Peds Final
1/426
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
427 Terms
segar's formula - on exam and final
used to determine the amount of fluid to give for maintenance ic for dehydration, divide total 24 hour amount by 24 hours to get ml per hour
check clinic educt
0-10kg 100ml/kg/24 hours
11-20kg 50ml/kg/24 hours
>20kg 20ml/kg/24 hours
uses 100ml/kg for first 10 kg, then use 50ml/kg for second 10 kg, then use 20ml/kg for rest weight
percent weight loss
check clinic educt
((normal weight- current rate) / normal weight) x 100
minimum urine output/expected fluid output
check clinic educt
1ml/kg/hr
more than minimum okay, weigh the diaper
why does dehydration effect kids more?
they have more percent water in the extracellular space which is one step away to be lost via kidneys, adults have it in intracellular fluid aka 2 steps away from kidney
rotavirus vaccine
prevents rotavirus that causes diarrhea
crying after pooping
painful or diaper rash
typical causes of dehydration
limited intake, fluid loss through: urinary, GI, skin and respiratory
fluid loss onset <3 days
EFC 40-50%
ICF 25%
fluid loss onset >7 days
EFC 50%
ICF 50%
more fluid is being pulled out of cells at this point
mild dehydration and thirst
normal thirst, usually not enough
moderate dehydration and thirst
drinks eagerly
severe dehydration and thirst
intense, but may be unable to drink enough
LOC - Mildly ill
alert and active
LOC - moderately ill
restless irritable anxious
LOC - severe illness
drowsy lethargy
mild illness vitals
normal HR or mild increase, BP normal
moderate illness vitals
tachycardia, BP normal or slightly low, othrostatic hypotension
severe illness vitals
rapid and thready HR, low BP
minimum expected systolic BP
70 + (2x age in years)
until adult normals
skin assessment dehydration mild
pale, dry, normal turgur
skin assessment dehydration moderate
pale/grey, poor turgur=, doughy
skin assessment dehydration severe
mottled tenting
fontanel assessment dehydration mild
usually normal (none after 18 months)
fontanel assessment dehydration moderate
may be sunken (none after 18 months)
fontanel assessment dehydration severe
sunken (none after 18 months)
dehydration assessment eyes mild
tearing with crying
dehydration assessment eyes moderate
slightly sunken eyes, decreased or no tears
dehydration assessment eyes severe
sunken eyes with dark circles, no tears
dehydration assessment mucous membranes mild
normal, slightly dry
dehydration assessment mucous membranes moderate
dry
dehydration assessment mucous membranes severe
parched, cracked
dehydration assessment perfusion mild
cal refill >2 sec, normal pulse
dehydration assessment perfusions moderate
cap refill 2-4 secs, weak, rapid pulses
dehydration assessment perfusions severe
cap refill >4 sec, pulses thready, cold extremities
mottled
spotted or blotched in coloring due to poor perfusion or cold
dehydration assessment labs
odium levels, BUN and Cr, Hct
BUN
goes high with dehydration because is more concentrated
Creatine
shows how kidneys are clearing, if dehydrated would be normal, if kidney disease then could be off
hospital treatment of severe dehydration
initial IV bolus, monitor lytes, maintenance fluids
mild dehydration percent weight loss
<5% infants
moderate dehydration percent weight loss
6-9% infants (6-8% child)
severe dehydration percent weight loss
>10% infants and child, signs and symptoms of shock
Diarrhea in infants and children
rotavirus, bacteria, protozoa, malabsorption, food allergy, response to meds, inflammatory bowel
causes dehydration!
meds to question with viral infections and diarrhea
you want them to poop! so don't give imodium, flagyl (for bacterial infections)
let time cure it!
home treatment of mild dehydration
ORT/ORS, (oral rehydration therapy/solution), has sugar and lytes, Powerade is not a substitute!
small frequent drinks, 2-5ml q2-3 mins, syringe or med cups, emesis -> wait 10 mins
cleft palate/lip
happens before most women know they are even pregnant, congenital abnormality due to the failure of closure of certain facial parts during embryonic development
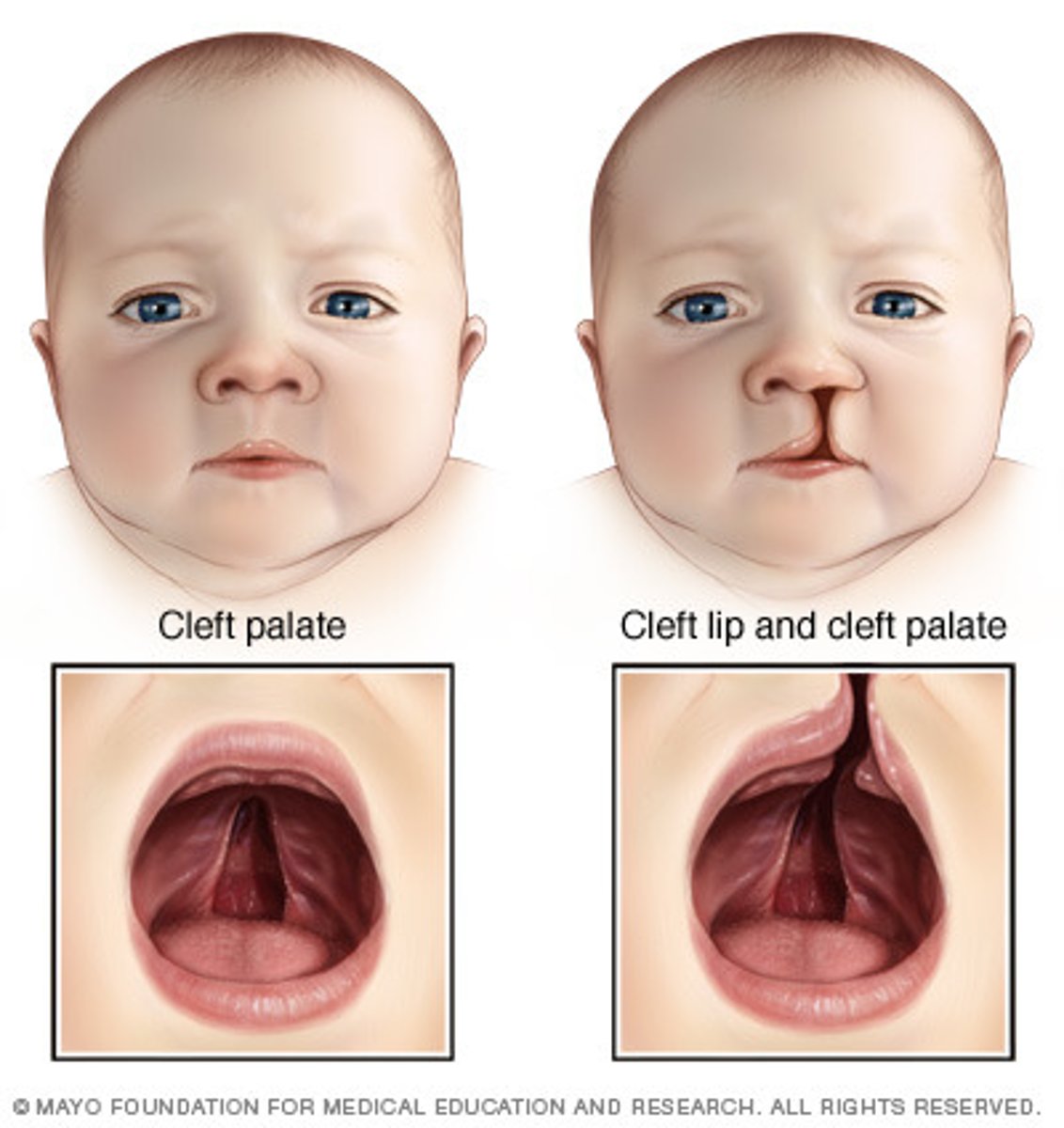
cleft palate/lip cause
genetic link, environmental (smoking, etoh, infections), meds (dilantin, retin A, steroids), low folate
Retin A
causes a lot of birth defects, dont give to women of child bearing age
cleft lip problems for infant
feeding difficulties (cant form suction), weight gain is difficult, risk for aspiration, nasal deformity, dental abnormalities, speech, social acceptance
special nipples for cleft lip
squeeze bottle: ross nipple, mead-johnson
nipple hole/valve: pigeon, haberman, special needs feeder
cleft lip treatment
surgery at 2-3 months, z plasty / cheiloplasty
arm restraints for cleft lip
medical restraint to prevent playing with lips
cleft palate problems for infant
feeding difficulties (weight loss risk for aspiration), ear infections increased risk (can decrease hearing, lead to speech problems), possible dental work, social acceptance
cleft palate treatment
nutrition, possible prep for reconstruction, surgery at 6-12 months -> palatoplasty
cleft palate feeding
use of a cup after surgery! no sucking, 10-15ml water chaser
before dischagre with cleft lip and palate
have to show that parents are able to feed them and they are feeding well by diaper wights and input
Hirschsprung's disease
absence at birth of the autonomic ganglia in a segment of the intestinal smooth muscle wall that normally stimulates peristalsis
ribbon-like stools, reluctance to pass meconium, back up of stool causing impaction, rectum empty of stool, can lead to cdiff
malnourished growth chart
loose weight first, then stop gaining height, then stop growing head circumference
(bodyweight lowest, height low, head circumference normal-ish)
Hirschsprung's disease possible tests
H&H, albumin, total protein, x-ray, barium enema, biopsy, anorectal manometry
Hirschsprung's disease opportunistic pathogen
high risk for C-Diff
Hirschsprung's disease treatment
colostomy, normal saline enama till clear then antibitoic enema, golytely
intussusception
telescoping of a segment of the small intestine into the large intestine, most common cause of intestinal obstruction in toddlers
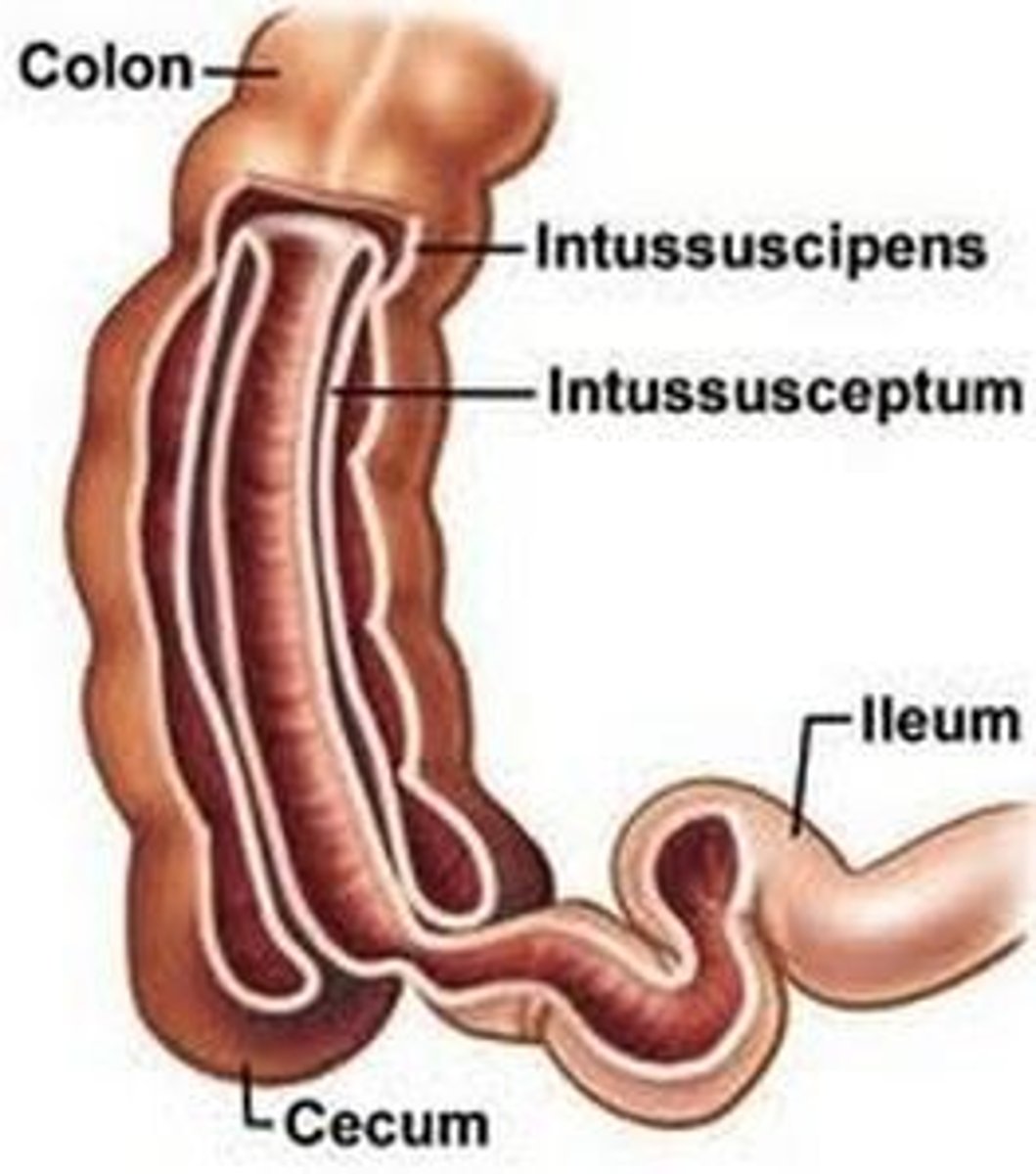
intussusception symptoms early
soft abdomen, intermittent colickly pain, normal stool, periods of no apparent distress
intussusception symptoms late
abd distended & firm, sausage shaped mass in RUQ, severe paroxysmal abd pain, currant-jelly stool, vomiting bile, dehydration -> shock
intussusception labs and tests
x-ray and ultrasound showing "target" and "crescent"
intussusception treatment
air enama or hydrostatic reduction
laparoscopic surgery
10% reduce on own without intervention
pushes small intestine out of large intestine
intussusception - when should hydrostatic reduction not be done
if there is a risk of perforation normally due to peritonitits
pyloric stenosis
narrowing of the opening of the stomach to the duodenum
Bile in the emesis suggests
not a pyloric stenosis
pyloric stenosis s/s
gradual onset, emesis or projectile emesis, no bile in emesis but blood possible, hungry after emesis, RUQ olive size mass, dehydration, metabolic alkalosis
pyloric stenosis treatment
rehydrate and stabilize lytes, pyloromyotomy
pyloric stenosis labs
metabolic alkalosis
pyloric stenosis postop nutrition
clear liquids -> full strength
slowly increase amount
usually full by 48 hours
GER/GERD will be on exam
Emesis, failure to thrive, esophagitis -> pin, gastric irritation -> anemia, aspiration pneumonia, apnea
cystic fibrosis
autosomal recessive genetic disorder, body makes too much mucus and salt, respiratory, GI, reproductive
sweat chloride test (need to know)
gold standard test for cystic fibrosis, at least 3 months old
neg <30,
diagnostic >60
cystic fibrosis treatment in order
exercise, albuterol, then percussion, then flutter device
pulmozyme (dnase)
nebulizer that works directly on mucus
tobramycin
nebulizer giving in cycles so child doesn't build immunity to medication
vaccines for cystic fibrosis
PPV (pneumococcal-23) and annual flu shot + all others
pancrease
check poop, if looking normal than have enough drug, if abnormal add more drug
Cystic fibrosis fat soluable
risk for not absorbing fat soluble things, supplement with A D E K vitamins
cystic fibrosis and meconium
1st sign of CF = not passing meconium in 24 hours
- when it comes out will be thick, sticky and small
- passing first meconium leads to rectal prolapse
cystic fibrosis diet
3 meals + 3 snacks a day, high calorie protein and fat diet, lots of salt
supplement with ADEK Iron Ca
Cystic fibrosis and oxygen
think like they have COPD, NC, mask if necessary, lower O2 rate better, 92-94% SaO2
cystic fibrosis signs
clubbing of nails, barrel chest, oral polyps, cracking of lungs, retractions, thick green blood tinged sputum, JVD, palpateable liver
cleanout for cystic fibrosis
No roommate, continue GI treatments, IV acess, cultured, antibiotics, oxygen, cultures, Frequent respiratory checks
What parts of the history are significant? Explain.
1) Respiratory – frequent infections
2) GI – delayed passage of meconium, malnourished, failure to thrive
3) Progression - worsening
What parts of the physical exam are significant? Explain.
1) Respiratory – crackles, wheezing, green mucus, CHF
2) GI – poor weight gain, failure to thrive,
3) Reproductive – delayed growth
The following labs and diagnostics ordered for Fred, and what do you expect the findings to be? (normal, increased, decreased
1) WBC - elevated
2) RBC, Hemoglobin & Hematocrit - low
3) Electrolytes – sodium if not supplemented, normal if supplemented
4) BUN, Creatinine – creatinine normal, BUN elevated (dehydration)
5) Chest Xray – stuff in xray
When you prepare to initiate oxygen when Fred (cystic fibrosis) is admitted to the Peds unit, which are you more likely to use, a nasal cannula or a non-rebreather mask? Explain.
nasal cannula, need to be able to expel sputum, 2-4L, don't want to stop breathing drive
What are your nursing actions at admission for cystic fibrosis? Prioritize your assessments and completion of orders that would be completed during the admission process.
after assessment; oxygen, albuterol, iv access, blood culture, start antibiotics
If the nurse manager was trying to assign a roommate for a new admission, postop tonsillectomy, would Fred (cystic fibrosis) be a good choice for a roommate (consider gender, possible infection, and age)? Explain
No, cystic fibrosis should not have roommate
Roomates
Determine gender if both children are > 2 YO, infection risk - prone to get, prone to give, Age (only if 2 roomates are available)
Give an example of foods that would follow the recommended diet for cystic fibrosis
high fat high protein high calorie
What medication must be given with the food cystic fibrosis
enzyme, with snacks also
cystic fibrosis, Long term, how will you know if the GI/Nutrition treatments are effective (expected findings)?
poop sinks
How will you know if the Respiratory treatments are effective (expected findings) cystic fibrosis
Os sat improves, pulse and resp decrease, temp decrease
Fred (cystic fibrosis) puts his call light on. When you enter the room, Fred appears to be in acute respiratory distress. Oximeter has dropped suddenly to 82%. He is diaphoretic with no lung sounds on the right side. What are your concerns and what do you do?
pneumothorax
How would you organize your care for Fred’s day shift? Include all meds, treatments and therapies (including Pancrease, Albuterol & Pulmozyme).
vitals, assessment, gentamycin IV
albuterol, pulmozyyme, chest PT, then tobramycin neb
weight
breakfast, pancrease, vitamins
snack, pancrease
bath/shower, linen change
vitals assessment, albuteral/chest PT,
lunch, pancrease
ceftazidime IV
snack, pancrease