4448 PCHEM SET - Vibration and Rotation Spectroscopy
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
FTIR
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy - an instrument that uses infrared light to collect the vibrational spectra of molecular substances, entered by DW
Raman Spectroscopy
A type of vibrational molecular spectroscopy that uses inelastic scattering of visible photons of light, entered by DW
Rule of Mutual Exclusion
In a molecule with an inversion center, symmetric molecular vibrations are seen only in Raman spectrum, while asymmetric molecular vibrations are only seen in infrared spectrum. From class notes, entered by Kyler Kelley.
Anharmonicity
The deviation of the actual vibrational potential energy away from the model harmonic potential (parabolic) energy. Atkins Physical Chemistry 11ed., page 444, entered by Aurelia Holifield, edited by DW
Electromagnetic Spectrum
The range of radiation frequencies from radio waves to gamma waves that is emitted and absorbed by various objects. From class notes, Entered by Kyler Kelley. edited by DW
Dispersive Spectrometer
The resolution of this type of instrument depends on grating, slits, source image, and number of diodes on an array detector. This type is best for kinetics because it is easier to monitor a single wavelength value over time. from class notes, entered by Ryan Goldstein, edited by DW
Interferometric Spectrometers
Uses a Michelson interferometer to give an interferogram, which a fast fourier transform converts into a spectrum. Resolution depends on max path length difference and displacement. from class notes, entered by Ryan Goldstein. edited by DW
Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR) attachment
This sampling technique enables samples to be examined in solid or liquid state with no sample preparation. from class notes, entered by Ryan Goldstein, edited by DW
Stokes scattering
Photons in this situation lose energy to the molecules and the emerging radiation has a lower frequency or longer wavelength. Atkins, pg. 419, entered by Aurelia Holifield, edited by DW
Anti-stokes scattering
Photons in this situation gain energy from the molecules and the emerging radiation has a higher frequency or shorter wavelength. Atkins, pg. 419, entered by Aurelia Holifield, edited by DW
Harmonic oscillator
A mass on a spring (bonded atom) that has a parabolic potential energy (a restoring force proportional to the square of its displacement, V=0.5kx², from the equilibrium position).
Atkins Physical Chemistry 11ed., pg. 273 entered by Marrisa Martinez, edited by DW
Normal mode
The vibration of the molecule in which the center of mass remains fixed, the orientation is unchanged, and the atoms move synchronously. Atkins Physical Chemistry 11ed., pg. 452 entered by Marrisa Martinez
Combination bands
Simultaneous excitation of more than one normal mode in a transition Atkins Physical Chemistry 11ed., pg. 453 entered by Marrisa Martinez
Fingerprint region (related to IR spectroscopy)
The regions where all the bending vibrations (and some heavy-atom stretches) are seen in the right hand side of the spectroscopy graph, Entered by Megan Mann, edited by DW
Fourier Transform
This transformation treats the interferogram as a superposition of cosines and converts the interferogram into a spectrum of the frequencies of those cosines. Atkins Physical Chemistry 11ed., pg. 511-512 entered by Phillip Paik, edited by DW
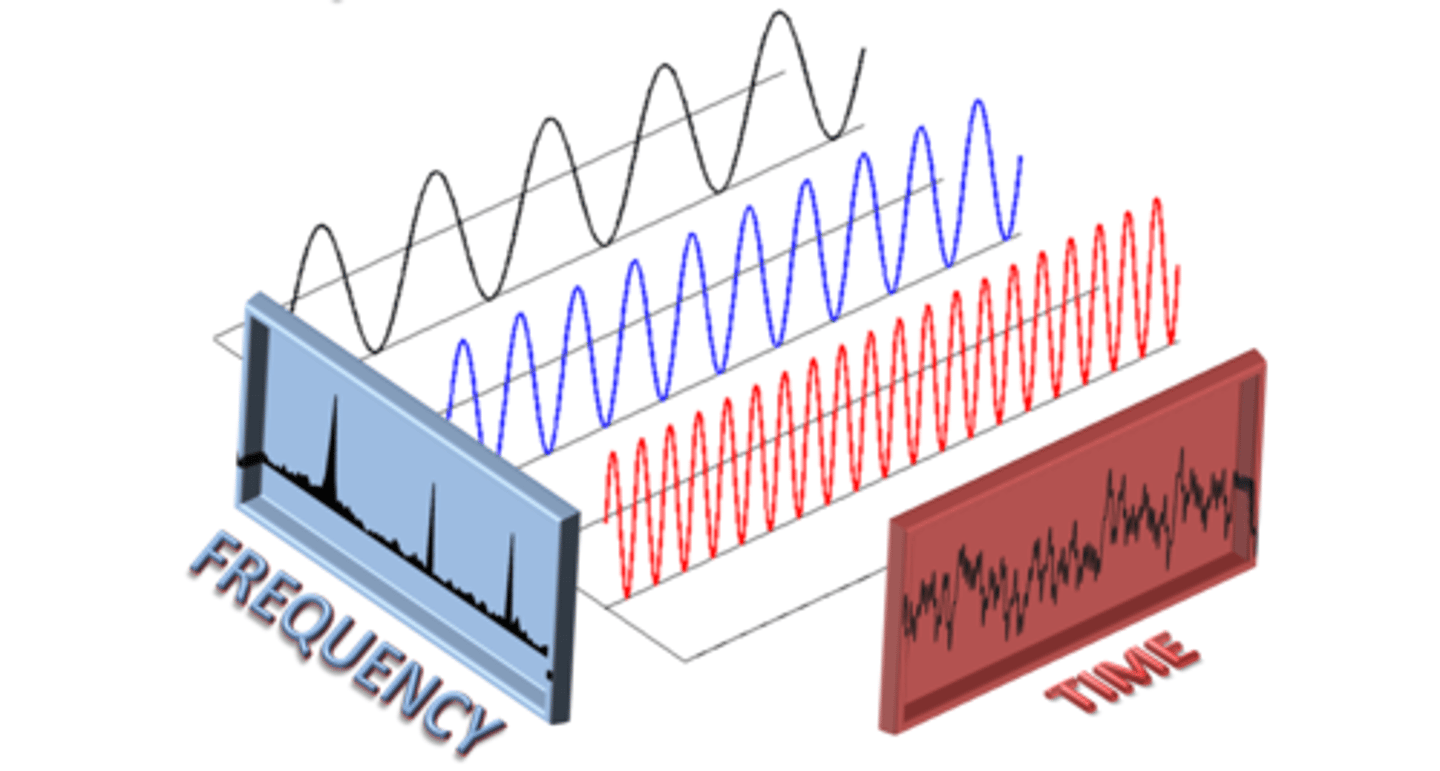
Force constant (related to harmonic oscillator)
The harmonic potential energy curve (V = 0.5kx² is scaled by this value (k). This variable shows the strength of potential energy and is expressed in newtons per meter (N m⁻¹). Atkins Physical Chemistry 11ed., pg. 274 entered by Phillip Paik, edited by DW
Harmonic potential energy equation
V(x)=(1/2)kx² Atkins Physical Chemistry 11ed., pg. 273 entered by Phillip Paik, edited by DW
Rayleigh Scattering
Photos in this situation change direction when colliding with a molecule, but they do not lose or gain energy. there are no changes to the frequency or wave length of light.From class notes, entered by Makenzie Kuehn, edited by DW
Reduced mass
The effective mass µ that moves in the vibration or rotation of a molecule. For a diatomic molecule, µ=(m1*m2)/(m1+m2) Atkins Physical Chemistry 11th ed., pg 443, entered by Makenzie Kuehn, edited by DW
Evanescent wave
When an IR beam is reflected internally by an ATR crystal, this is the wave that penetrates a small distance into the sample ThermoFisher Scientific, Dr. Michael Bradley, entered by Makenzie Kuehn, edited by DW
Microwave Spectral Region
In this spectral region the molecule is only rotating, no vibrations. Will only effect molecules with a permanent dipole. Notes from Lecture notes, entered by Patricia Hernandez
MIR Spectral Region
400-4000 cm^-1. This region shows you the different vibrational modes of a molecule. It can tell you how a molecule is bonded together. From Lecture notes, entered by Patricia Hernandez
Dissociation energy (D subscript o)
The energy difference between the lowest vibrational state (V=0) and infinitely separated atoms. Atkins Physical Chemistry 11th ed., pg 445, entered by Breanna Nelson
Centrifugal Distortion Constant
Dj - a measure of the distortion of the bond length of a molecule as the angular momentum, or rotation, increases. Bonds that are easily stretched have lower vibrational energies, weaker force constants, and thus high centrifugal distortion. Atkins Physical Chemistry 11th ed, pg 434, entered by Taylor Shelley, edited by DW
Rotation-vibration Coupling Constant
ae (alpha-e) - a measure of how the change in internuclear distance of a bond during vibration affects the moment of inertia and therefore the rotation of the molecule. From Nibler Exp #37 Handout from the Rovibrational spectroscopy lab, entered by Taylor Shelley
Rotational Constant
Be - a measure of how the moment of inertia and bond length affect the energy of rotation. Heavier molecules have larger moments of inertia, so they have smaller transition energies and closely spaced rotational energy levels. Atkins Physical Chemistry 11th ed, page 432, entered by Taylor Shelley
Polarizability
A measure of the ability of an electric field to induce a dipole moment in a molecule. Atkins Physical Chemistry 11th ed, page 592, entered by Marrisa Martinez
Permanent dipole moment
The partial charges on the atoms in the molecule, which arise from differences in electronegativity or variations in electron density through the molecule. Atkins Physical Chemistry 11th ed, page 585, entered by Marrisa Martinez
P branch
A spectral branch in vibration-rotation spectra that consists of all transitions with ΔJ = -1. This branch consists of lines extending to the low wavenumber side of the spectrum. Atkins Physical Chemistry 11th ed, page 447, entered by Marrisa Martinez, edited by DW
Raman Shift
Using visible light to measure vibrational properties in the Mid-IR energy range. From lecture notes L17. Entered by Breanna Nelson
R branch
A spectral branch in vibration-rotation spectra that consists of all transitions with ΔJ = +1. This branch consists of lines extending to the high wavenumber side of the spectrum. Atkins Physical Chemistry 11th ed, page 447, entered by Marrisa Martinez, edited by DW
Q branch
A spectral branch in vibration-rotation spectra that consists of all transitions with ΔJ = 0. This branch consists of lines that fall on the vibrational frequency. Entered by DW
S branch
A spectral branch in vibration-rotation spectra that consists of all transitions with ΔJ = +2. This branch consists of lines extending to the high wavenumber side of the spectrum. Entered by DW
O branch
A spectral branch in vibration-rotation spectra that consists of all transitions with ΔJ = -2. This branch consists of lines extending to the low wavenumber side of the spectrum. Entered by DW