Lecture 2- psychoanalytic and humanistic approaches
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Who are the 4 major psychoanalysts?
Freud
Adler
Jung
Horney
What was Freud influenced by?
Conservation of energy
Hypnosis as treatment for hysteria
What did Freud conclude about mental disorders?
Examining brain anatomy could not sufficiently explain mental disorders
What does ‘conscious’ refer to?
Thoughts that we are aware of at any given moment
What does ‘preconscious’ refer to?
Thoughts that we can become easily aware of, e.g date of birth
What does ‘unconscious’ refer to?
Content that we are unaware of or can only become aware of in certain situations
What is the ‘id’?
Seeks release of unconscious and primal needs/desires (food, sex etc)
Wants immediate gratification
Not concerned with moral or social rules
What principle does the id work on?
Pleasure principle
What is the ‘superego’?
Controls moral/rule-bound behaviour, including ideals and ethics
Rewards good behaviour and punishes bad
Conflicts with the id
What is the ‘ego’?
Balances the id’s urges with superego’s constraints
Wants long-term gratification
Logical, rational, resilient
= you
What principle does the ego work on?
Reality principle
What did Freud suggest about personality?
Psychosexual development occurs in stages
In which personality and individual differences develop
What happens at each stage of psychosexual development?
Sexual energy is focused on a different target
What happens if sexual energy is stuck or fixated at a stage?
Conflicts can occur and these can leave a deep imprint on adult personality
What are the 5 stages of psychosexual development?
Oral stage
Anal stage
Phallic stage
Latency stage
Genital stage
Describe the oral stage of psychosexual development
Up to 2 years
Focus on oral pleasure
e.g feeding, thumb sucking
Describe the anal stage of psychosexual development
2-3 years
Tension between pleasure (release) from toileting and social pressure to delay
Describe the phallic stage of psychosexual development
4-5 years
Focus on genitals
Realisation of physical male/female differences
Leads to psychological gender differentiation
Oedipus/Electra complexes
What is a Oedipus complex?
A son’s feelings of desire for their opposite-sex parent (mother)
Resentment toward the same-sex parent (father)
Who they view as a rival
What is a Electra complex?
Penis envy
A daughter’s feelings of desire for their opposite sex parent (father)
Describe the latency stage of psychosexual development
6 years until puberty
Key conflicts resolved
Child represses sexuality
Channels energy into social and intellectual pursuits
Describe the genital stage of psychosexual development
Puberty until death
Sexual and aggressive drives return
Seeks pleasure through sexual contact with others
Ego and superego now fully developed
What can too much/too little gratification at one stage cause cause?
Fixation
According to Freud’s theory of psychosexual development, what may happen to adults under stressful conditions?
May regress to the stage they were previously fixated on
What behaviours may result from oral fixation?
Eating
Drinking
Smoking
What personality types may result from oral fixation?
Demanding
Impatient
Envious
Depressed
Dependent on others
What behaviours may result from anal fixation?
Rigid organisation (anal retentive)
Carelessness (anal expulsive)
What personality types may result from anal fixation?
Need for power/control
Anxiety over losing control
Rigid and perfectionistic
Concerned with pleasure
Cruel
Intense emotionality
Messy
What behaviours may result from phallic fixation?
Seductive
Flirtatious
Promiscuous
What personality types may result from phallic fixation?
Male
Exhibitionistic
Vain
Aggressive
Female
Naive
Seductive
Submissive
What behaviours may result from latent fixation?
Asexual
Disengaged
Lacks close friends
What personality types may result from latent fixation?
Immaturity
Inability to form deep and lasting adult relationships
What behaviours may result from genital fixation?
Maladaptive fixation not possible
What personality types may result from genital fixation?
If the individual transitions successfully through the prior stages, can now form heterosexual relationships
What did Jung suggest about personality?
Believed Freud over-emphasised sexuality
Embraced a ‘mythological’ approach
Rejected scientific method
Proposed a ‘collective conscious’
Focused on dual aspects of the personality (private self vs persona presented to others)
Therapy should help the expression of the unconscious
What does the ‘collective unconscious’ proposed by Jung refer to?
Plato’s Meno
Soul is immortal, reincarnated
All knowledge is kept within the soul
We forget everything at birth due to trauma
What did Adler suggest about personality?
Believed Freud over-emphasised sexuality
People consciously strive to improve their lives
Relationships (parents, peers etc) and desire to contribute to society shape individuals
Individuals focus on compensating for painful inferiorities (inferiority complexes)
What did Horney suggest about personality?
Culture is a primary influence on personality
Personality types relate to strategies to reduce interpersonal anxiety
Women are more likely to envy men’s status, power and freedom than their penises
Women are socialised into gender roles
What does humanistic psychology propose about personality?
People have an innate tendency towards self-actualisation
Personality is a result of you trying to become your best self
Personality is NOT fixed, development is lifelong
Describe humanistic psychology as a discipline
Concerned with more developed and healthier aspects of human behaviour
Emphasis on the present
Self-reflection and choice are key to development
Focus on goals/outcomes of behaviour rather than individual differences or behavioural mechanisms
According to humanistic psychology, how does personality change over time?
Internal experiences influence our personality when we are young
As we age, external rules replace internal experiences
Changing our personality
What is the ‘self’?
An organised pattern of perceptions, consciously available
How is the ‘self’ integrated and organised?
Endures over time
Characterises who you are
Maintained and updated as the ‘self’ changes
How do the ‘self’ and our actions interact?
We try to behave in ways consistent with our ‘self’
Aim for consistency and congruence between ‘self’ and actions
What happens if there is incongruence between the ‘self’ and behaviour?
Creates distress
‘Not being myself’
Who are 2 key humanist psychologists?
Maslow
Rogers
What did Maslow suggest about personality?
Focused on a person-centered approach
Criticised psychology’s focus on psychopathology to understand personality (abnormal behaviours)
Thought focus on health and thriving was more important (positive psychology movement)
HIERARCHY OF NEEDS
What is Maslow’s hierarchy of needs?
Development begins with basic needs, similar to animals
Such as food, water, warmth, rest
Once lower needs satisfied, more uniquely human motives drive behaviour
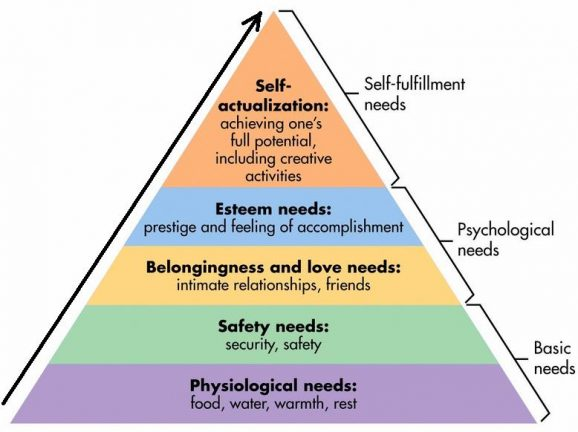
What are some criticisms of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs?
Signs of self-actualisation can appear at early levels of the hierarchy (e.g talents during starvation/war)
Humans don’t reliably follow the sequence (e.g refuse to eat another human even if starving)
What are some strengths of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs?
Humans do broadly evolve through the stages as they age (e.g physiological needs important in childhood, belongingness important for teens etc)
What is self-actualisation?
Hard to define!
Realisation or fulfilment of one’s talents or potential
Maslow’s examples: Albert Einstein, Eleanor Roosevelt

When do peak experiences occur?
When people are engaged in self-actualising activities
What is ‘flow’?
Activity is challenging and useful
One’s attention is completely absorbed by the activity
Clear goals and feedback
Concentration can only be on the current task
Achievement of personal control
Loss of self-consciousness and sense of time
What did Rogers suggest about personality?
Focused on therapeutic method and use of person-focused therapy
What is person-centered therapy?
Goal is to make patients more fully functioning and happier
Involves creating a proper relationship with patients
Open and genuine
Uses reflection to help patients understand their personality
What is personality controlled by, according to the psychodynamic approach and humanistic approach?
Psychodynamic → unconscious forces
Humanistic → our own actions/choices
Is personality fixed or fluid, according to the psychodynamic approach and humanistic approach?
Psychodynamic → fixed (based on early life experiences)
Humanistic → not fixed (lifelong development)
What is the adult psychological experience, according to the psychodynamic approach and humanistic approach?
Psychodynamic → repeating conflicts of the past
Humanistic → achieving self-actualisation
What is healthy personality functioning, according to the psychodynamic approach and humanistic approach?
Psychodynamic → denying impulses
Humanistic → congruence
What is anxiety caused by, according to the psychodynamic approach and humanistic approach?
Psychodynamic → impulses of the id
Humanistic → incongruence between ‘self’ and one’s experience