to 3 distinct cell layers
What does blastula allow?
For cells to become specialized into different tissues and organs
What do most animals need?
Sense and respond to the environment, acquire and digest food molecules, exchange respiratory gases (O2 & CO2), eliminate wastes, protect against injury and disease, and reproduce
Cells interact physically (__ ______) and functionally to form ____
cell junction, tissues
What is genome?
The total amount of native DNA in organism’s cell
What is gene expression?
The act of transcribing and/or translating genes- segments of DNA that make functional RNAs or proteins
What are differential gene expressions?
The expression of the same genes in different ways (timing and/or quantity) or expressing different combinations of genes from the same genome resulting in different cellular outcomes
What are the four general tissue types?
Connective, muscle, epithelial, nervous
All animal tissues are cells embedded in what?
Extracellular matrix
What is extracellular matrix?
A network of filamentous proteins, carbohydrates and interstitial fluid secreted by the cells in a tissue
What does extracellular matrix provide?
Tissue structure, support, and facilitates cell to cell communication
What are epithelial tissues?
Tightly packed cells covering the internal and external surfaces of the body
What are examples of epithelial tissues?
Skin, mucus membranes, the lining of the digestive tract, lung lining
What are the three main epithelial functions?
Protection, absorption and secretion
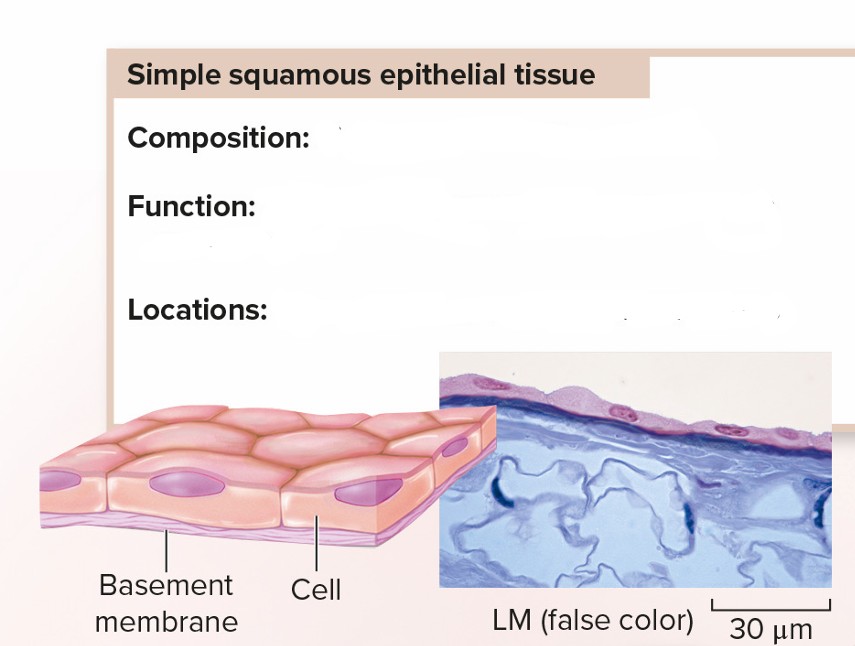
Simple Squamous Epithelial Tissue
Composition: Single layer of flattened cells Function: Allows substances to pass through the process of diffusion and osmosis Location: Lining of blood vessels; alveoli of lungs
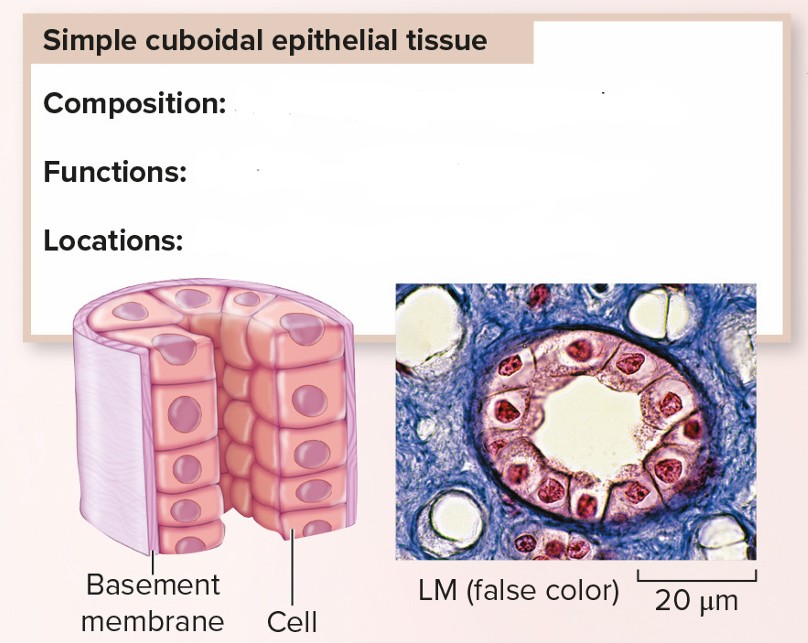
Simple Cuboidal Epithelial Tissue
Composition: Single layer of cube-shaped cells
Function: Secreted & absorbs substances
Location: Glands: lining of kidney tubules
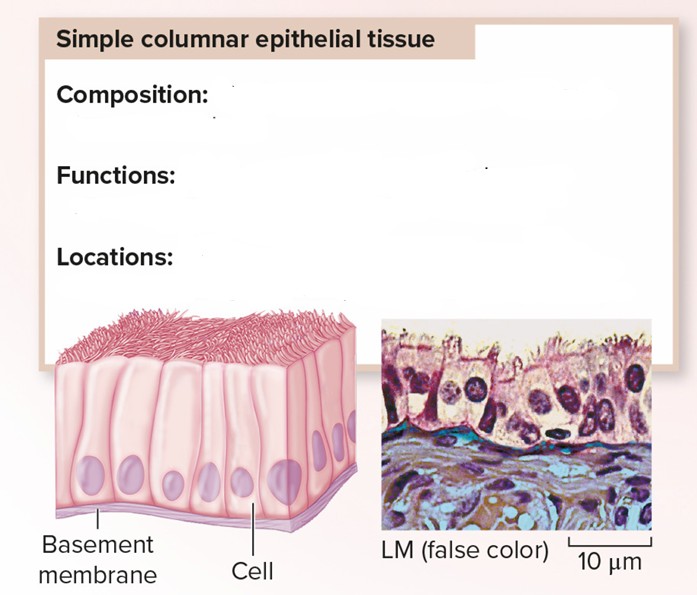
Simple Columnar Epithelial Tissue
Composition: Single layer of column-shaped cells (may be ciliated)
Functions: Secretes and absorbs substances; sweeps egg/embryo along uterine tube
Locations: Lining of digestive tract (not ciliated); bronchi of lungs (ciliated); uterine tubes (ciliated)
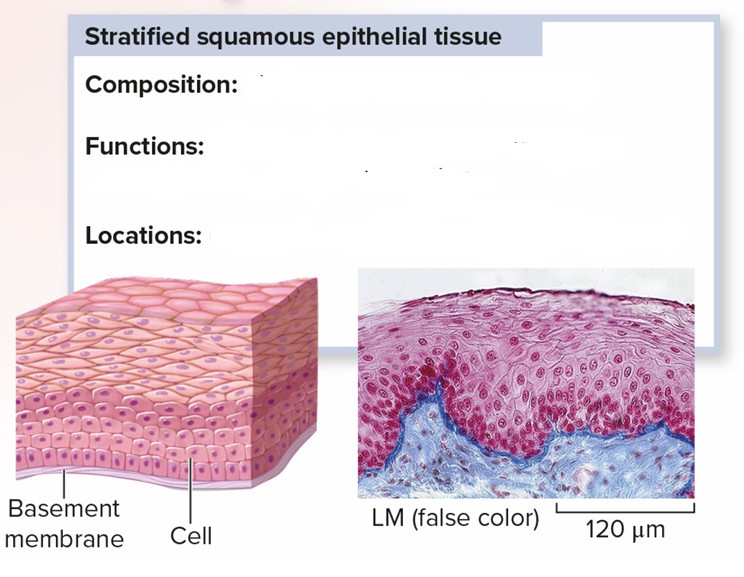
Stratified Squamous Epithelial Tissue
Composition: Multiple layers of flattened cells
Functions: Protects areas subject to abrasion; prevents water loss and infection
Locations: Outer layer of skin; lining of body openings
What are epithelial tissues two polarities?
Apical and Basal
What is the apical side of EPI. Tissues
The side exposed to an internal cavity or external surface
What is the basal side of EPI. Tissues
The side connected to other tissues via basement membrane (reduced extracellular matrix)
What does the basement membrane/reduced extracellular matrix do?
Glues epithelial tissue to underlying tissues like connective tissue or muscle
What are epithelial tissues classified by?
Shape and cell layer numbers
What are connective tissues and what do they do?
Serve to connect tissues, fill spaces in the body, protect organs, provide structural support and systemic transport
Connective tissue often contains relatively few cells in an what?
Extensive extracellular matrix
Out of all the general body tissue types, which is the most diverse?
Connective tissue (ranges from liquid to solids)
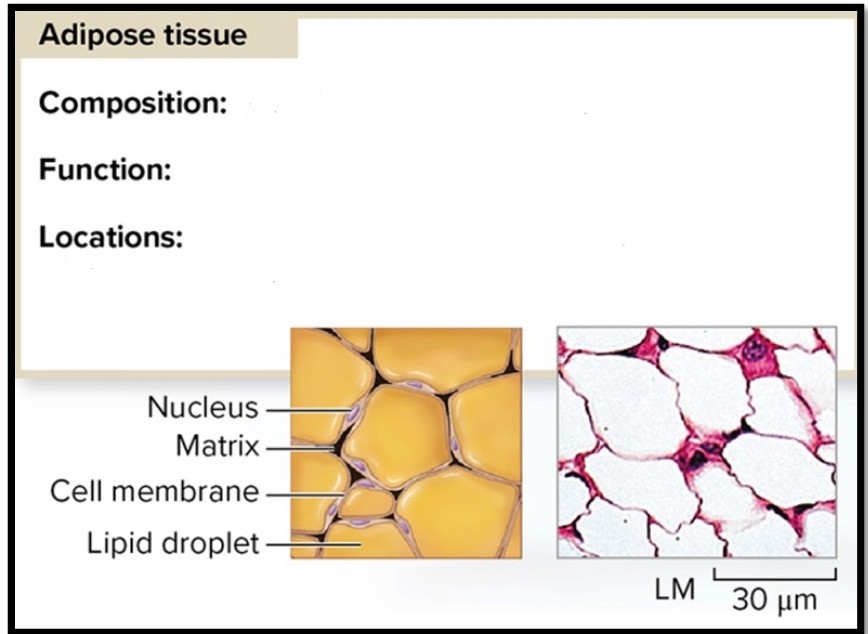
Adipose Tissue
Composition: Fat cells in minimal matrix Function: Stores fat for energy and insulation Locations: Beneath skin; between muscles; around heart and joints
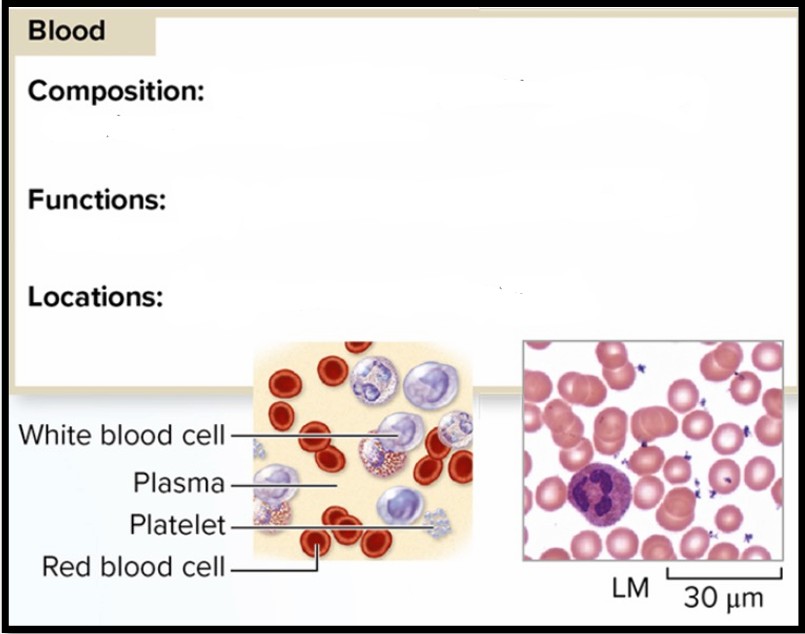
Blood
Composition: Red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets in plasma matrix
Function: Transport gases, nutrients, wastes, and hormones
Locations: In arteries, veins, and capillaries
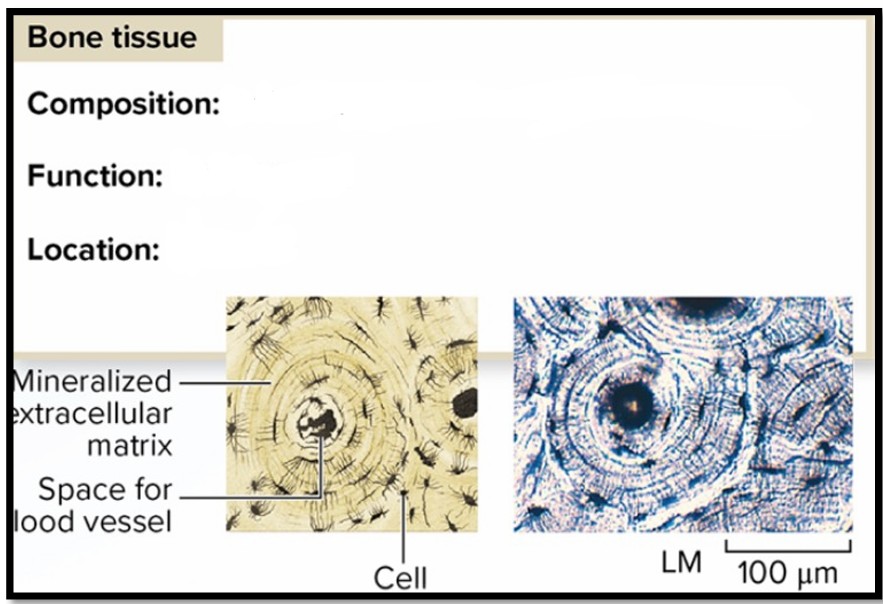
Bone Tissue
Composition: Cells in matrix of collagen and minerals
Function: Firm support
Location: Skeleton
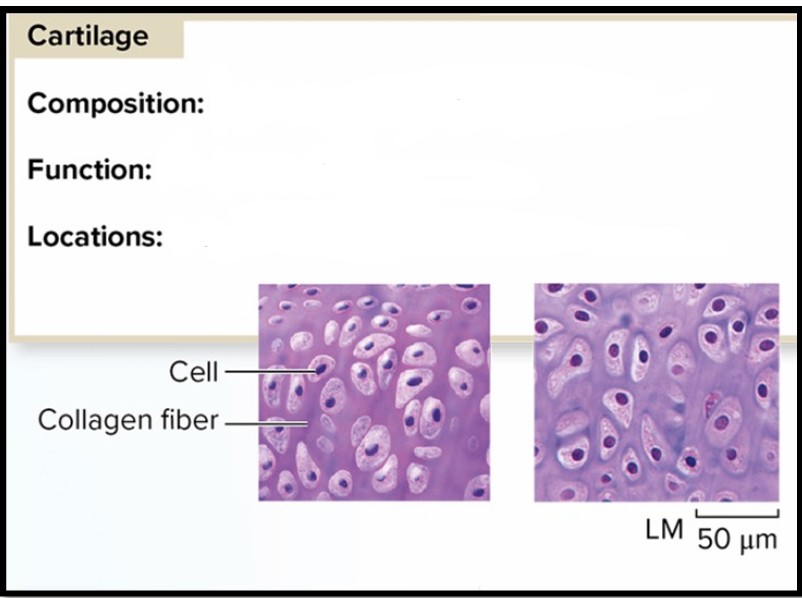
Cartilage
Composition: Cells in matrix of fine collagen fibers
Function: Flexible support
Locations: Ears; joints; bone ends; respiratory tract
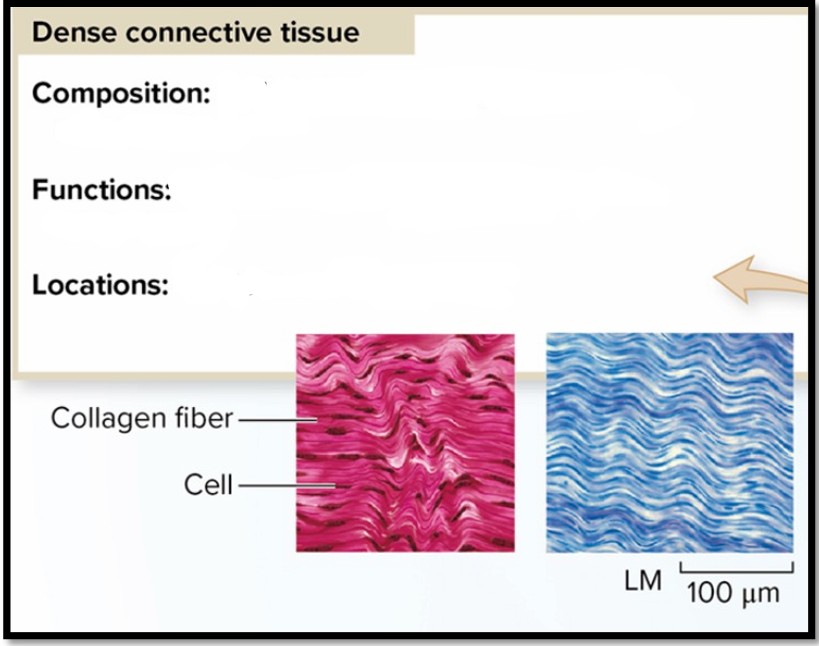
Dense Connective Tissue
Composition: Cells in dense matrix of elastin and collagen fibers
Functions: Connects muscle to bone; connects bone to bone
Locations: Tendons and ligaments
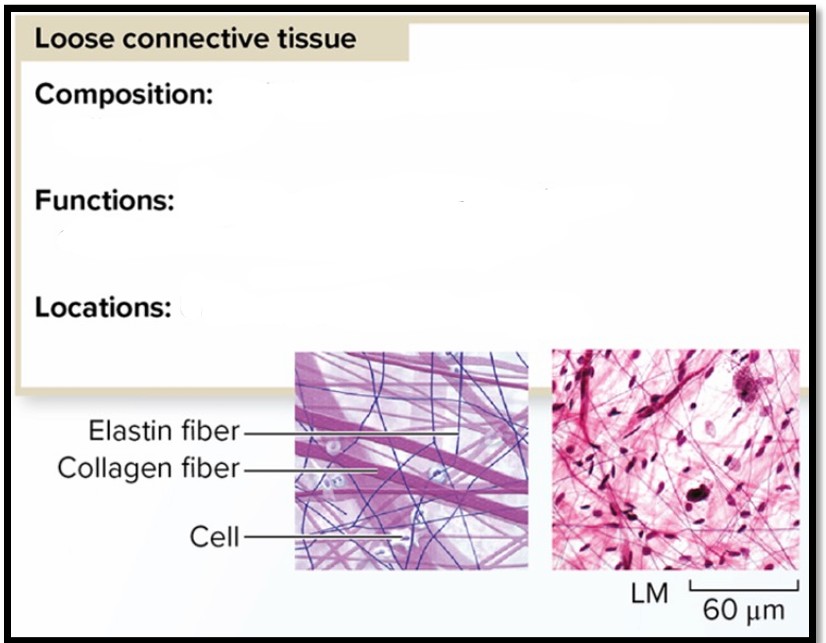
Loose Connective Tissue
Composition: Cells in loose matrix of elastin and collagen fibers
Function: Holds organs in place; attaches epithelial tissue to underlying tissue
Locations: Under skin; between organs
Muscle tissues create and are specialized to what?
Create movement and specialized to contract when stimulated electrically
What two proteins work together to mediate muscle cell contractions using ATP?
Actin and Myosin
What are the three muscle tissue types?
Skeletal, Cardiac, and Smooth
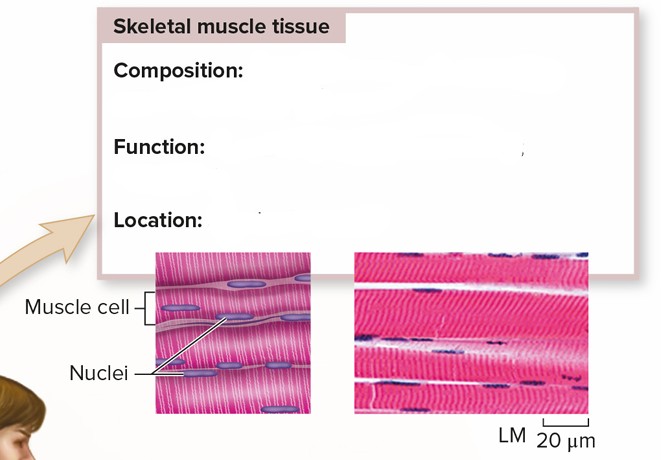
Skeletal Muscle Tissue
Composition: Elongated cells, each containing many nuclei; striated
Function: Moves the bones of the skeleton; voluntary
Location: Attached to bones
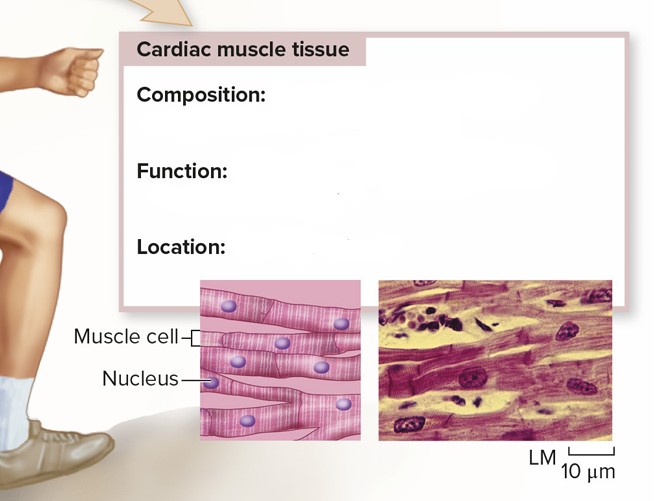
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
Composition: Short, branched cells each containing one nucleus; striated
Function: Contraction of atria and ventricles in heart: involuntary
Location: Walls of the heart
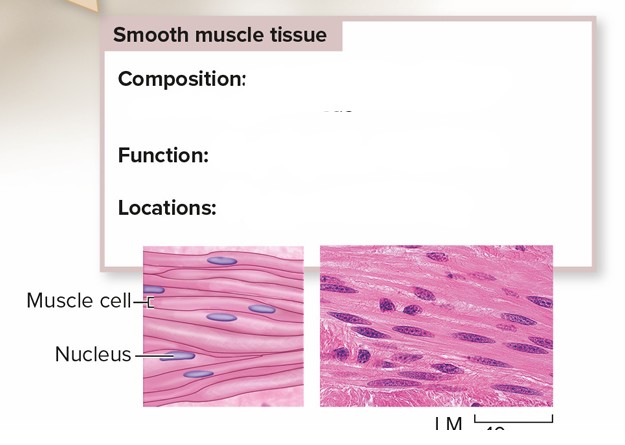
Smooth Muscle Tissue
Composition: Spindle-shaped cells, each containing one nucleus
Function: Slow, involuntary movements
Locations: Digestive tract, Arties
What do Nervous tissues do?
Rapidly transmits information through body
What do nervous tissues use and why?
Electrochemical signals, to rapidly transmit information throughout an animal’s body and conveys information throughout the body
What are the two major nervous tissues cell types?
Neurons and neuroglia
What are neurons?
Directly transmit signals and form extensive communication networks
What are neuroglia?
Surround, support and protect neurons
Where is nervous tissue found in?
Brain, Spinal cord, and nerves
What are the two communication systems?
The nervous and endocrine system
What does the nervous system do?
Rapidly electrical communication
What does the endocrine system do?
Produces and secretes hormones that travel around the body and regulate numerous body functions
What are the two support and movement systems?
Skeletal and Skeletal muscle Systems
What does the skeletal system do?
Provides framework for muscles to attach and make movement possible
What does the skeletal muscle system do?
Supports posture and enable body to move, plus it helps maintain body temperature
What are the three energy acquisition systems?
Digestive, Circulatory, Respiratory systems
Cellular ATP generation requires what three systems?
Digestive, Circulatory, Respiratory
What does the digestive system do?
Breaks down food into simple molecules to be moved into the blood
What does the circulatory system do?
Heart moves blood around body that contains food molecules or respiratory gases
What does the respiratory system do?
Supply oxygen for aerobic cellular respiration and removes CO2
What are the four protection systems?
urinary, immune, integumentary and lymphatic systems
What do the urinary, immune, and lymphatic system do?
Eliminate toxic substances and infectious microorganisms that harm the body
What does the integumentary system do?
Provide a physically barrier to the external environment
What other systems does the reproductive system require to function?
Nervous, endocrine and circulatory systems
What are the various physiological parameters that are maintained at high level of homeostasis?
temperature, blood pressure, internal fluid composition
What is homeostasis often maintained by?
Feedback loops
What are the three components of a feedback loop?
Sensor(receptor), control center (integrator), and effectors
What is a sensor(receptor)
Senses the current physiological condition
What is a control center (integrator)
Compared current condition to a “set point”
What are effectors?
Mechanisms that can effect changes in the condition
What is negative feedback?
When a change in physiological condition triggers a response that directly reverses the change
What is positive feedback?
When a change in a physiological condition further amplifies/increases changes which rapidly drives some event to tis end point
What is part of many homeostasis feedback loops?
hypothalamus
What is the hypothalamus?
Master control center, responds to sensors in multiple systems and can regulate organs in each system to limit changes and maintain homeostasis
What is thermoregulation?
Control of the body temperature via physiological or behavioral means
Extreme temperatures can alter what?
Biological molecules
What happens if it’s too cold?
Cell lysis, which is when ice crystals form
What happens if its too hot?
Enzymes malfunction and proteins can denature
What does endothermic mean?
Body temperature remains elevated over environment as high metabolic rate results in high metabolic heat production
What are examples of endothermic?
Birds and mammals
What does ectothermic mean?
External conditions primarily determine body temperature
What are examples of ectothermic?
All invertebrates, fishes, amphibians, non avian reptiles
What do endothermic animals use to maintain body temperature?
Fat/Blubber, fur ,feathers
What do ectotherm animals use to maintain body temperature?
Basking, shade, underground burrow
Ectotherm metabolism is _____ than endotherms and require less ___
Much lower and food/energy